+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!

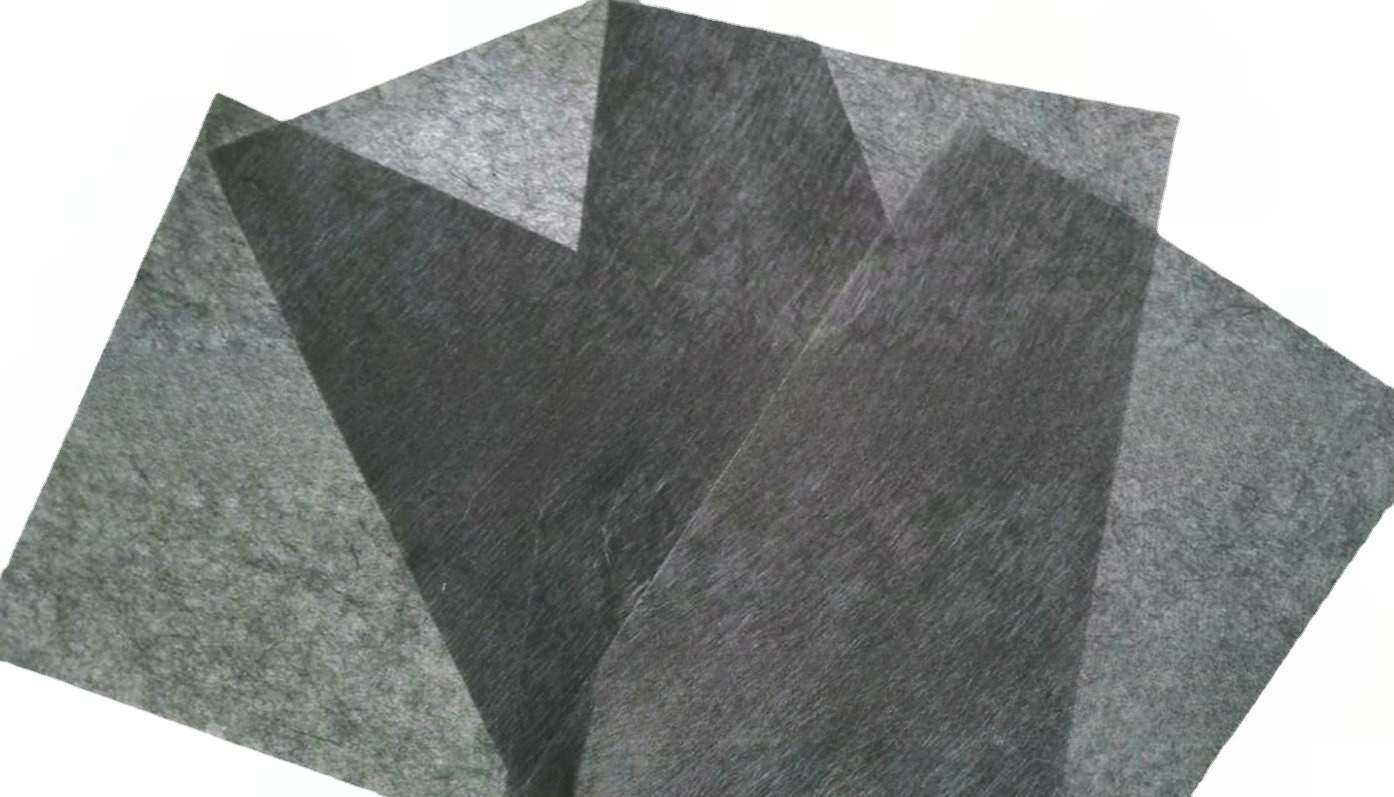
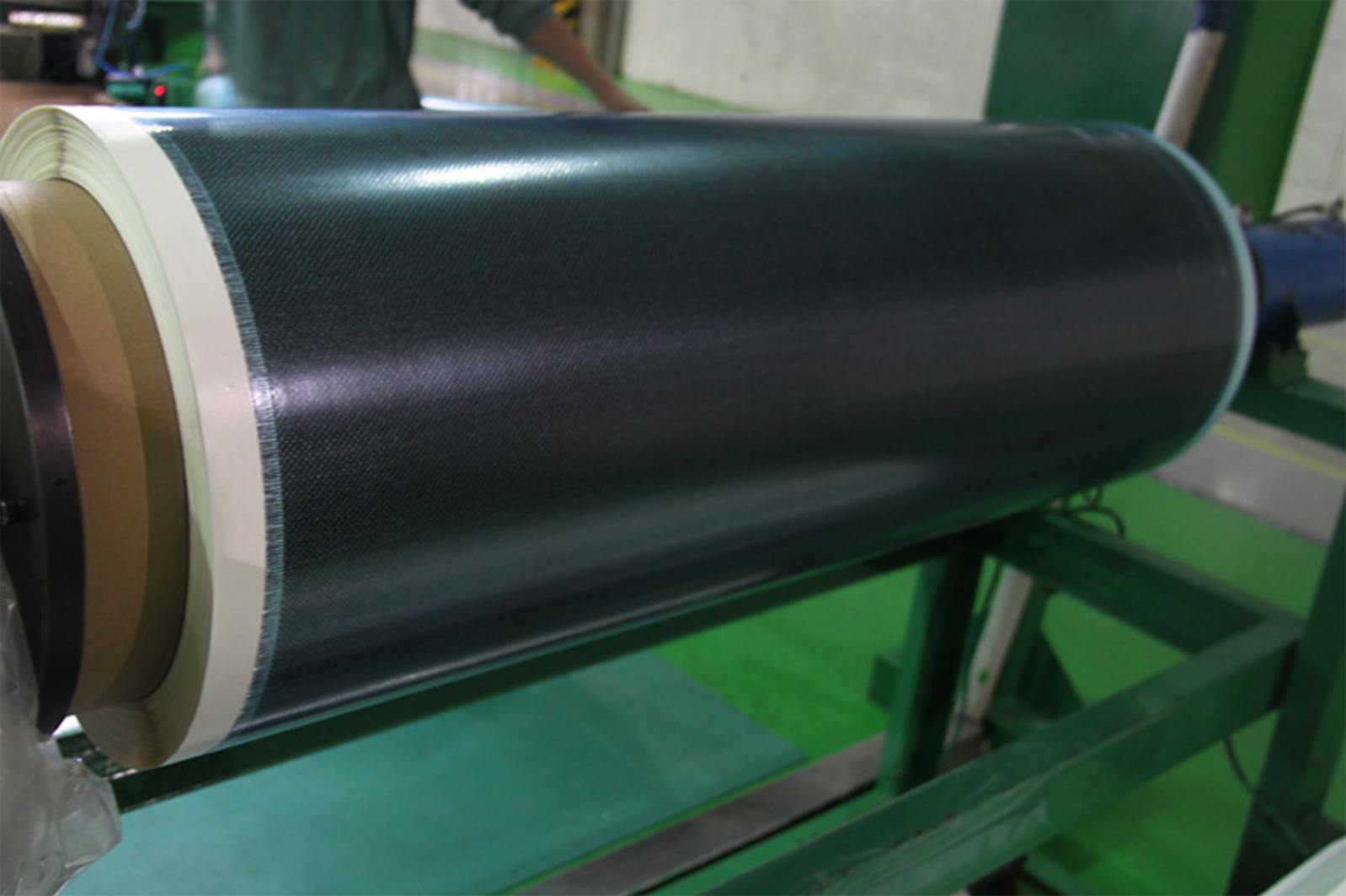
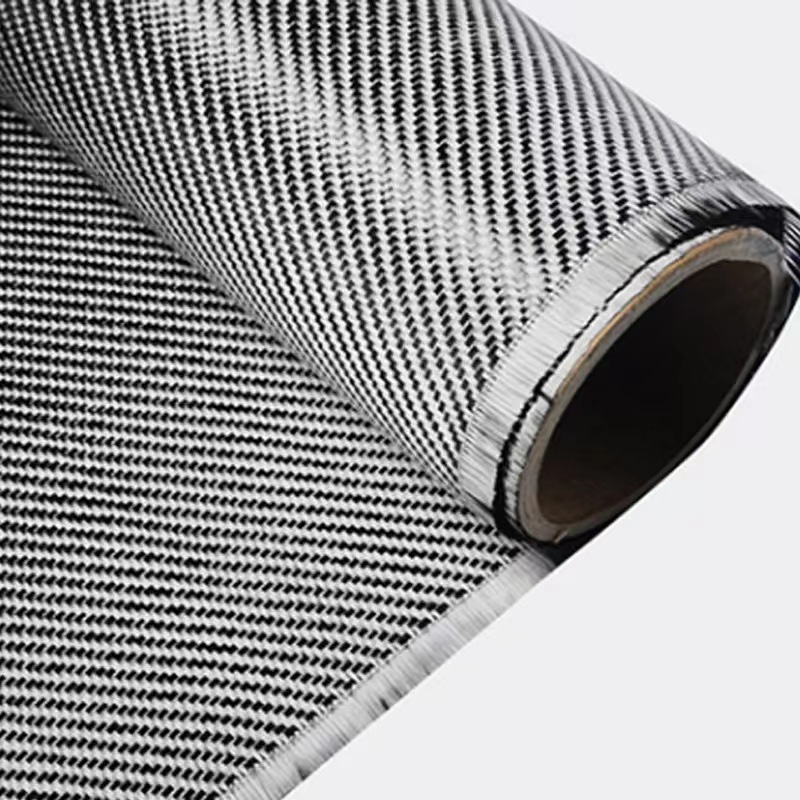
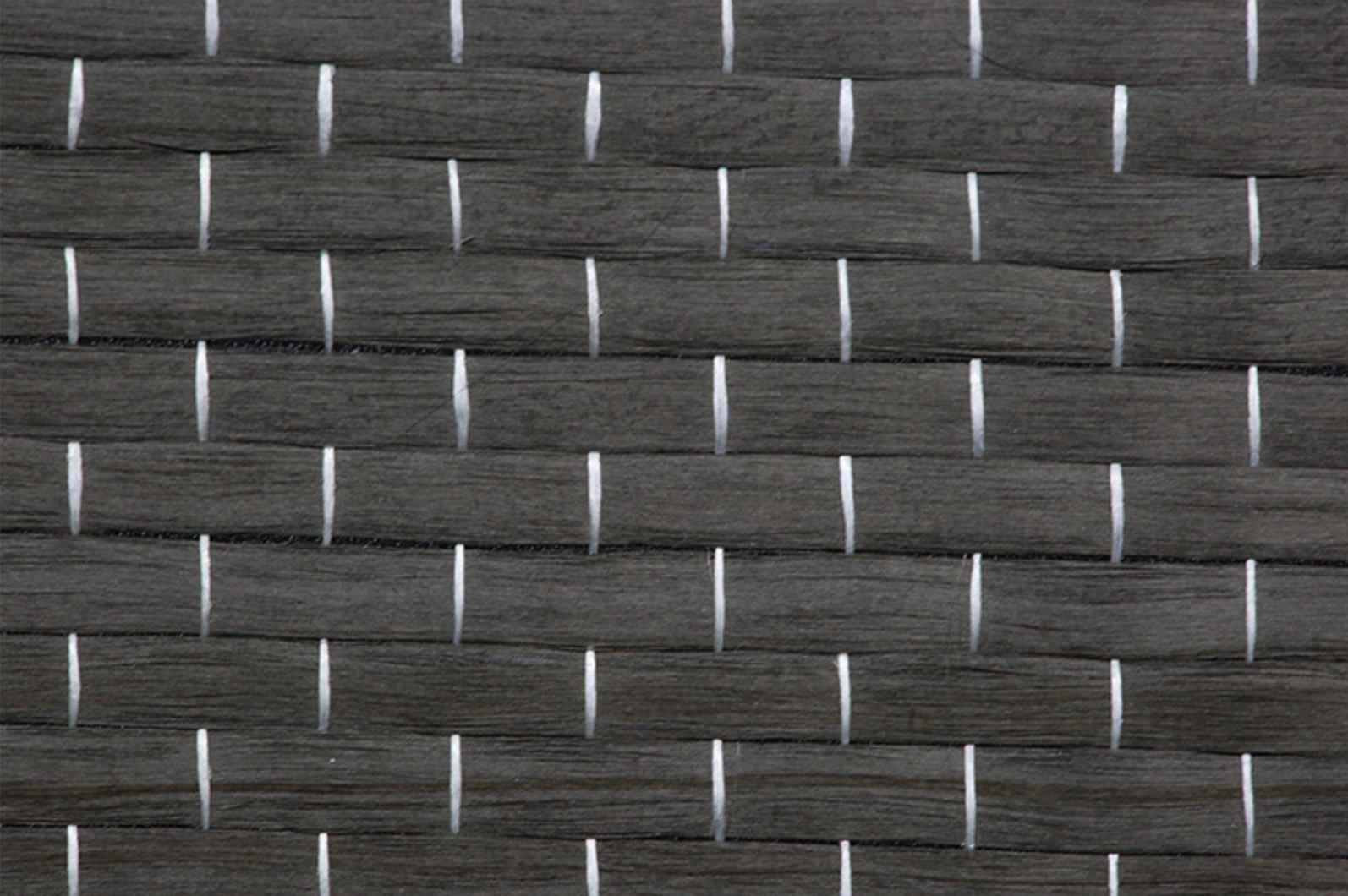
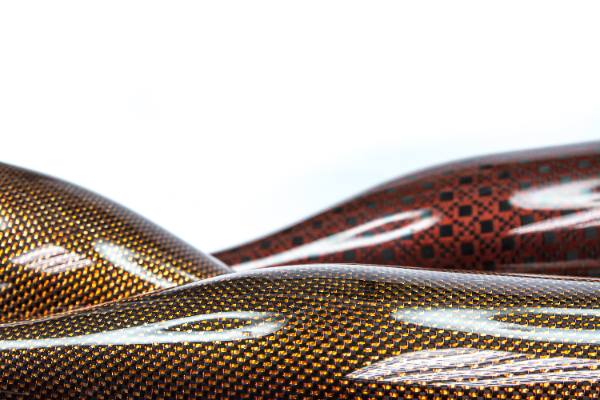
