+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!
Reinforcement material for Electronics
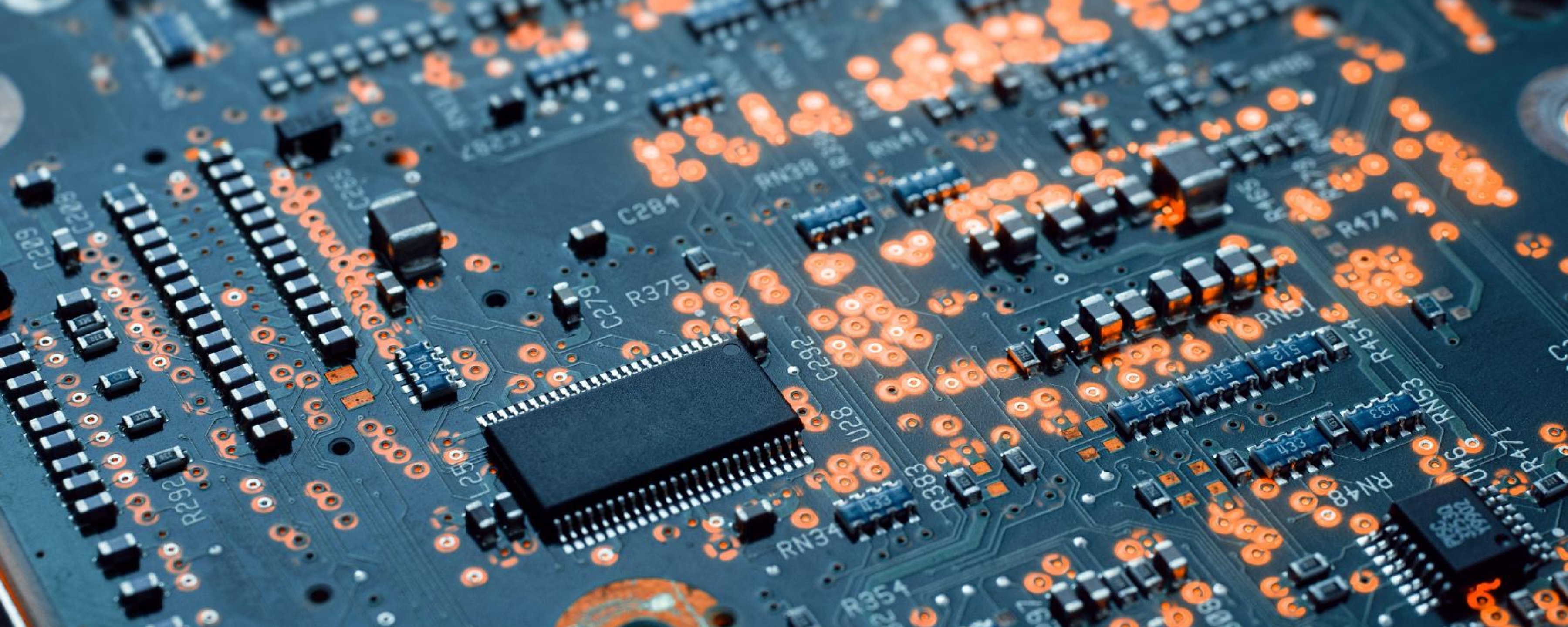
Reinforcement material for Electronics
Carbon fiber electronics are gaining popularity due to their lightweight, durability, and heat resistance. A key carbon fiber application is in protective casings and structural components for high-performance devices. Additionally, a fiberglass electronics box offers excellent insulation and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for housing sensitive electronic equipment.
