+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!
A Beginner's Guide to Working with Woven Fiberglass Cloth
Fiberglass is a material that has revolutionized industries by providing an unmatched combination of strength, durability, and versatility. One of the most commonly used forms of fiberglass in manufacturing, construction, automotive, and marine industries is woven fiberglass cloth. It’s a material that offers a variety of benefits, such as high tensile strength, fire resistance, and the ability to be molded into complex shapes when combined with resins. If you're new to working with woven fiberglass, this guide will help you understand its types, applications, and step-by-step instructions on how to use it.
What is Woven Fiberglass Cloth?
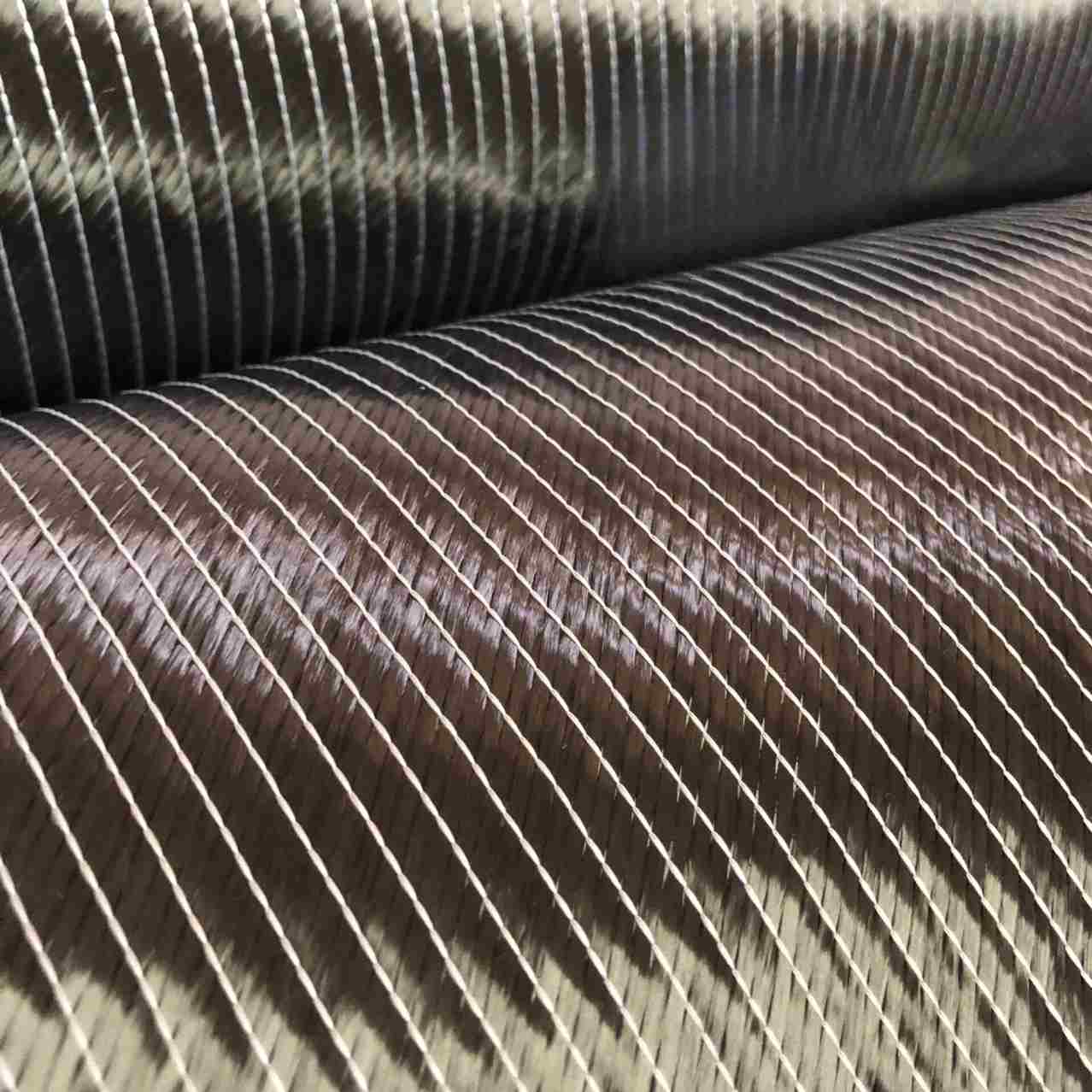
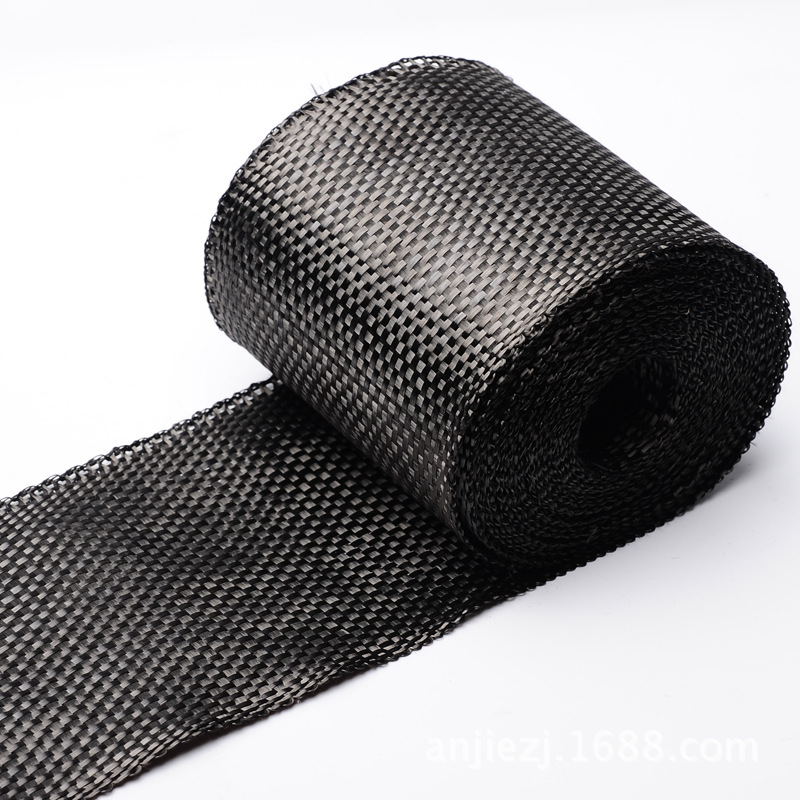
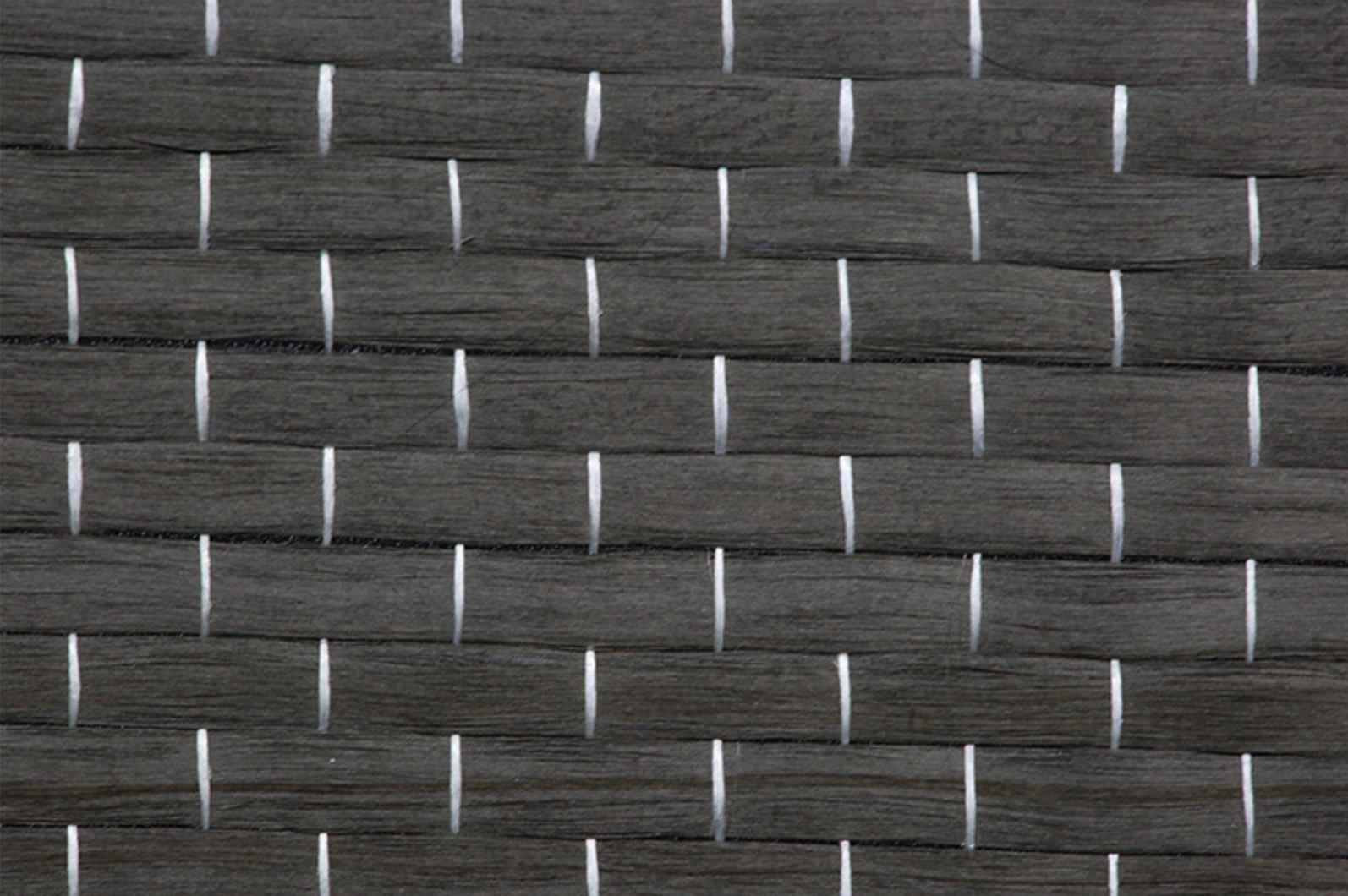
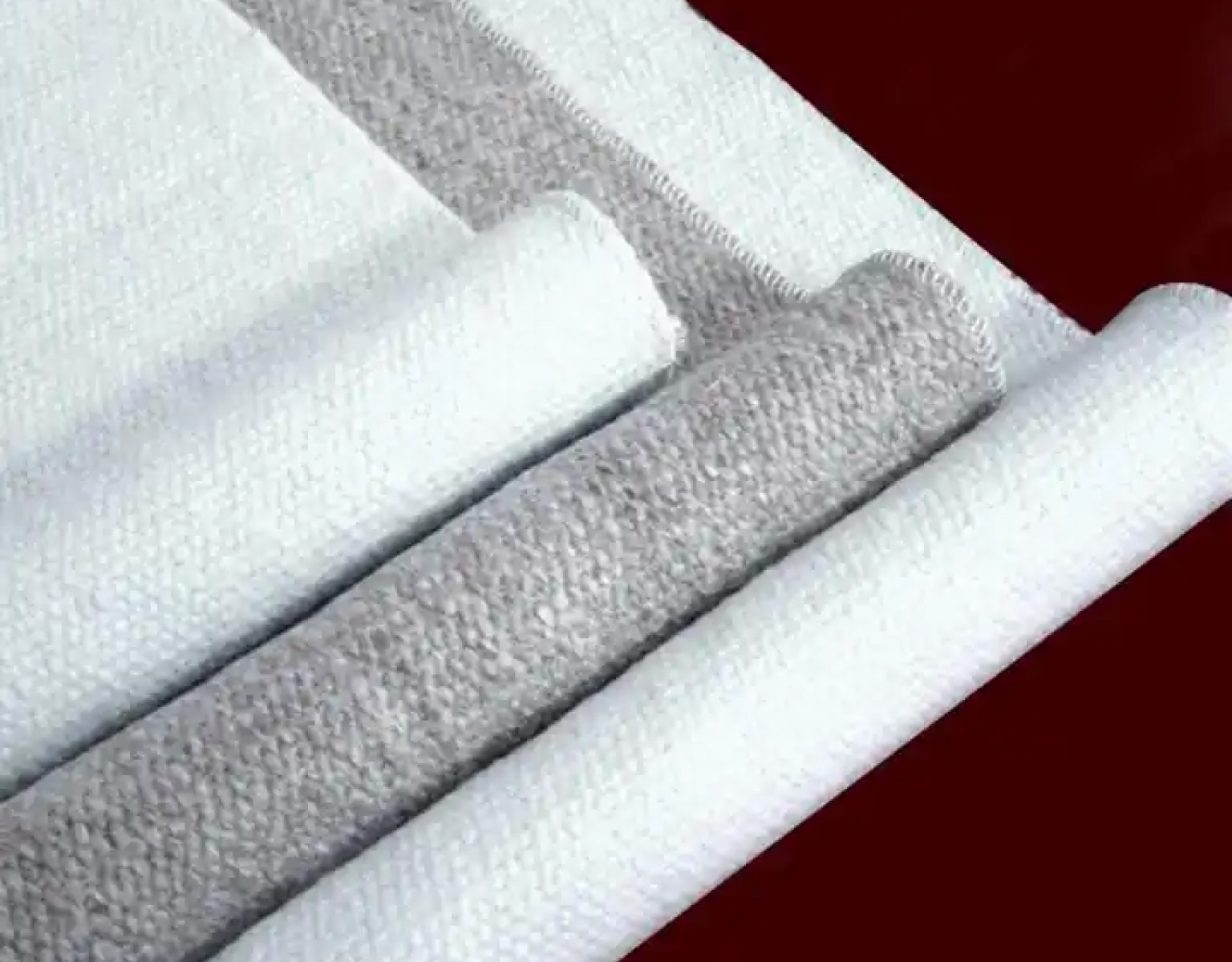
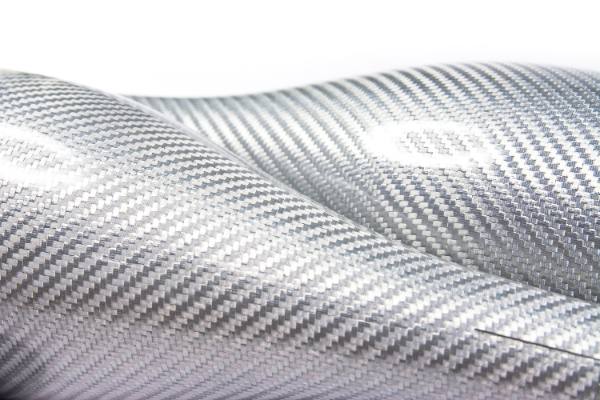