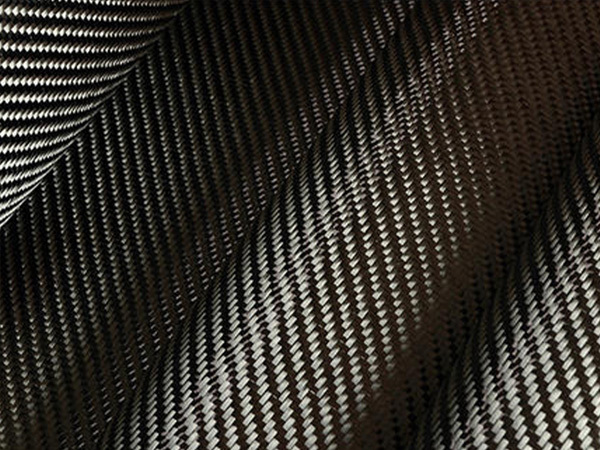
Carbon Fiber Multiaxial Fabric
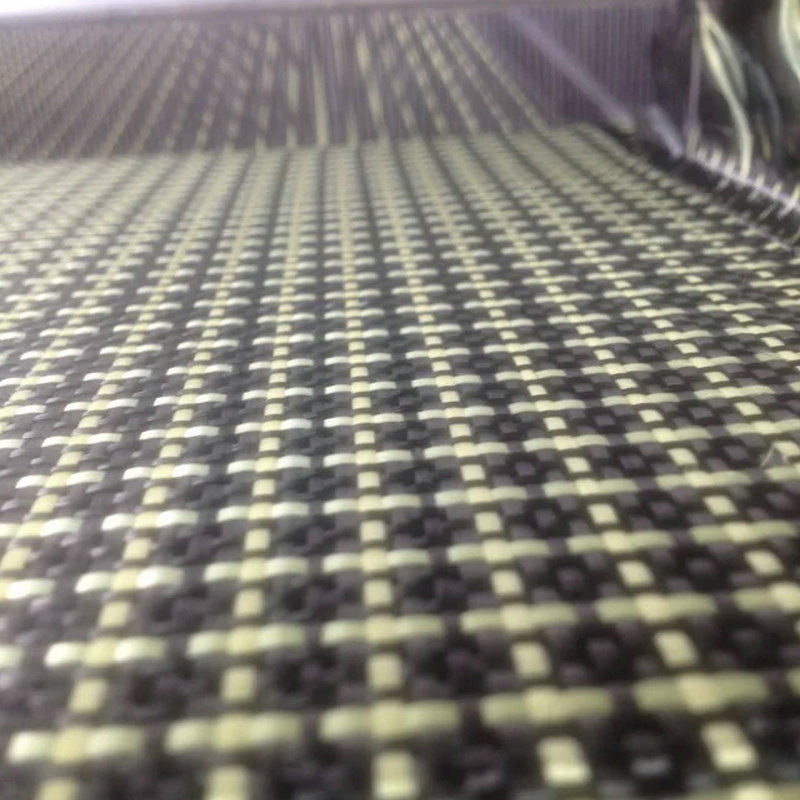

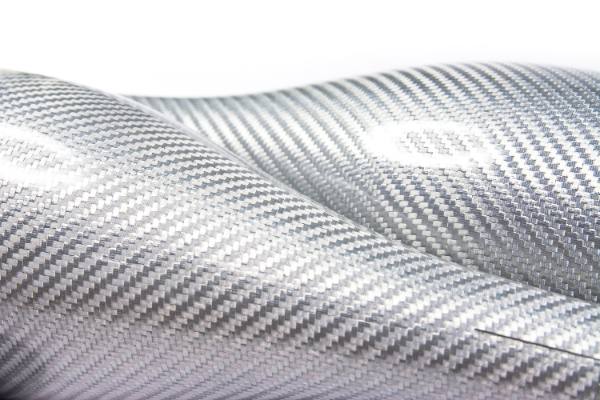
Hybrid Woven Fabric
+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!