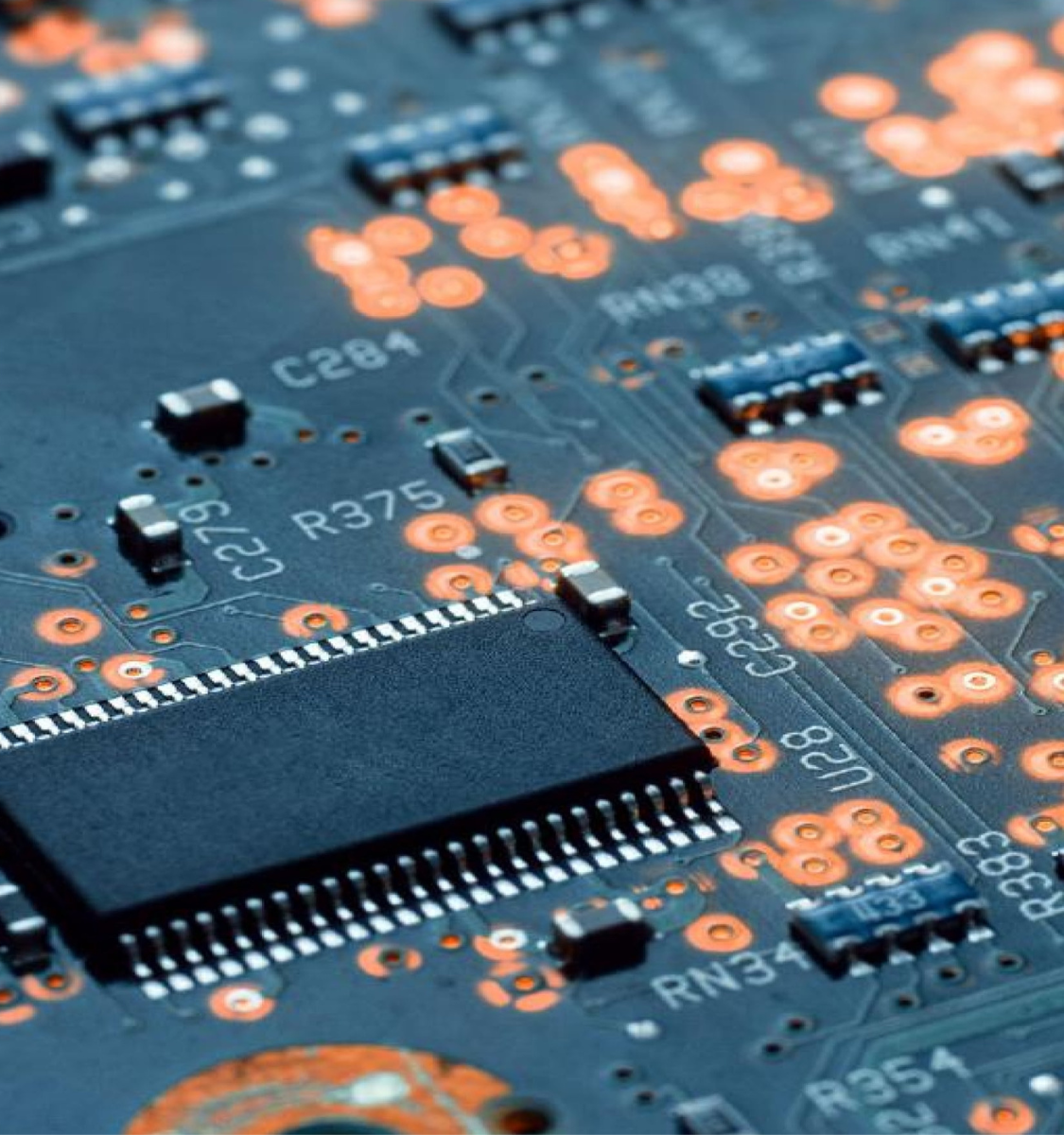
Reinforcement material for Electronics
Carbon fiber electronics are gaining popularity due to their lightweight, durability, and heat resistance. A key carbon fiber application is in protective casings and structural components for high-performance devices. Additionally, a fiberglass electronics box offers excellent insulation and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for housing sensitive electronic equipment.
Electronics
Electronics
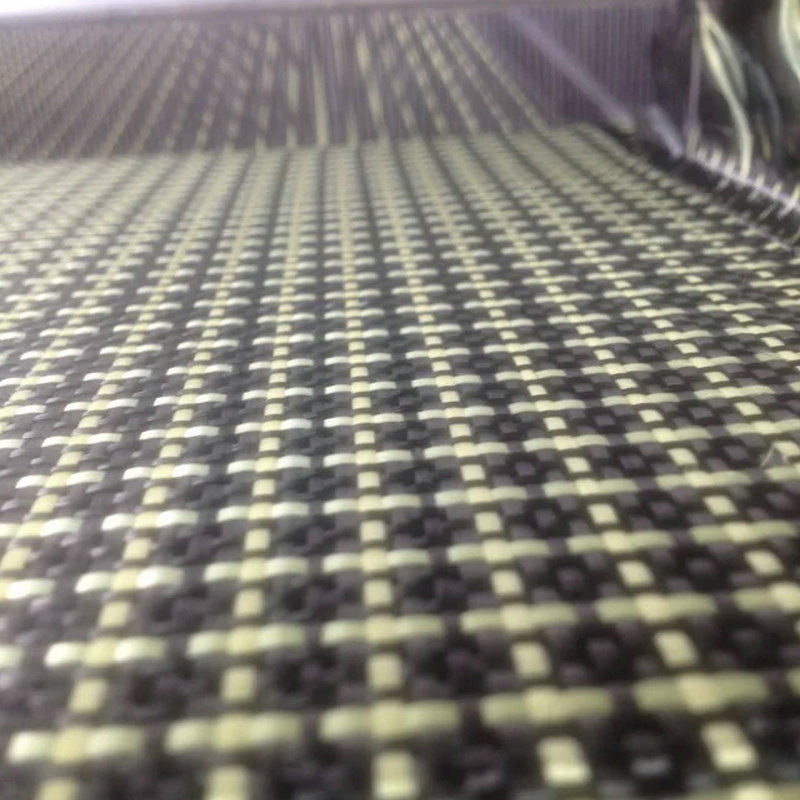
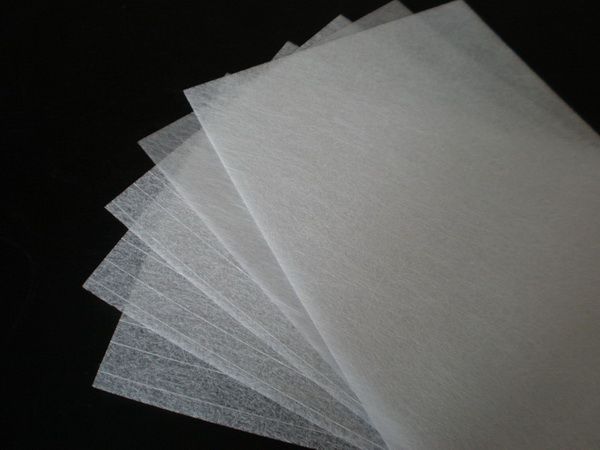
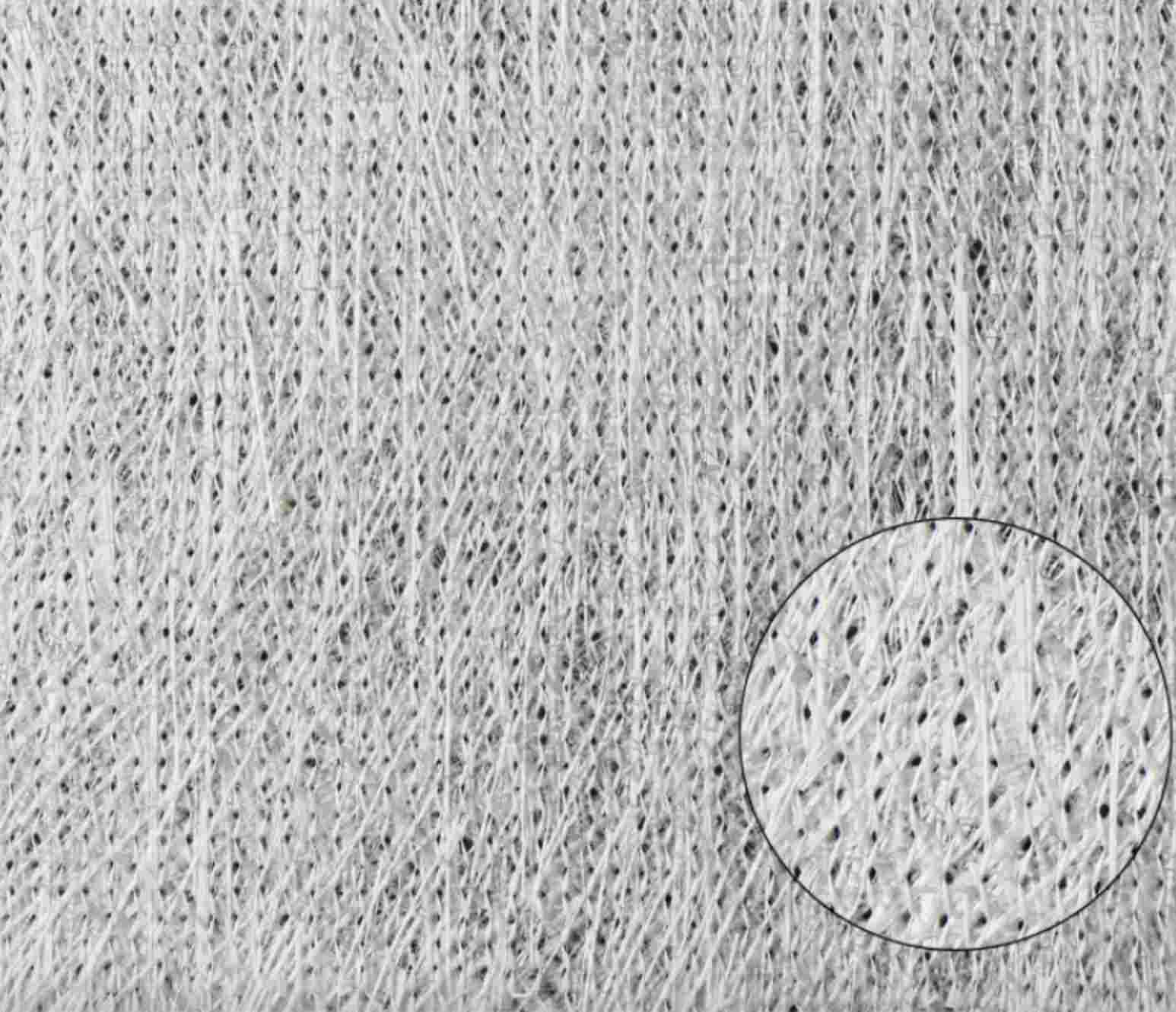
Fiberglass plays a crucial role in the realm of electronic products. Initially employed for electrical insulation, fiberglass has become an integral component in the electronic market owing to its electrical resistance and heat tolerance. Woven into fabrics, it serves as the framework for printed circuit boards (PCBs), imparting the necessary structural integrity to these PCBs. As digital circuits evolve towards higher speeds and frequencies, the demands for the electrical performance of PCB substrates have escalated, necessitating the reduction of the PCB's dielectric constant and dielectric loss tangent. In this regard, low dielectric constant glass laminate stands out as an effective means to achieve this objective.