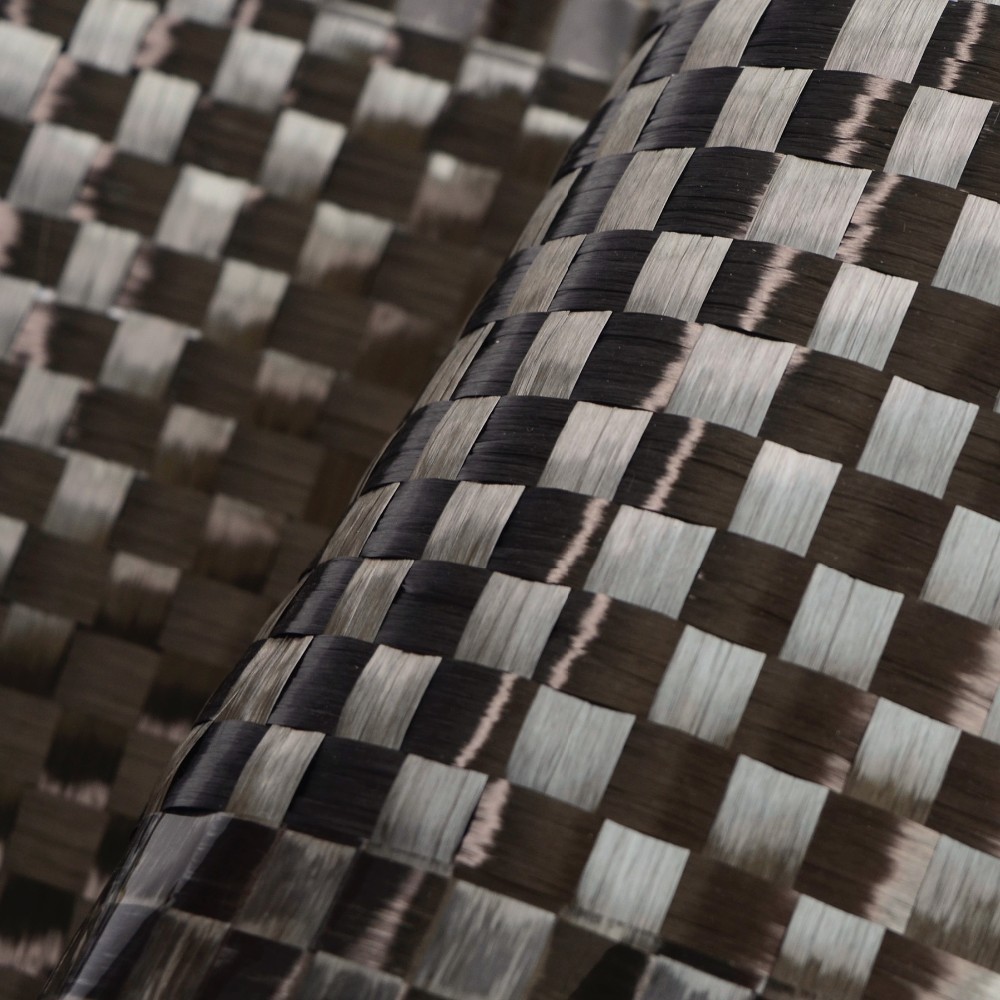
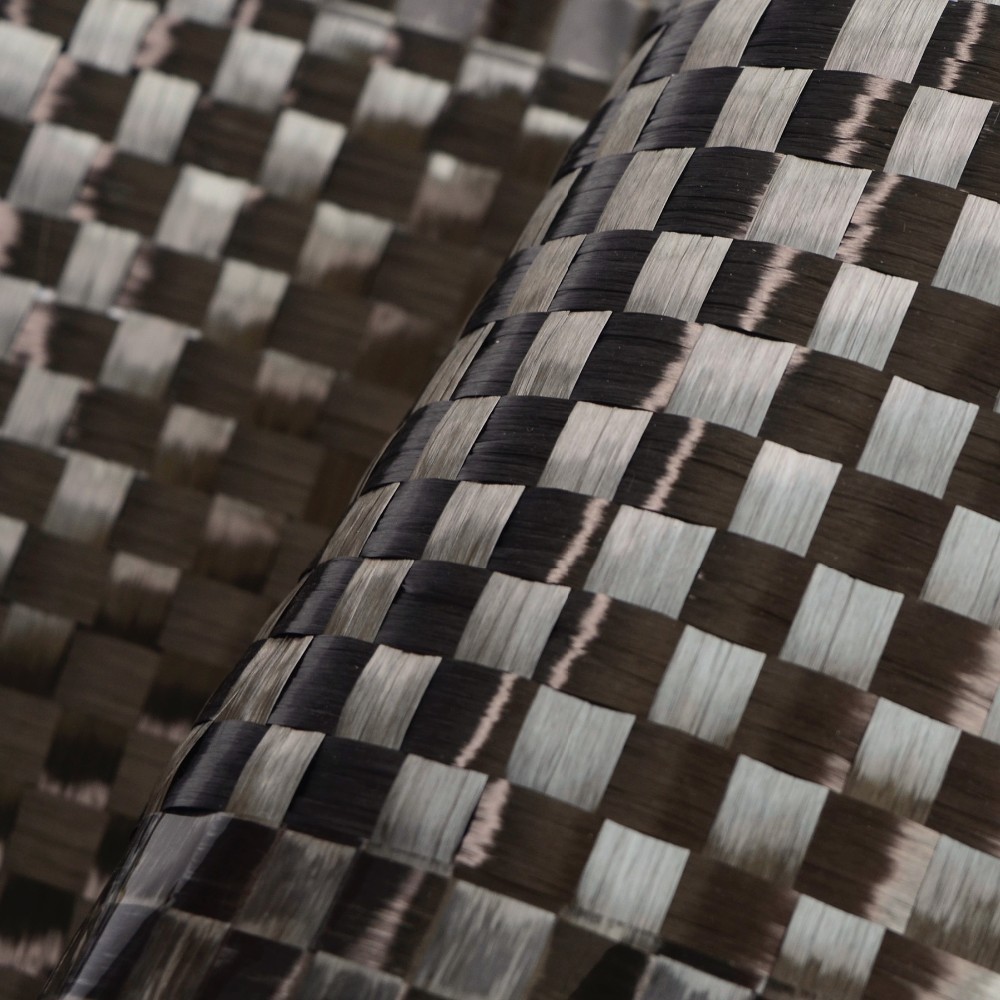
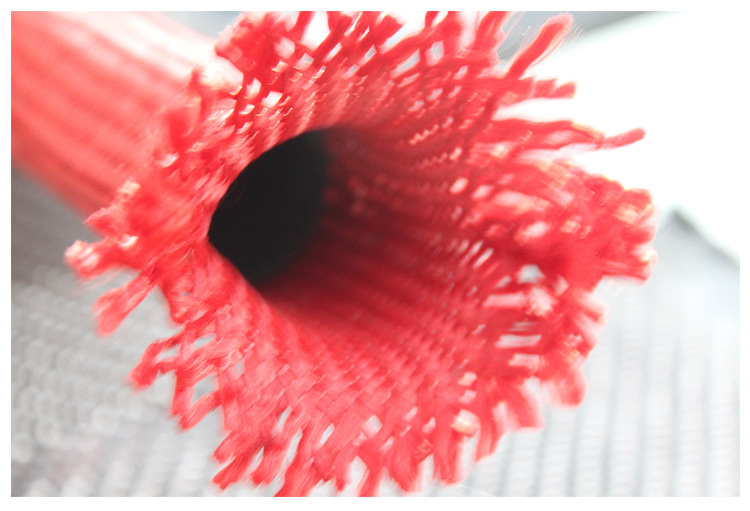
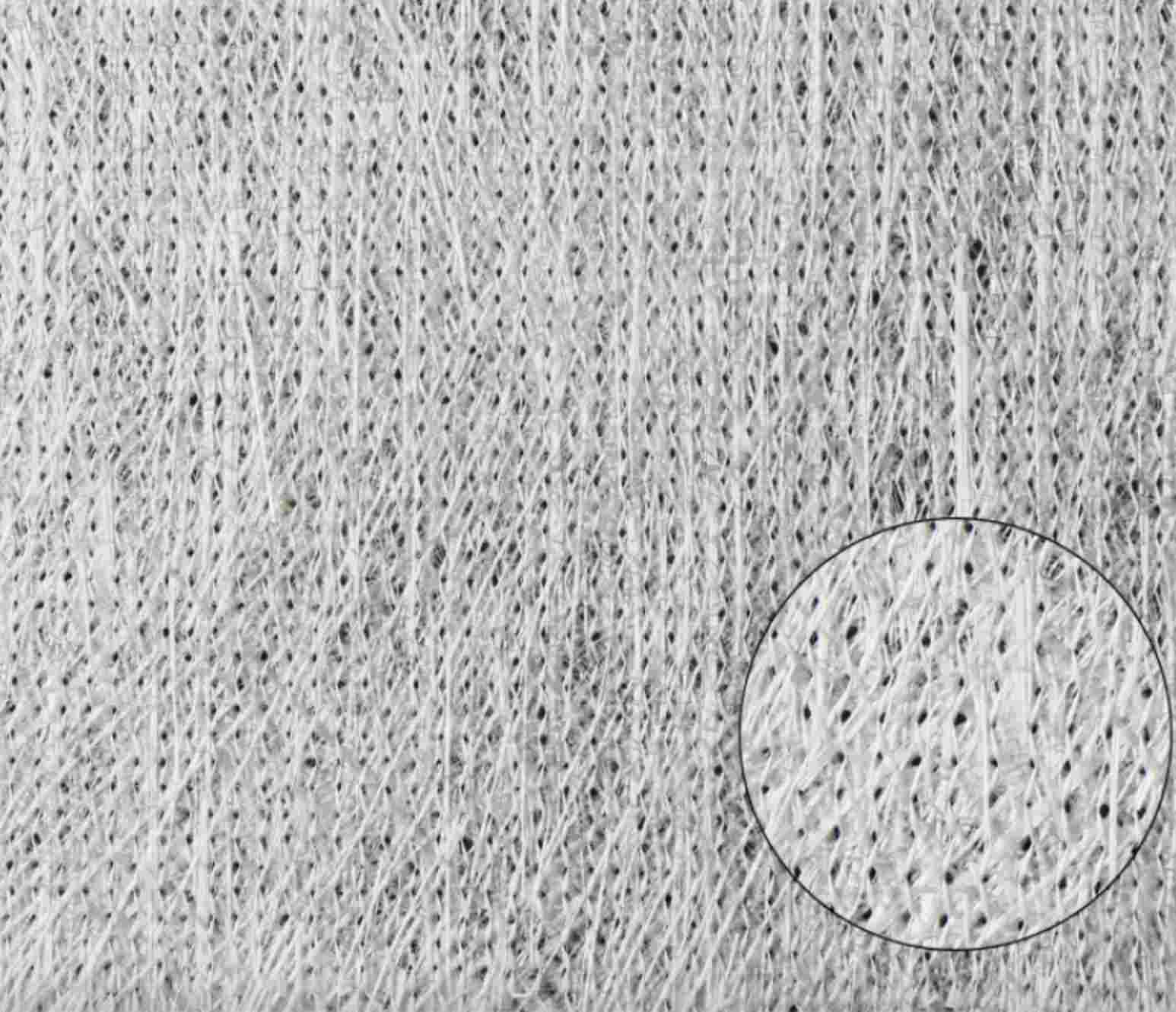
Woven fiberglass cloth is a fabric made from individual glass fibers that are woven into a tight, interlacing mesh pattern. The result is a material that is lightweight yet incredibly strong. The fibers themselves are made from silica, which gives the cloth its strength and heat-resistant properties. The cloth is typically used as a reinforcement material for composite structures, where it is combined with resins like epoxy, polyester, or vinyl ester to create a strong, durable product.