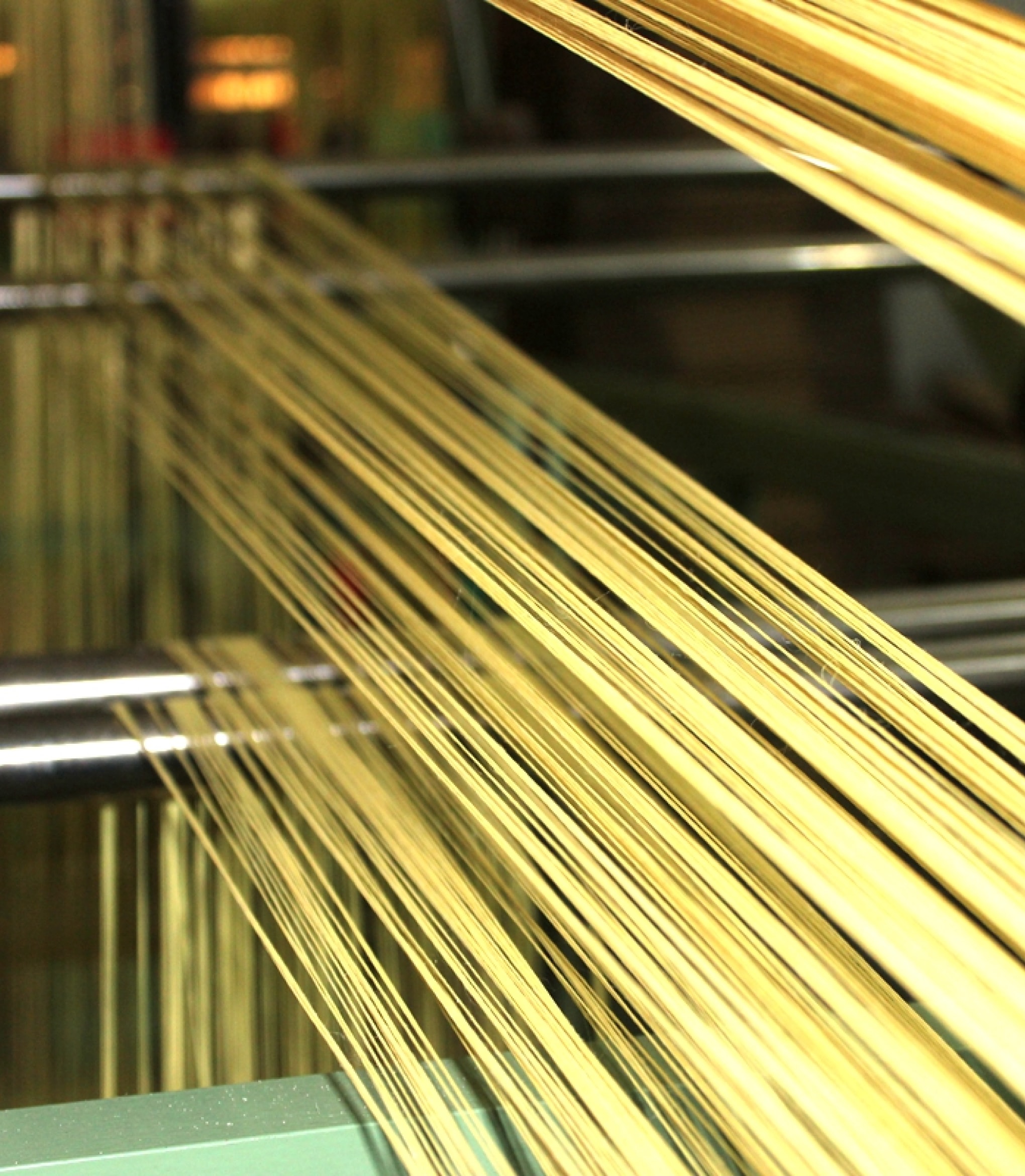



Weaving
In the realm of reinforced textile composite materials, woven fabrics stand as a common form of textile structure and are primarily categorized into three types: planar biaxial structures, planar multiaxial structures, and spatial three-dimensional structures. The design of woven fabrics can be custom-tailored to achieve superior structural performance and robust stability, ensuring high coverage within the large area of warp and weft yarns.
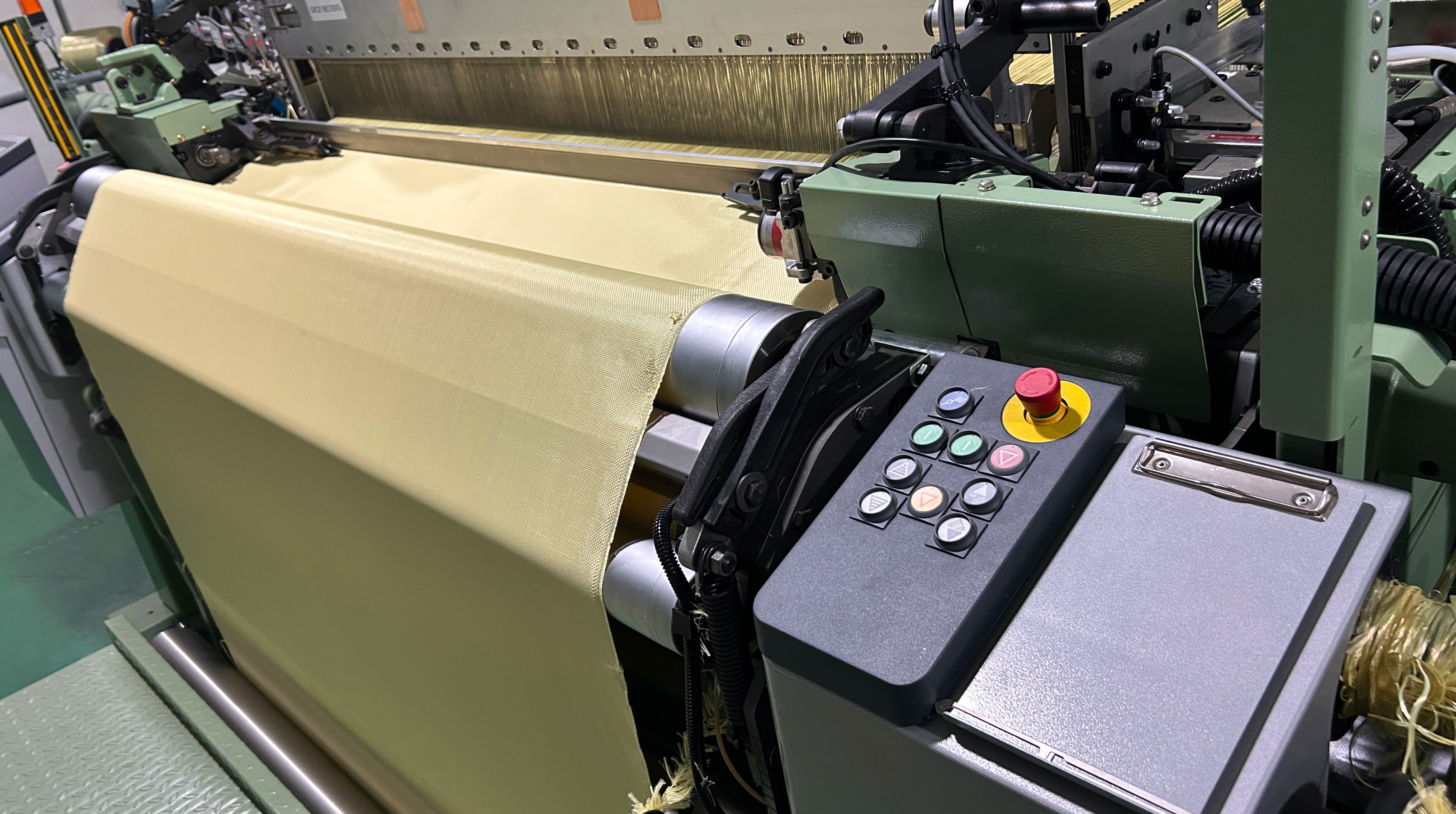
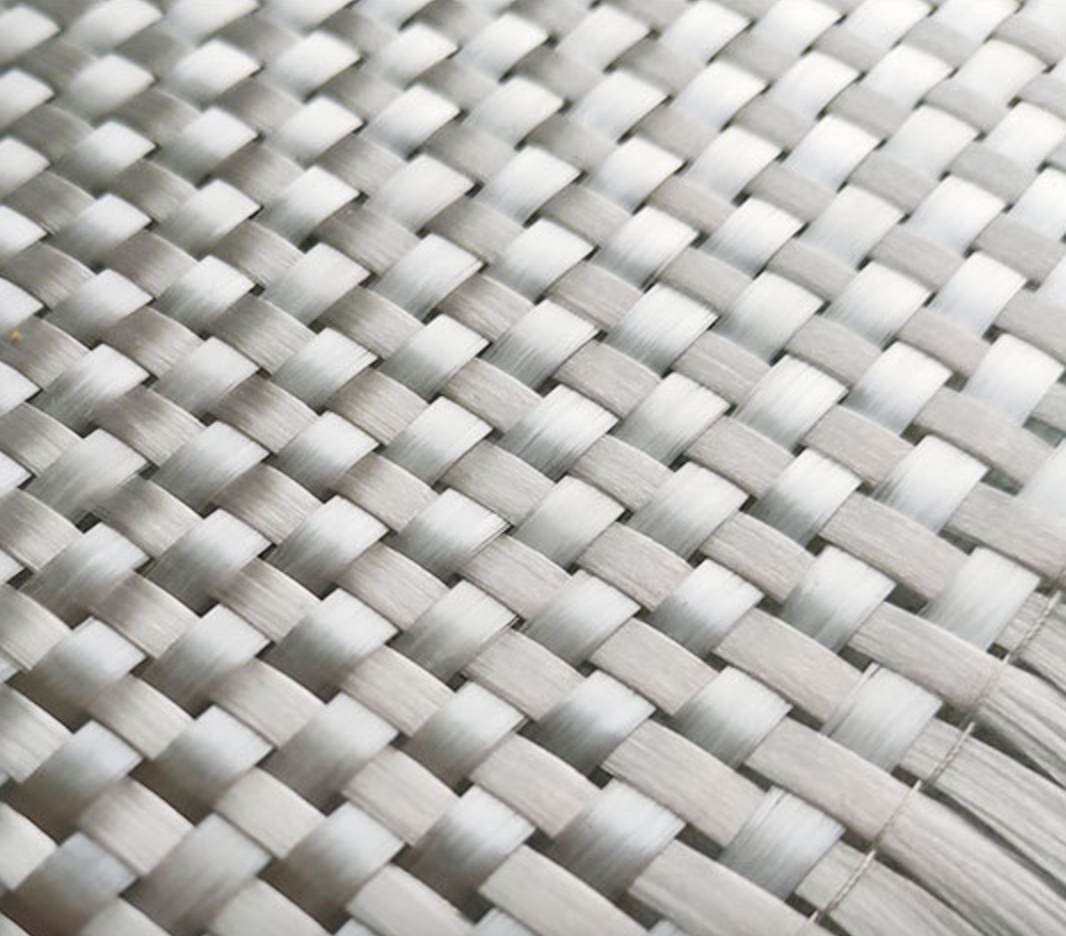

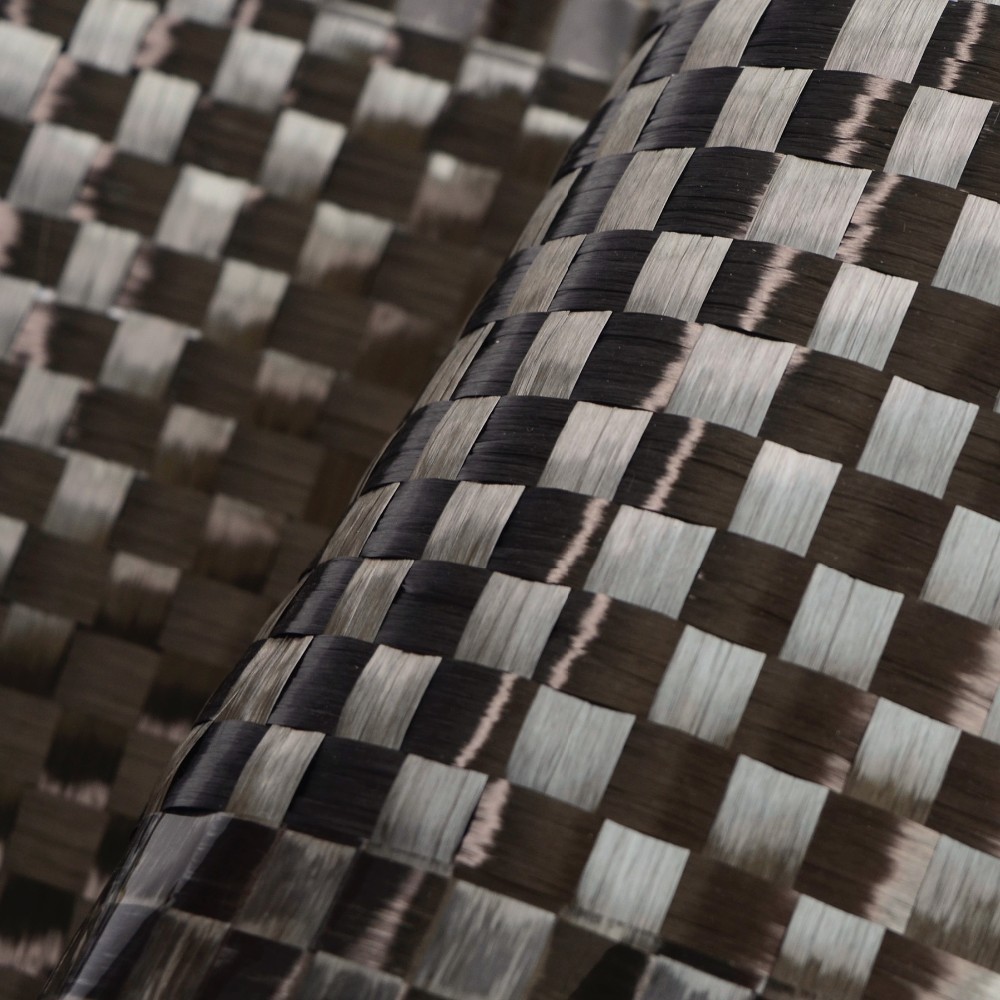
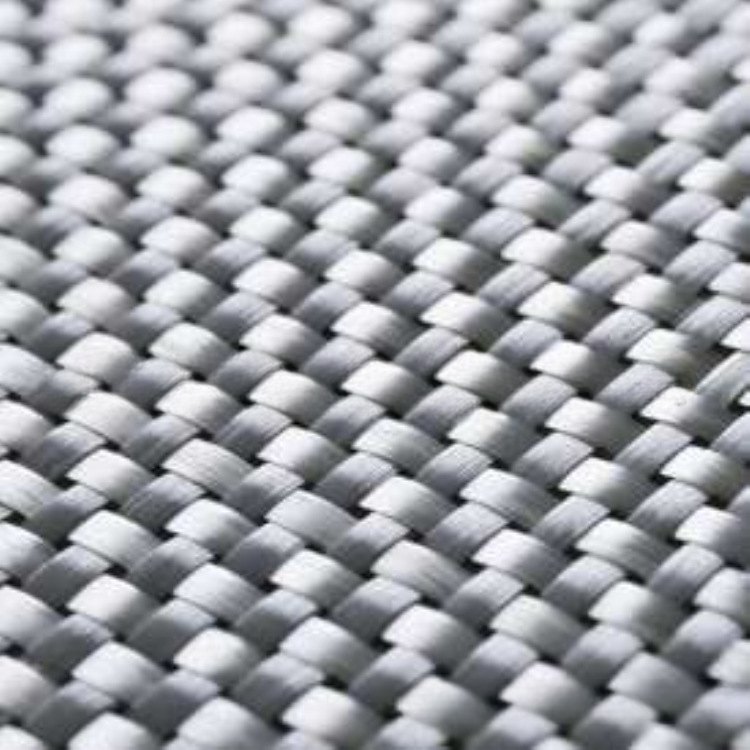
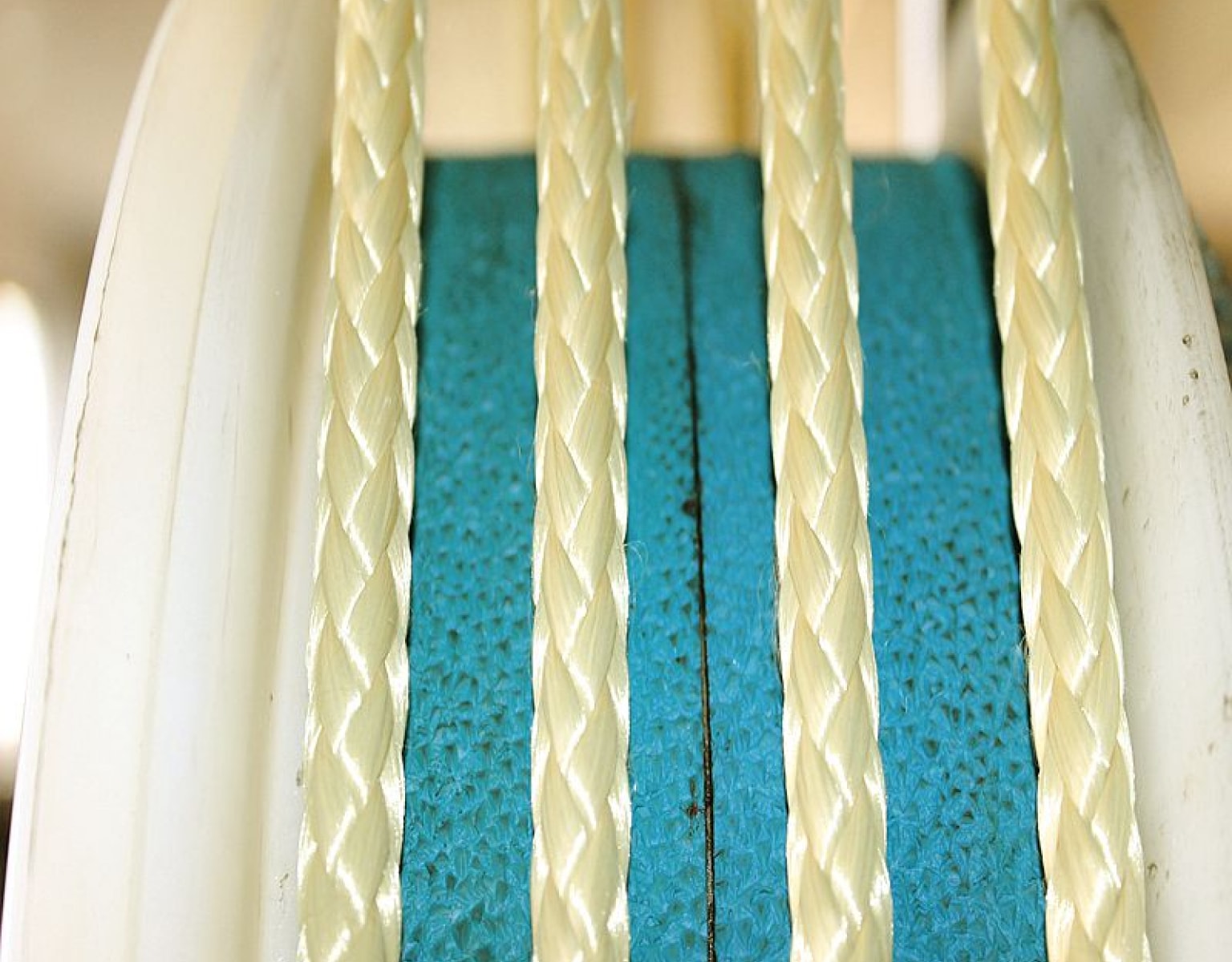
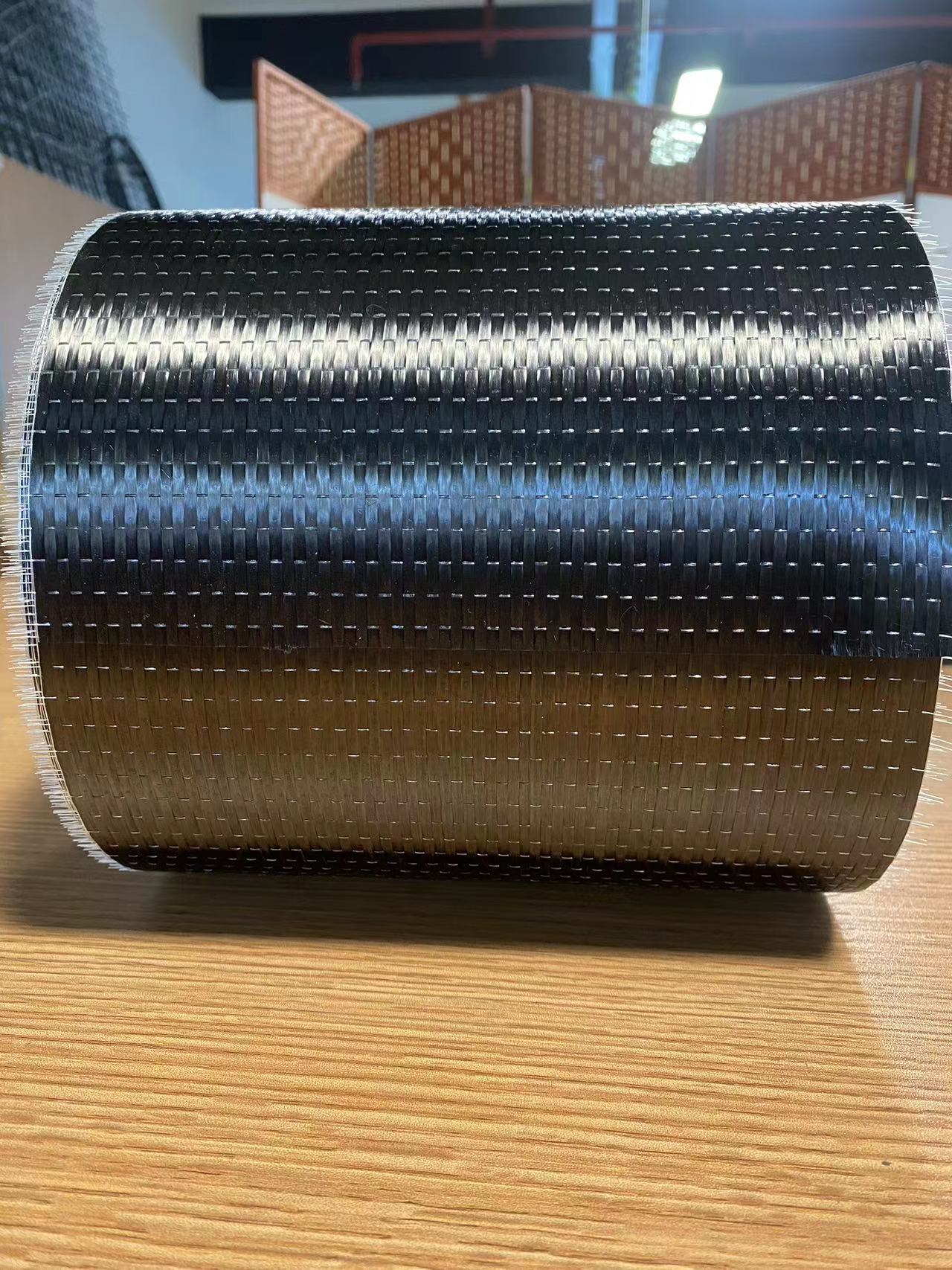
Planar Biaxial Woven Structures