Fiberglass plays a crucial role in the realm of electronic products. Initially employed for electrical insulation, fiberglass has become an integral component in the electronic market owing to its electrical resistance and heat tolerance. Woven into fabrics, it serves as the framework for printed circuit boards (PCBs), imparting the necessary structural integrity to these PCBs. As digital circuits evolve towards higher speeds and frequencies, the demands for the electrical performance of PCB substrates have escalated, necessitating the reduction of the PCB's dielectric constant and dielectric loss tangent. In this regard, low dielectric constant glass laminate stands out as an effective means to achieve this objective.
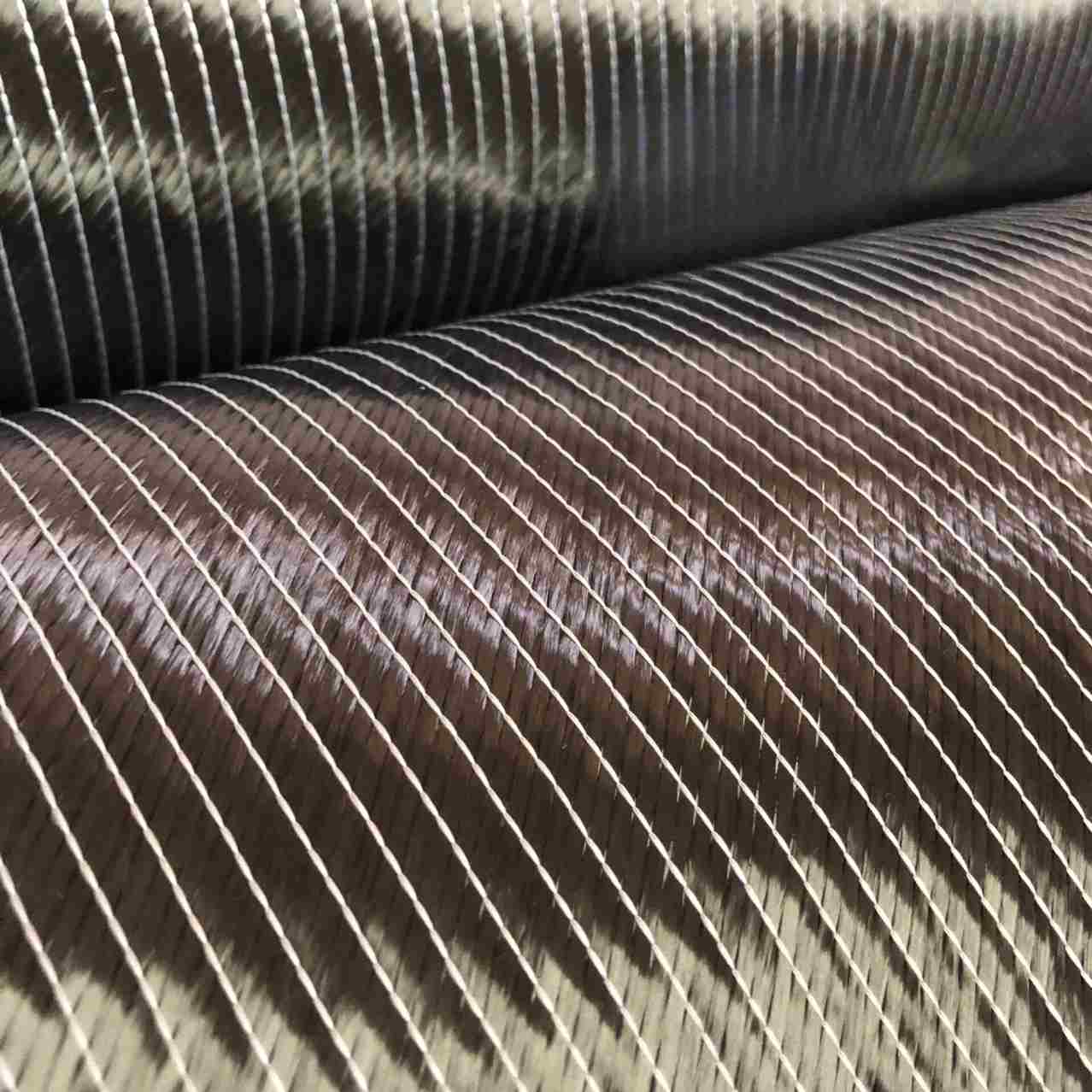
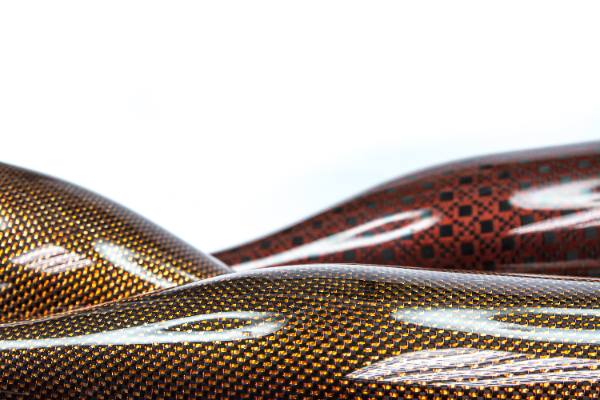
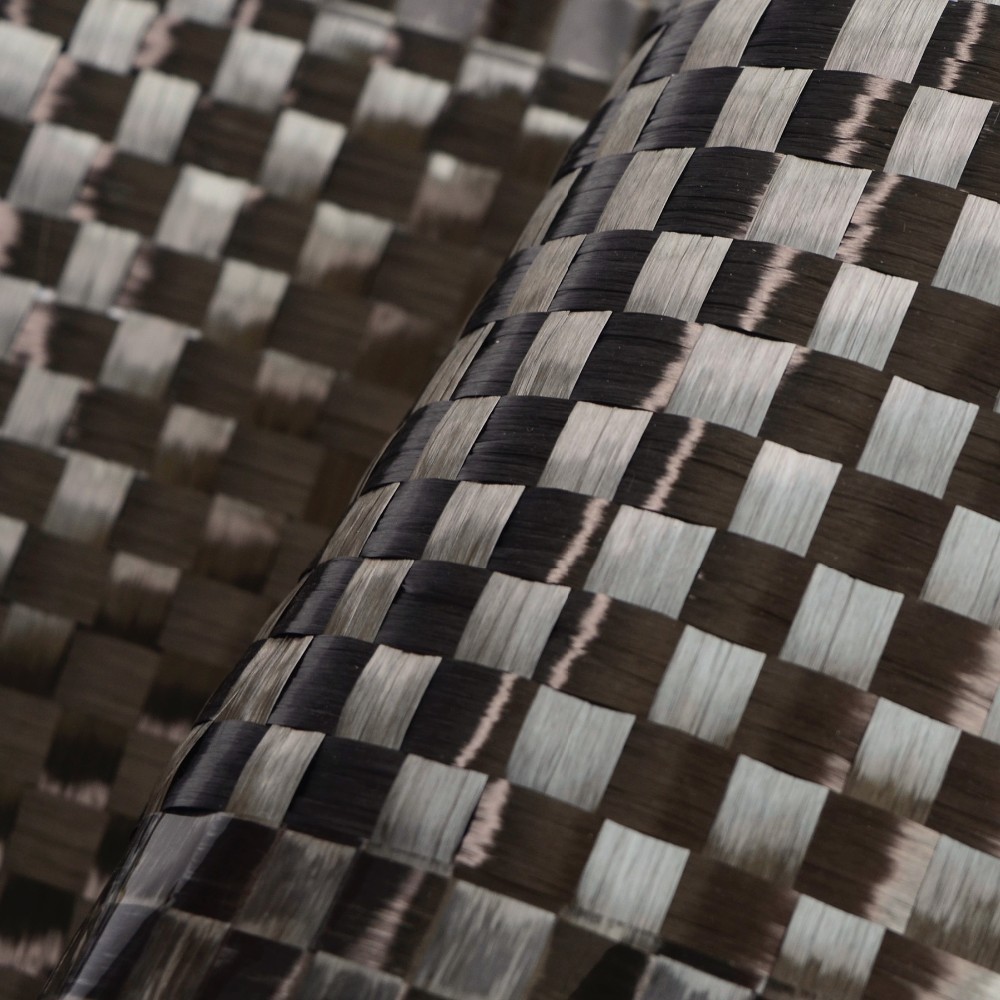
Aramid fiber, as an organic reinforcement material, offers a lightweight, high-strength, low-dielectric alternative compared to inorganic glass fiber. It is easily processable and well-suited for high-end PCBs used in electronic communication devices, aerospace applications, and military domains. Since the 1990s, with the rapid advancement of the electronic information industry and the trend towards lighter, thinner, smaller, and higher-density solutions, the demand for novel substrates has heightened. Aramid fiber has emerged as a pivotal choice for PCB manufacturers due to its suitability for laser drilling, lightweight nature, low dielectric constant, and excellent thermal stability. Aramid fiber contributes to enhancing the operating frequency of electronic products and supports the development of high-density integrated circuit packaging substrates. Consequently, the application of aramid fiber in the realm of PCBs constitutes a critical avenue for manufacturers' advancement.