The process of making woven fiberglass involves weaving fine glass fibers into a fabric, much like you would weave cotton into a shirt. However, the fibers used in woven fiberglass cloth are much thinner, often thinner than a human hair. These fibers are woven in various patterns to create different grades of cloth, each tailored for specific applications.
Some of the common weave patterns include:
- Plain Weave: The simplest form of weaving where the fibers alternate over and under each other. It is strong and flexible, ideal for most general applications.
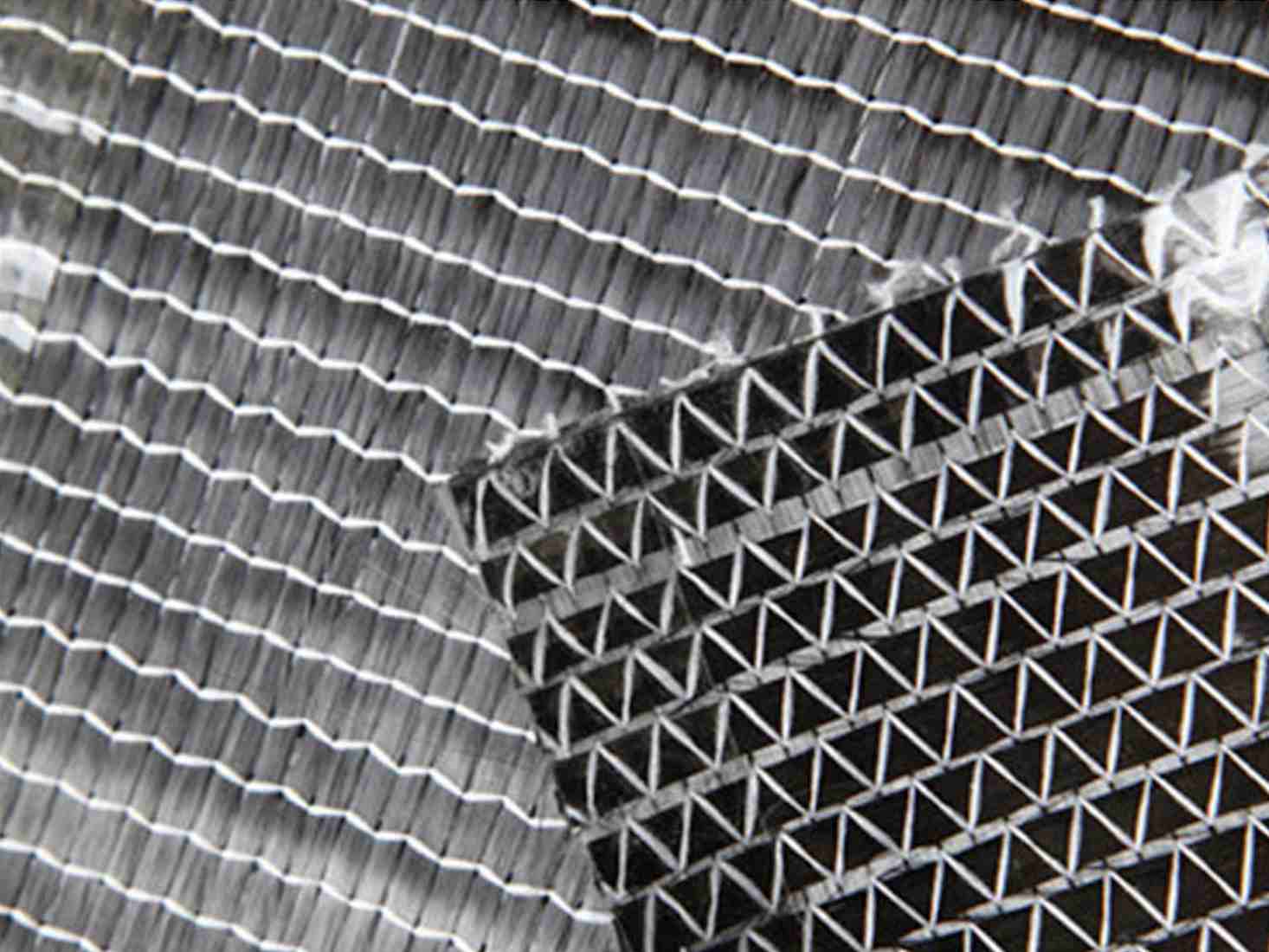
- Twill Weave: A more complex weave where the fibers cross in a diagonal pattern. This creates a fabric that is more flexible and has a characteristic diagonal pattern.