This two-dimensional woven fabric is crafted by intertwining two sets of vertically arranged yarns (warp and weft) according to specific weave patterns. Planar biaxial woven fabrics, based on the organization of the textile, can be further divided into plain weaves, twill weaves, satin weaves, and unidirectional fabrics. Plain weaves, through the adjustment of yarn densities and alignment of warp and weft, can achieve isotropic reinforcement of the structure; twill weaves provide enhanced deformability; satin weaves exhibit superior effects during impregnation with the matrix material due to fewer yarn interlacings; while unidirectional fabrics cater to diverse reinforcement needs through variations in yarn density and warp/weft densities.
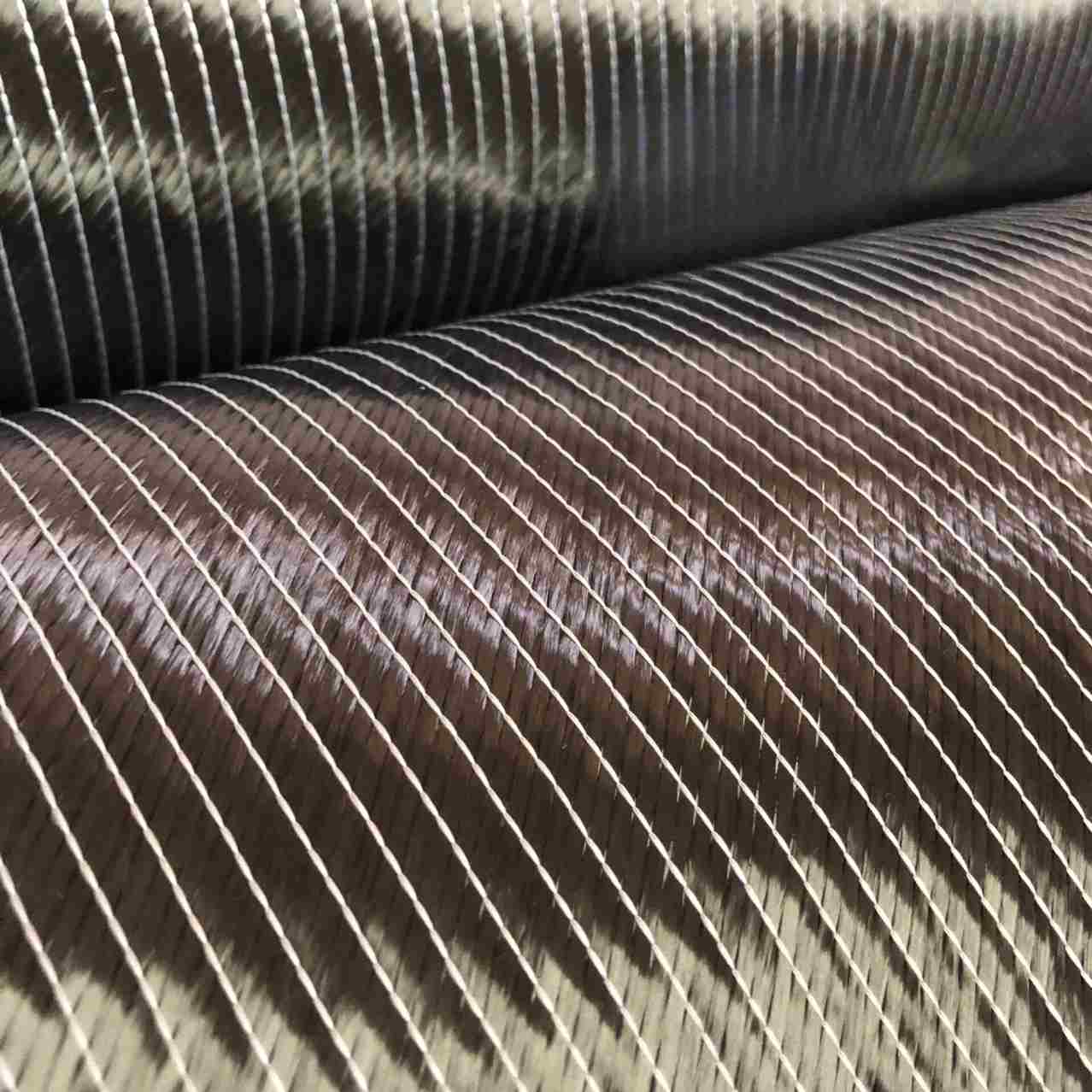
Planar Multiaxial Woven Structures
Yarns in the 0° and 90° directions of planar multiaxial woven fabrics are not fully stretched, resulting in comparatively lower rigidity and strength. Among these, plain triaxial fabrics stand out as a common multiaxial structure where three sets of yarns are interlaced at 120° angles, with warp yarns arranged diagonally and weft yarns horizontally. Possessing isotropic characteristics, plain triaxial fabrics offer superior mechanical properties compared to conventional two-dimensional woven fabrics, including enhanced shear resistance, tear strength, and puncture performance. However, their production efficiency is lower due to the intricate weaving process, and with the continuous emergence of novel structures, the market dominance of this fabric structure is gradually waning.