Aramid fiber, as an organic reinforcement material, offers a lightweight, high-strength, low-dielectric alternative compared to inorganic glass fiber. It is easily processable and well-suited for high-end PCBs used in electronic communication devices, aerospace applications, and military domains. Since the 1990s, with the rapid advancement of the electronic information industry and the trend towards lighter, thinner, smaller, and higher-density solutions, the demand for novel substrates has heightened. Aramid fiber has emerged as a pivotal choice for PCB manufacturers due to its suitability for laser drilling, lightweight nature, low dielectric constant, and excellent thermal stability. Aramid fiber contributes to enhancing the operating frequency of electronic products and supports the development of high-density integrated circuit packaging substrates. Consequently, the application of aramid fiber in the realm of PCBs constitutes a critical avenue for manufacturers' advancement.
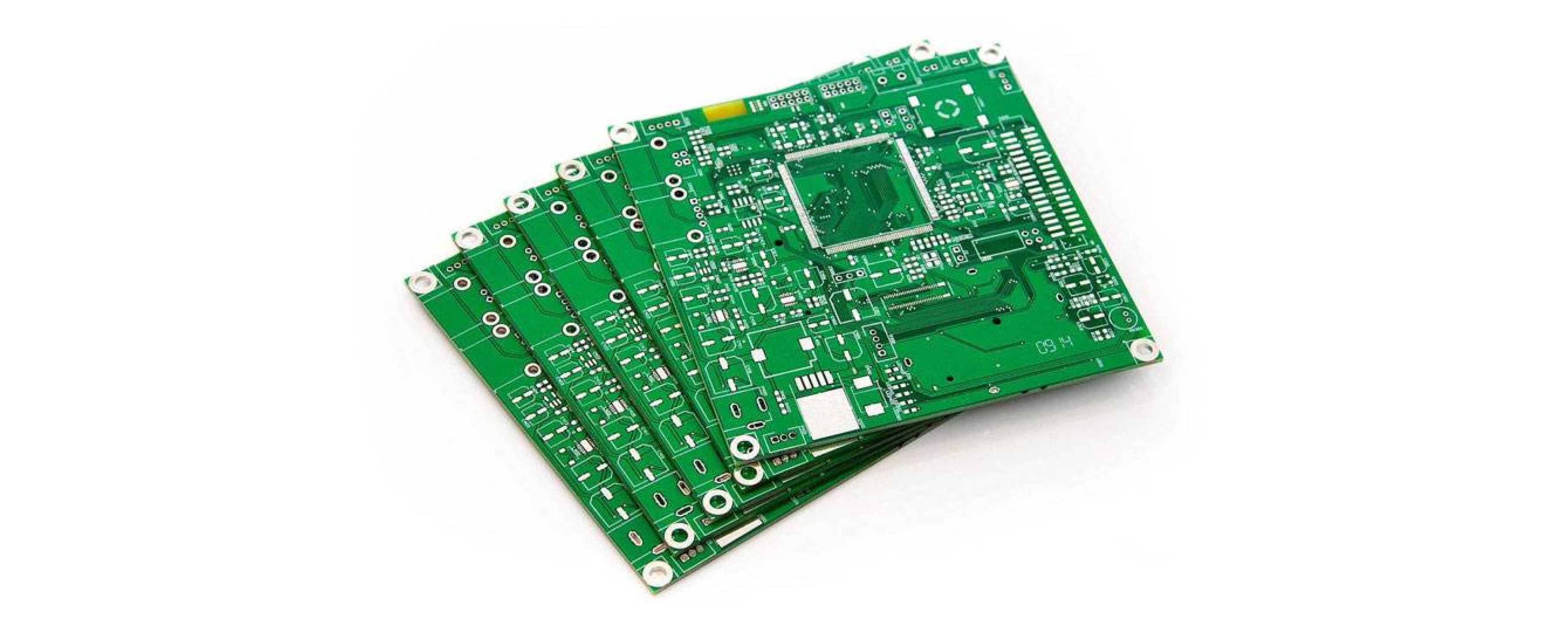


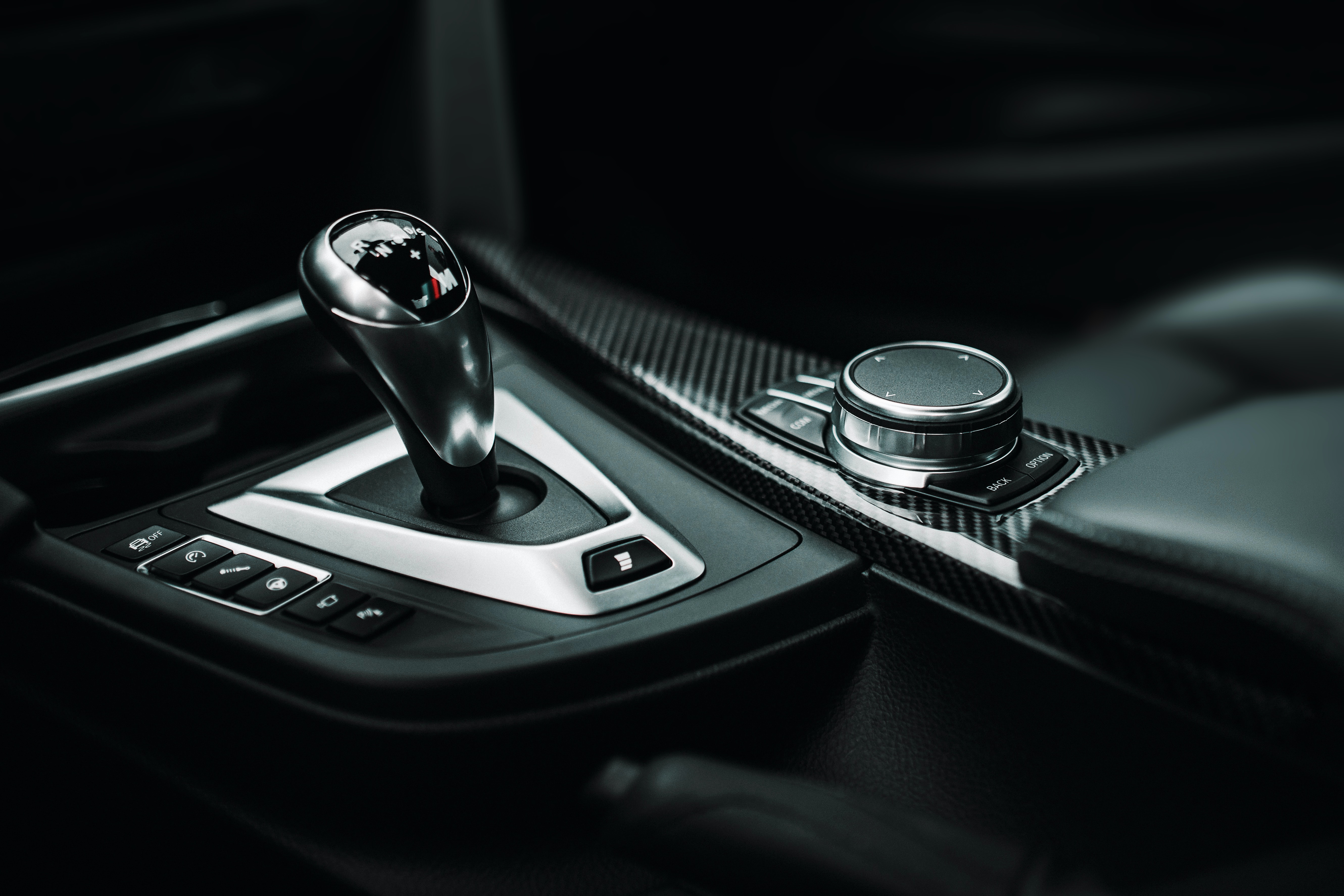
3C electronic products, including computers, communication devices, and consumer electronics, are progressively evolving to be more portable and lightweight. Currently, the shells and structural components of most electronic products are typically crafted from materials such as metal, engineering plastics, and composites. With a focus on achieving lightweight designs while considering cost-effectiveness and manufacturing processes, the utilization of engineering plastics, aluminum (magnesium) alloys, carbon fiber composites, and other advanced materials is poised to rise.