- Satin Weave: An even more intricate weave that creates a smooth surface. This is often used for high-end applications in aerospace or automotive industries.
Types of Woven Fiberglass
Woven fiberglass is not a one-size-fits-all material. There are different types of woven fiberglass cloth designed for specific applications. The characteristics of each type depend on the weave pattern, fiber thickness, and the material's intended use. Below are the primary types:
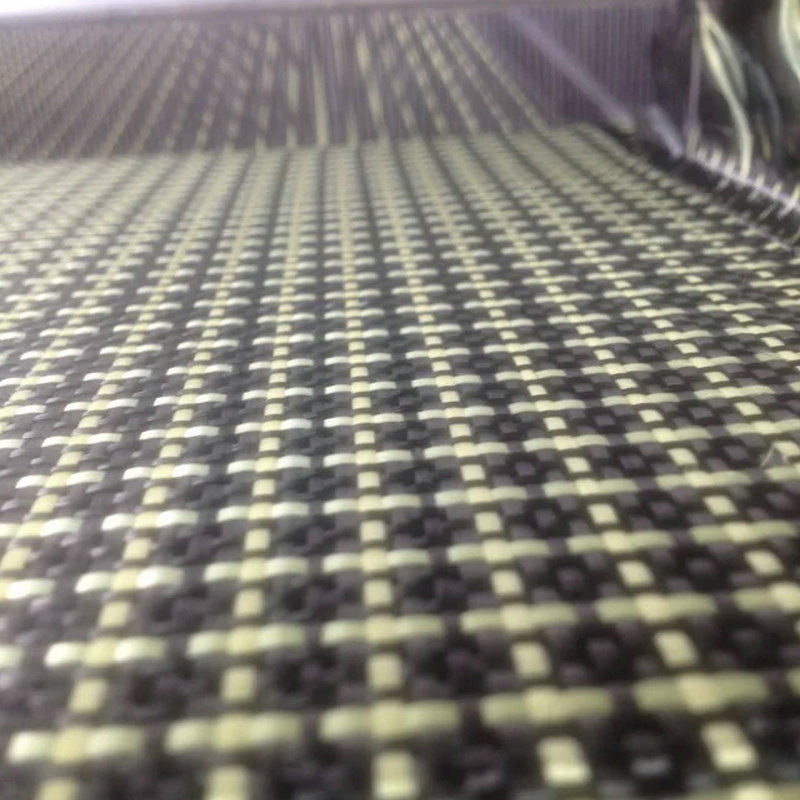
1. Plain Weave Woven Fiberglass Cloth
Plain weave woven fiberglass cloth is the most common and widely used type of fiberglass fabric. In a plain weave, the fibers cross over and under at right angles to each other, forming a basic and strong mesh. This type of cloth is relatively smooth and provides excellent dimensional stability, meaning it will not distort or shrink when applied in composite applications. It is widely used in applications such as:
- Boat Building: For hull construction and fiberglass repair.
- Automotive Manufacturing: To reinforce body panels and components.
- General Reinforcement: For any application requiring a durable, lightweight material.
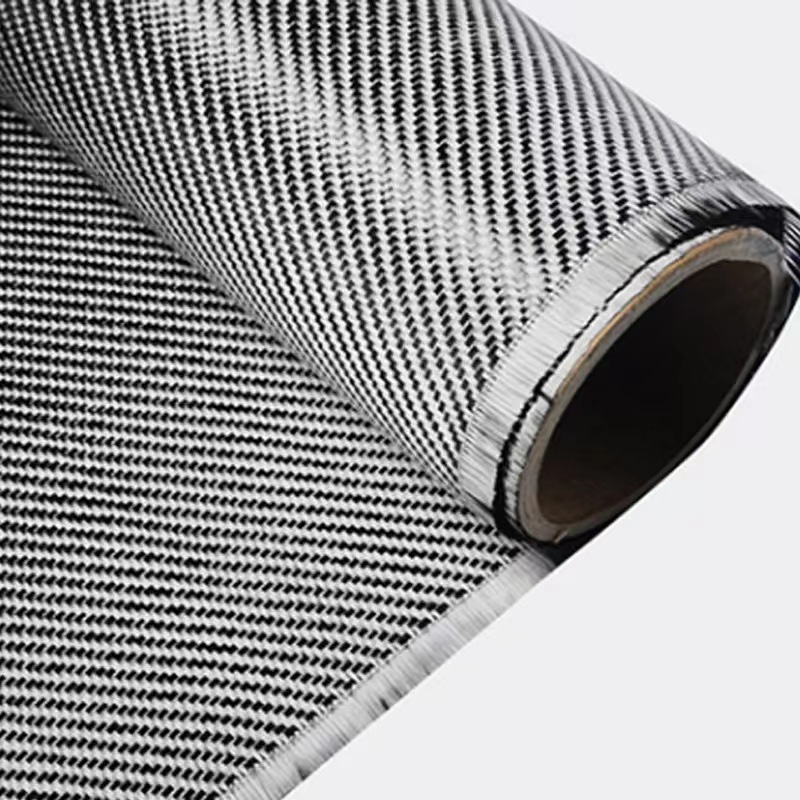
2. Twill Weave Woven Fiberglass Cloth
Twill weave woven fiberglass features a more intricate pattern in which the fibers cross over two or more threads at a time, creating a diagonal or "twill" effect. This gives the cloth enhanced flexibility and increased conformability to curves, making it ideal for situations where the fabric needs to stretch or mold to a particular shape. Common uses include:
- Boat Building: For shaping around rounded hulls.