Spatial Three-Dimensional Woven Structures
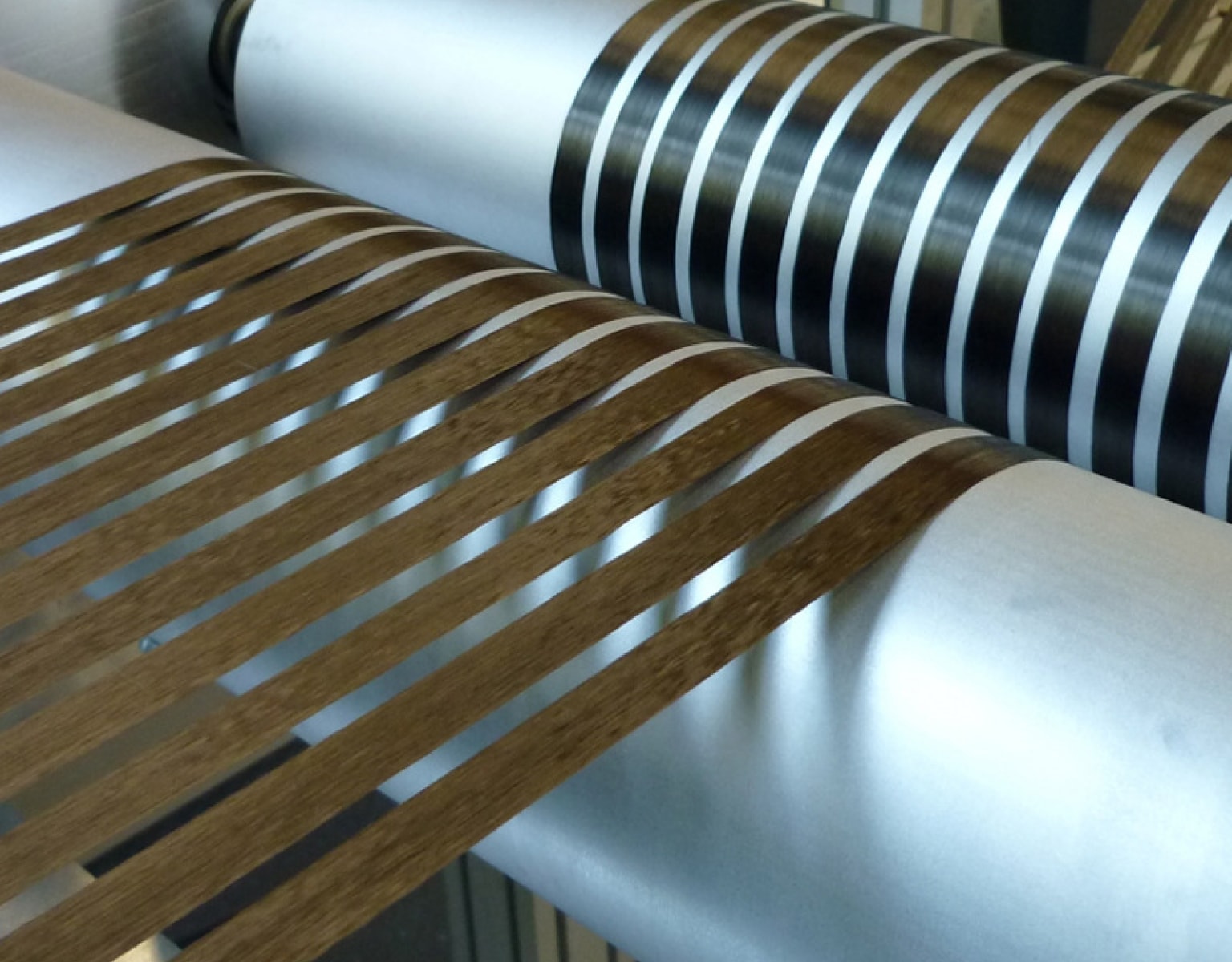
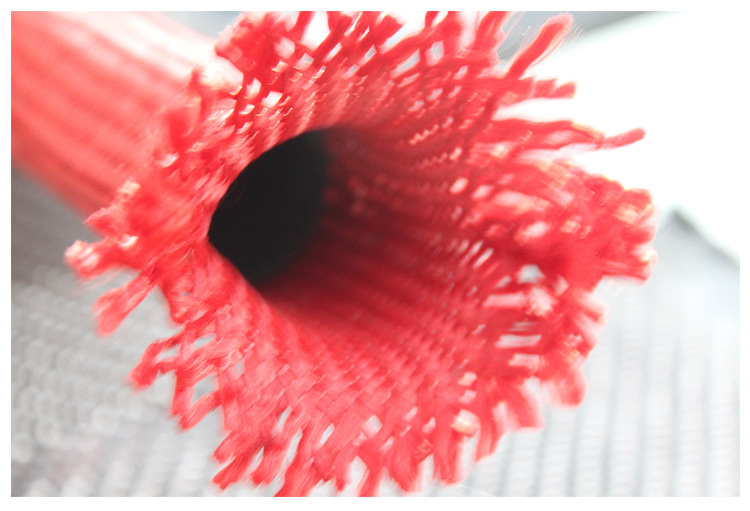
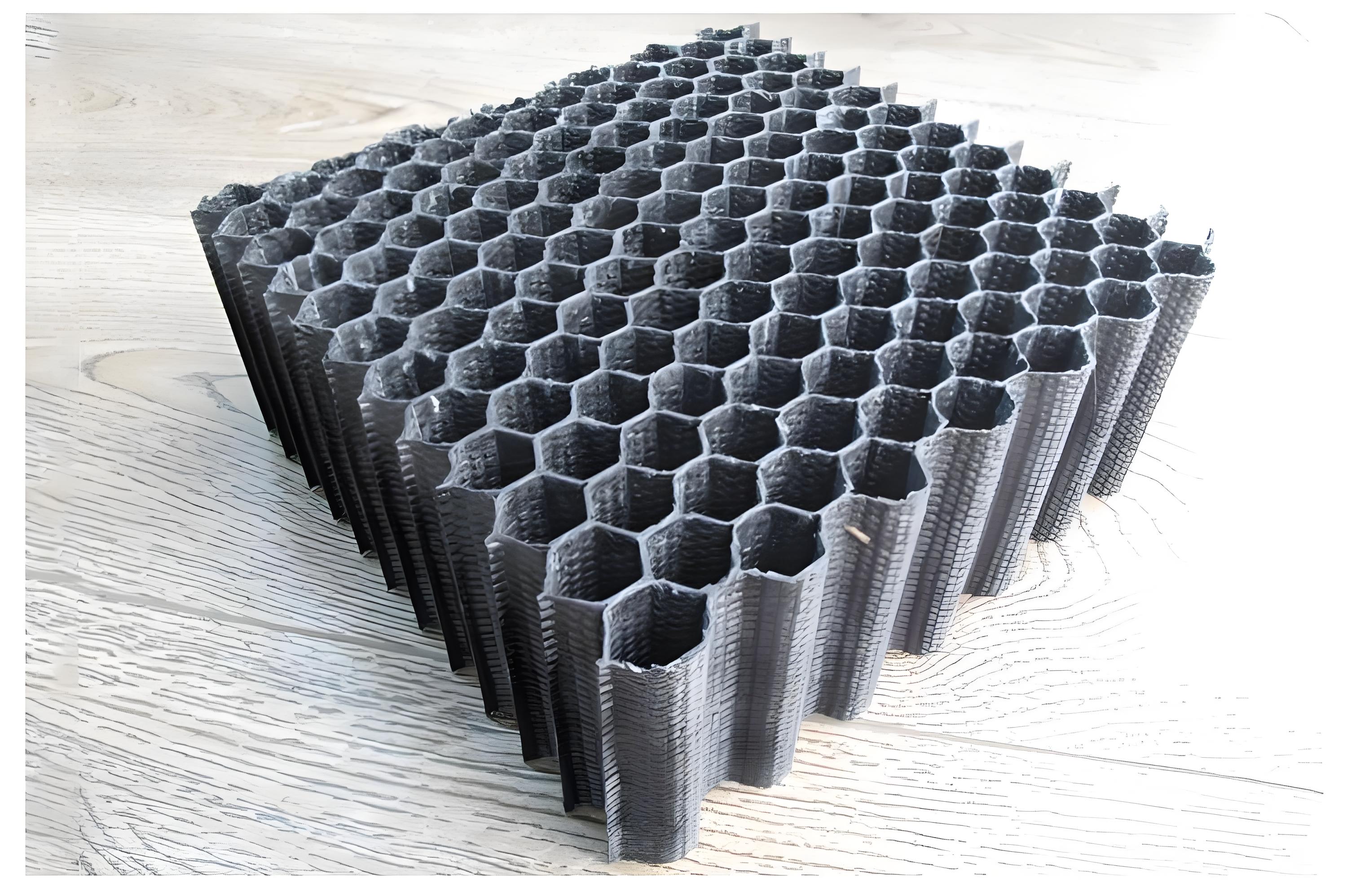
Three-dimensional woven structures utilize multi-layer warp weaving techniques to interconnect warp and weft yarns from different layers through Z-direction yarns, creating a solid three-dimensional fabric. This structure can be categorized into orthogonal triaxial structures, spacer fabrics, and angle-interlock structures. Orthogonal triaxial structures align yarns at 90° angles in the X, Y, and Z directions, forming structures with specific cross-sections like T-sections or I-beams; spacer fabrics connect two layers of fabric using Z-direction yarns, enabling the creation of lightweight, high-performance hollow structures; angle-interlock structures vary based on the direction of additional yarn insertions. Compared to two-dimensional structures, three-dimensional woven structures can produce more complex shaped prefabricated components, exhibiting higher impact damage tolerance and delamination resistance. However, the complexity of their structure poses challenges in modeling and simulating their mechanical properties, necessitating ongoing research.