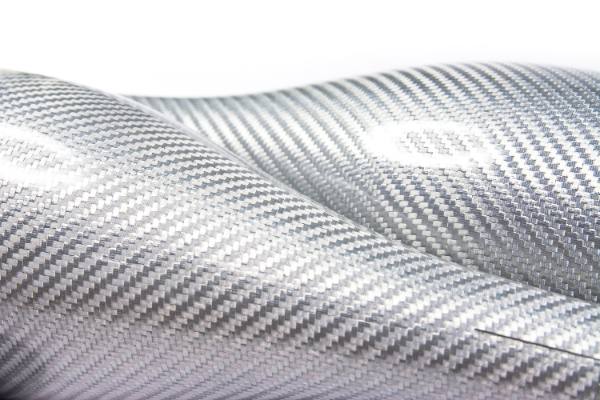
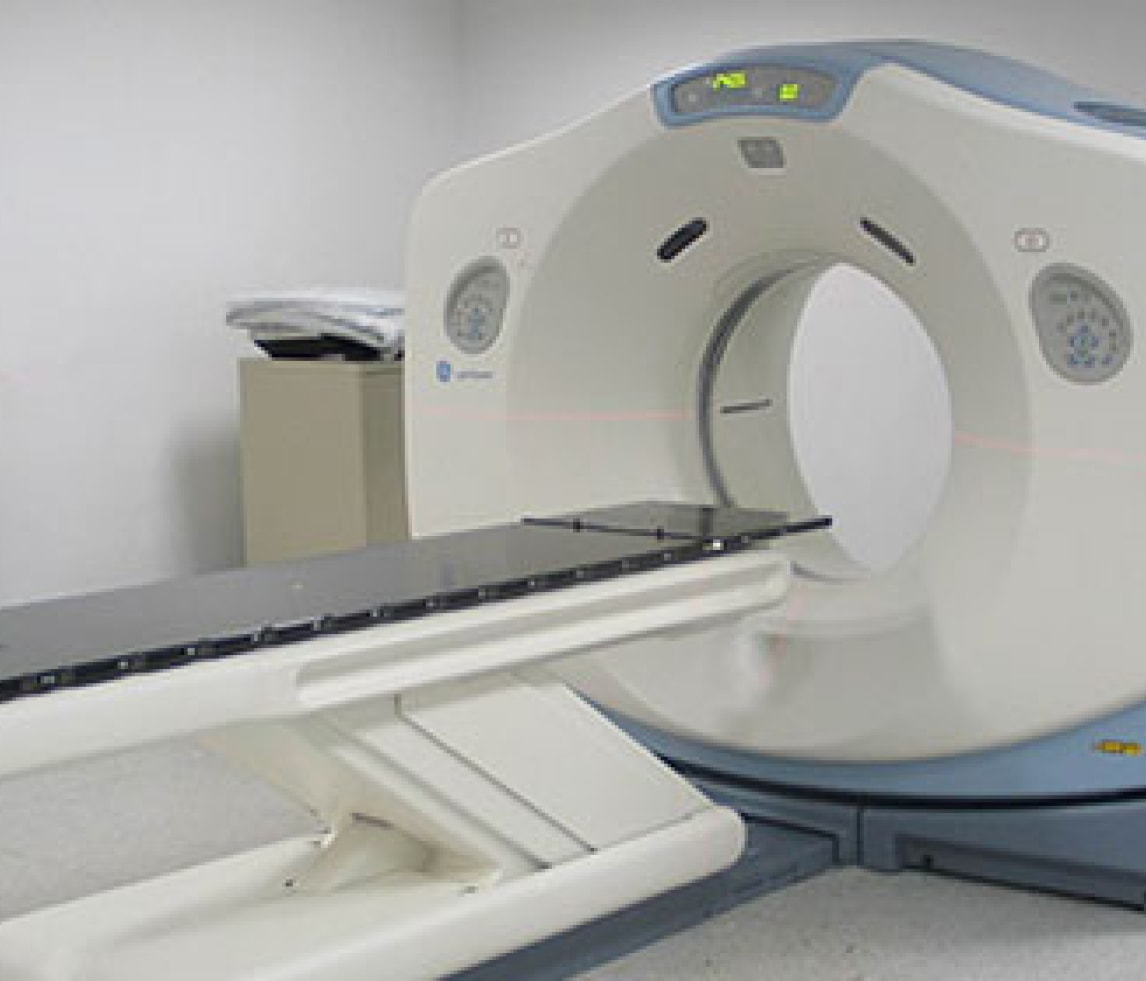
Carbon fiber, renowned for its lightweight properties, aligns perfectly with the trend towards smaller, lighter, and more portable electronic devices. Its versatility allows for widespread integration into products like laptops and televisions. Furthermore, carbon fiber composites possess unique characteristics, including electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, high X-ray transparency, and electromagnetic wave absorption.
3C electronic products, including computers, communication devices, and consumer electronics, are progressively evolving to be more portable and lightweight. Currently, the shells and structural components of most electronic products are typically crafted from materials such as metal, engineering plastics, and composites. With a focus on achieving lightweight designs while considering cost-effectiveness and manufacturing processes, the utilization of engineering plastics, aluminum (magnesium) alloys, carbon fiber composites, and other advanced materials is poised to rise.
Carbon fiber, renowned for its lightweight properties, aligns perfectly with the trend towards smaller, lighter, and more portable electronic devices. Its versatility allows for widespread integration into products like laptops and televisions. Furthermore, carbon fiber composites possess unique characteristics, including electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, high X-ray transparency, and electromagnetic wave absorption.

Get In Touch With Us!
To know more about our composite products and solutions, contact our experts! Here is how you can reach us.

Get In Touch With Us!
To know more about our composite products and solutions, contact our experts! Here is how you can reach us.
Popular Composite Materials
Popular Composite Materials
Related Composite Materials Industries
Related Composite Materials Industries
Composites Knowledge Hub
Composites Knowledge Hub