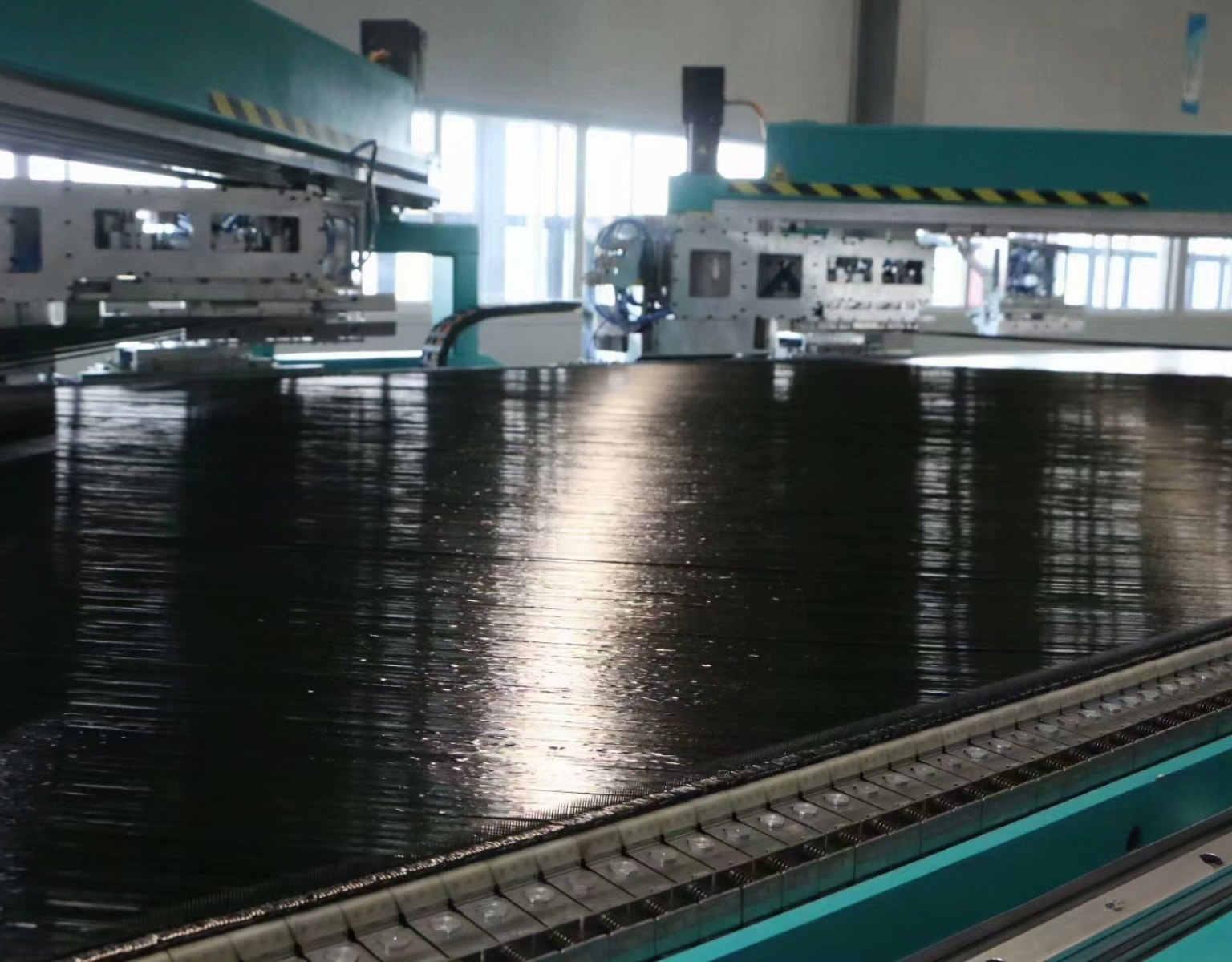
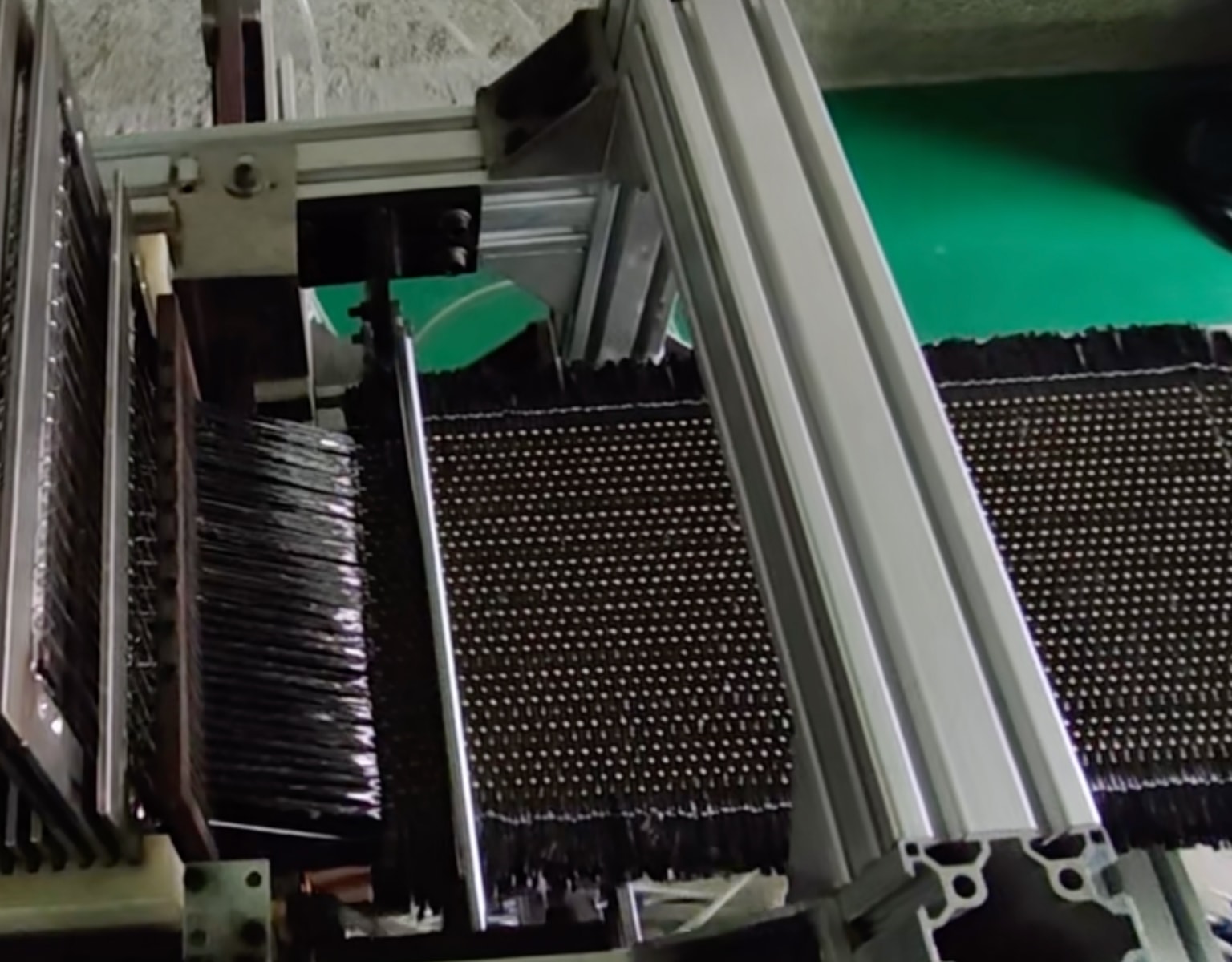
Three-Dimensional Woven Technology and Equipment
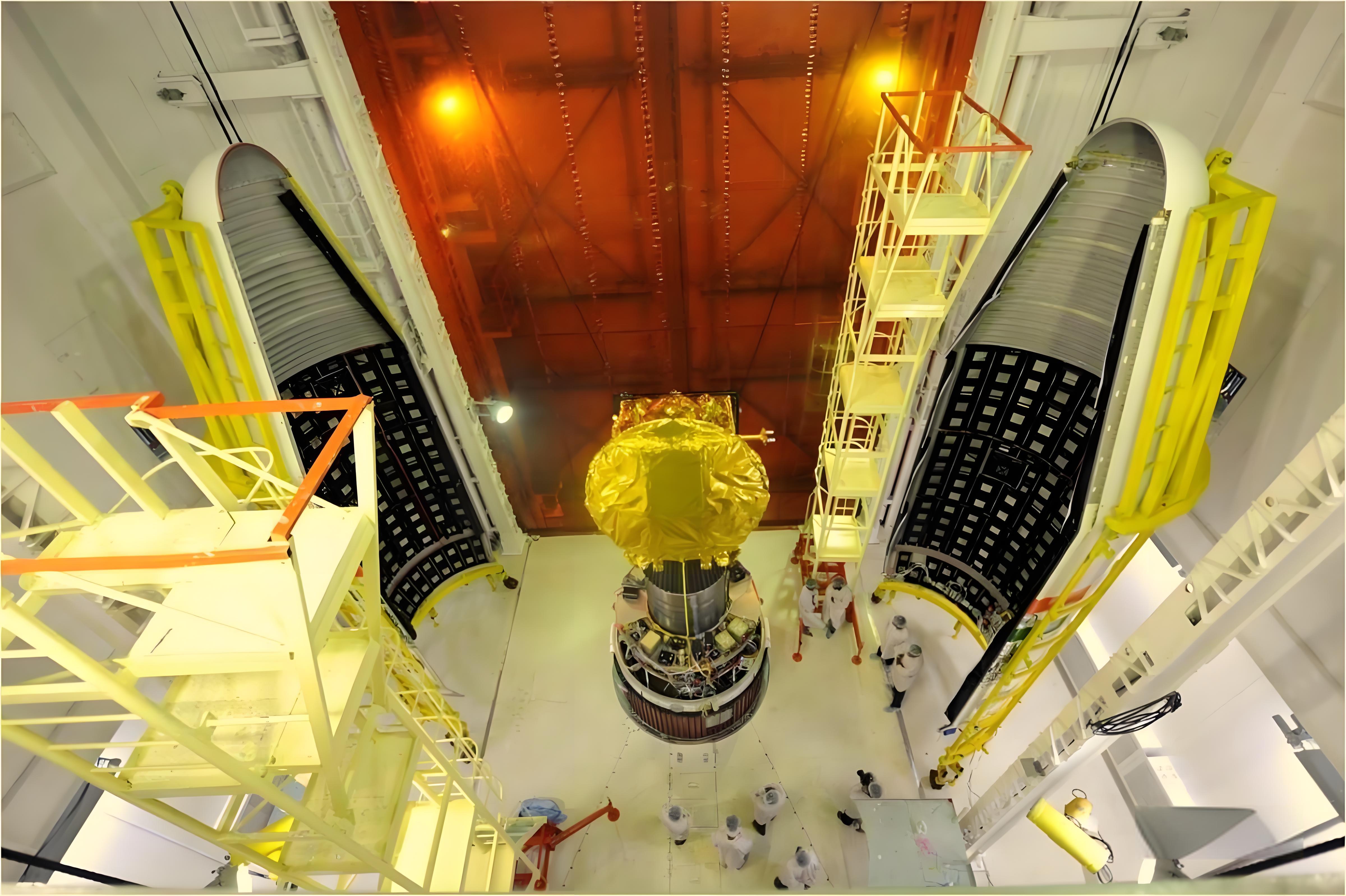
Advancing in the realm of high-speed loading domain materials technology, textile composite materials are gradually substituting traditional metallic materials, playing pivotal roles in structural components requiring strength and protection. Among the advanced composite materials, three-dimensional woven composites showcase outstanding structural integrity, ideal for fields demanding elevated material performance, such as the front fuselage or tail structure of manned spacecraft, coupling or fixing components of sounding rockets, and rotors or blades of turbine engines. The three-dimensional weaving equipment developed by Xcellent Composites focuses on the technological processes of three-dimensional woven sheets, enabling the automated production of three-dimensional woven fabrics with widths up to 600mm and thicknesses of 20mm.




Planar Biaxial Woven Structures
This two-dimensional woven fabric is crafted by intertwining two sets of vertically arranged yarns (warp and weft) according to specific weave patterns. Planar biaxial woven fabrics, based on the organization of the textile, can be further divided into plain weaves, twill weaves, satin weaves, and unidirectional fabrics. Plain weaves, through the adjustment of yarn densities and alignment of warp and weft, can achieve isotropic reinforcement of the structure; twill weaves provide enhanced deformability; satin weaves exhibit superior effects during impregnation with the matrix material due to fewer yarn interlacings; while unidirectional fabrics cater to diverse reinforcement needs through variations in yarn density and warp/weft densities.
Planar Multiaxial Woven Structures
Yarns in the 0° and 90° directions of planar multiaxial woven fabrics are not fully stretched, resulting in comparatively lower rigidity and strength. Among these, plain triaxial fabrics stand out as a common multiaxial structure where three sets of yarns are interlaced at 120° angles, with warp yarns arranged diagonally and weft yarns horizontally. Possessing isotropic characteristics, plain triaxial fabrics offer superior mechanical properties compared to conventional two-dimensional woven fabrics, including enhanced shear resistance, tear strength, and puncture performance. However, their production efficiency is lower due to the intricate weaving process, and with the continuous emergence of novel structures, the market dominance of this fabric structure is gradually waning.
Spatial Three-Dimensional Woven Structures
Three-dimensional woven structures utilize multi-layer warp weaving techniques to interconnect warp and weft yarns from different layers through Z-direction yarns, creating a solid three-dimensional fabric. This structure can be categorized into orthogonal triaxial structures, spacer fabrics, and angle-interlock structures. Orthogonal triaxial structures align yarns at 90° angles in the X, Y, and Z directions, forming structures with specific cross-sections like T-sections or I-beams; spacer fabrics connect two layers of fabric using Z-direction yarns, enabling the creation of lightweight, high-performance hollow structures; angle-interlock structures vary based on the direction of additional yarn insertions. Compared to two-dimensional structures, three-dimensional woven structures can produce more complex shaped prefabricated components, exhibiting higher impact damage tolerance and delamination resistance. However, the complexity of their structure poses challenges in modeling and simulating their mechanical properties, necessitating ongoing research.
Three-Dimensional Woven Technology and Equipment
Advancing in the realm of high-speed loading domain materials technology, textile composite materials are gradually substituting traditional metallic materials, playing pivotal roles in structural components requiring strength and protection. Among the advanced composite materials, three-dimensional woven composites showcase outstanding structural integrity, ideal for fields demanding elevated material performance, such as the front fuselage or tail structure of manned spacecraft, coupling or fixing components of sounding rockets, and rotors or blades of turbine engines. The three-dimensional weaving equipment developed by Xcellent Composites focuses on the technological processes of three-dimensional woven sheets, enabling the automated production of three-dimensional woven fabrics with widths up to 600mm and thicknesses of 20mm.
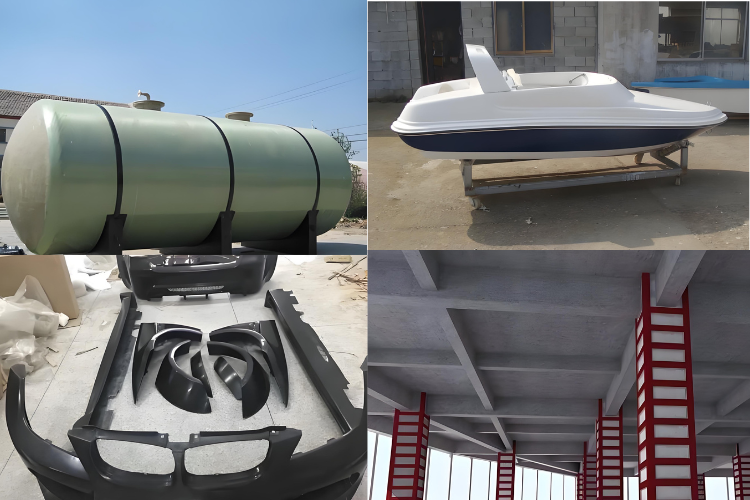
Popular Composite Materials
Popular Composite Materials








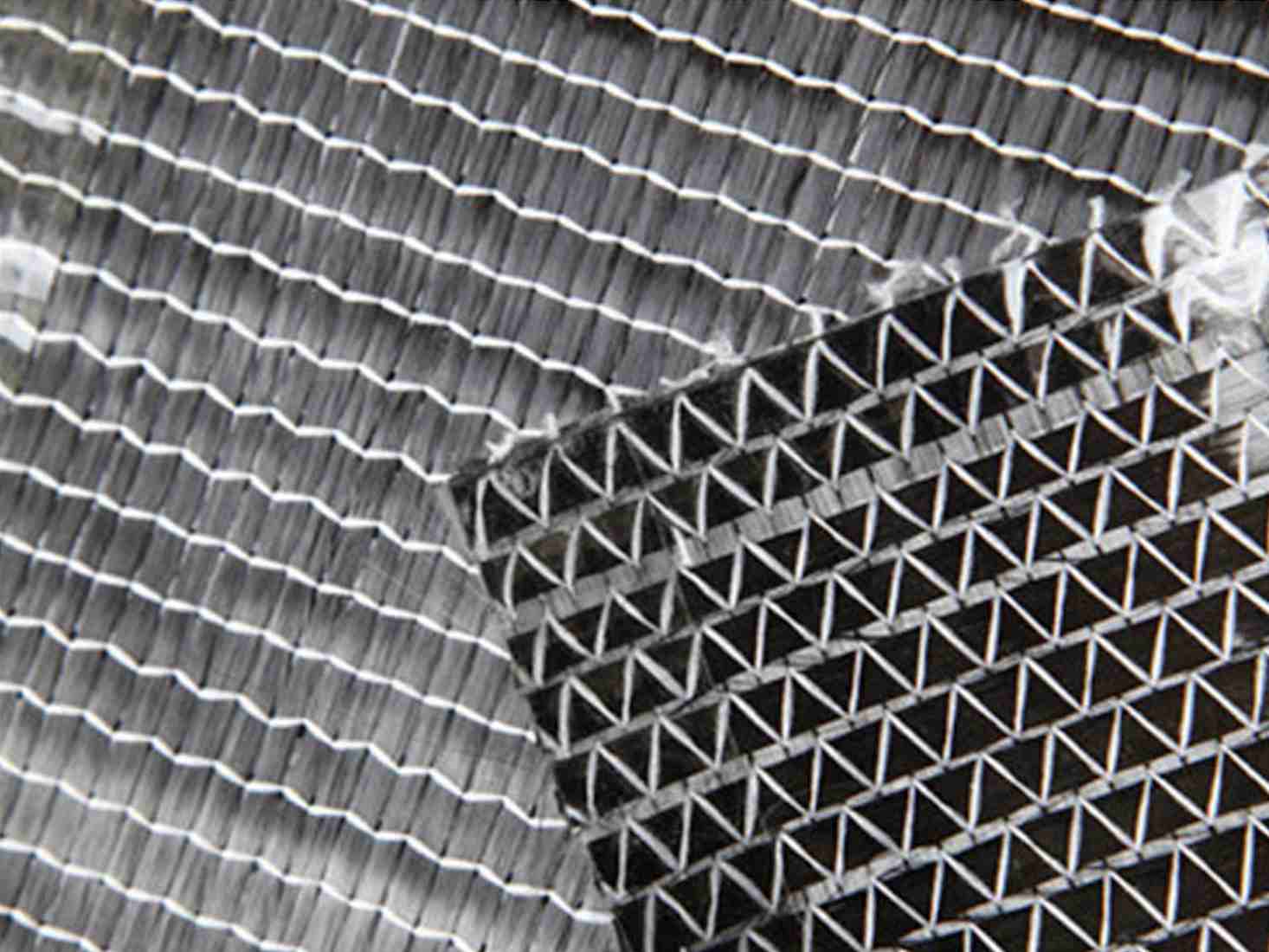
Related Composite Materials Capabilities
Related Composite Materials Capabilities
Composites Knowledge Hub
Composites Knowledge Hub




























Tel:
86-13732282311
E-mail:
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Copyright © Hangzhou Xcellent Composites Limited. All Rights Reserved.