- Aerospace: In applications where parts need to withstand stress but maintain flexibility, such as wing components.
Twill weave woven fiberglass also provides a smoother surface than plain weave, making it ideal for visible surfaces, as it has a polished and professional look.
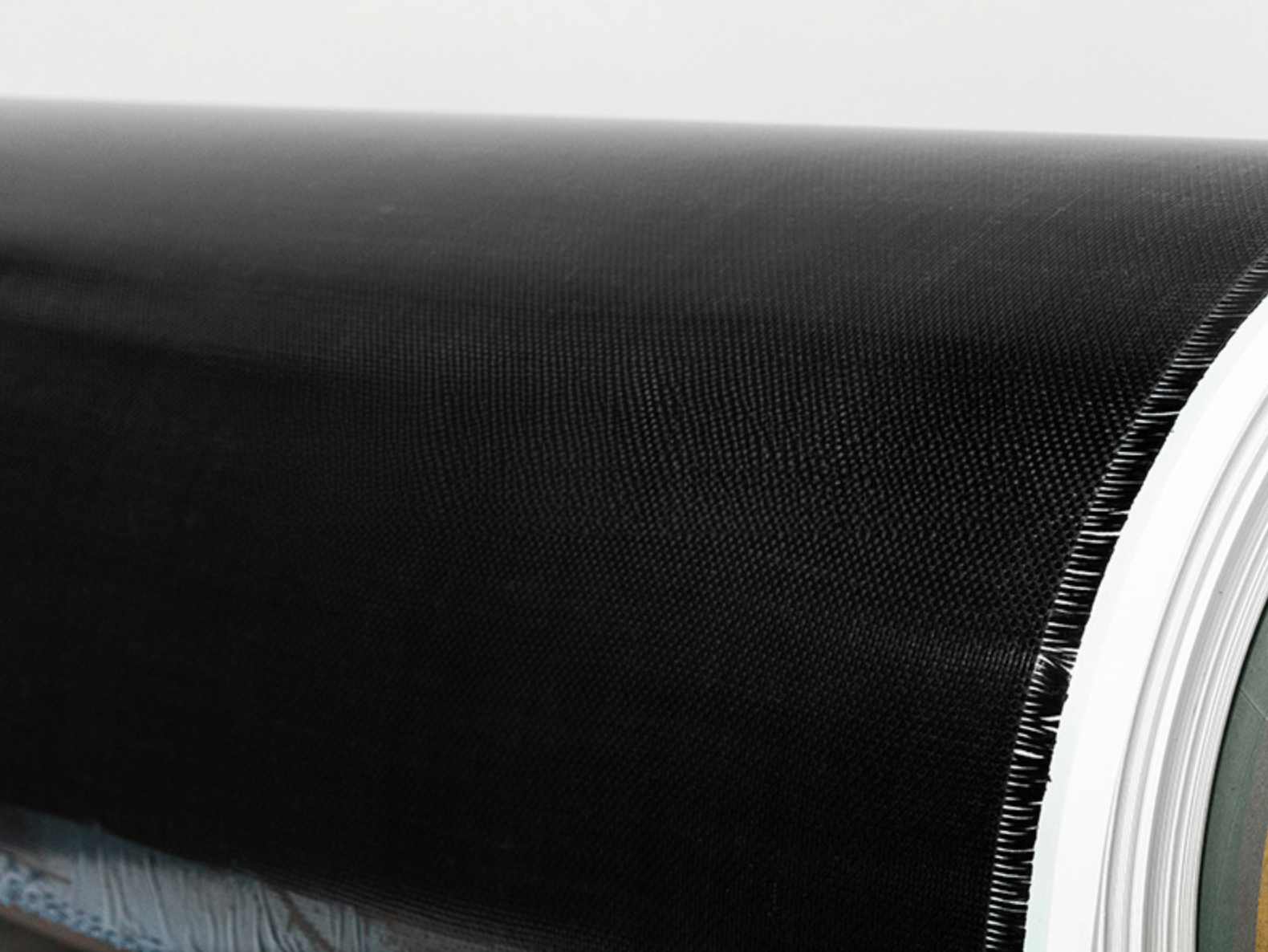
3. Satin Weave Woven Fiberglass Cloth
Satin weave is the most complex of the woven patterns, where the fibers cross over multiple threads, creating a very smooth, shiny surface. This type of weave is often used in applications where the aesthetic quality of the material is important, or where low friction is required. Satin weave woven fiberglass cloth is ideal for:
- Aerospace and Aviation: For lightweight but high-strength components such as airplane wings or fuselage panels.
- Luxury Vehicles and High-End Manufacturing: For cosmetic or performance parts, such as custom car body panels.
While satin weave woven fiberglass is more aesthetically appealing, it is typically used in combination with high-performance resin systems to enhance strength without sacrificing the material’s visual appeal.
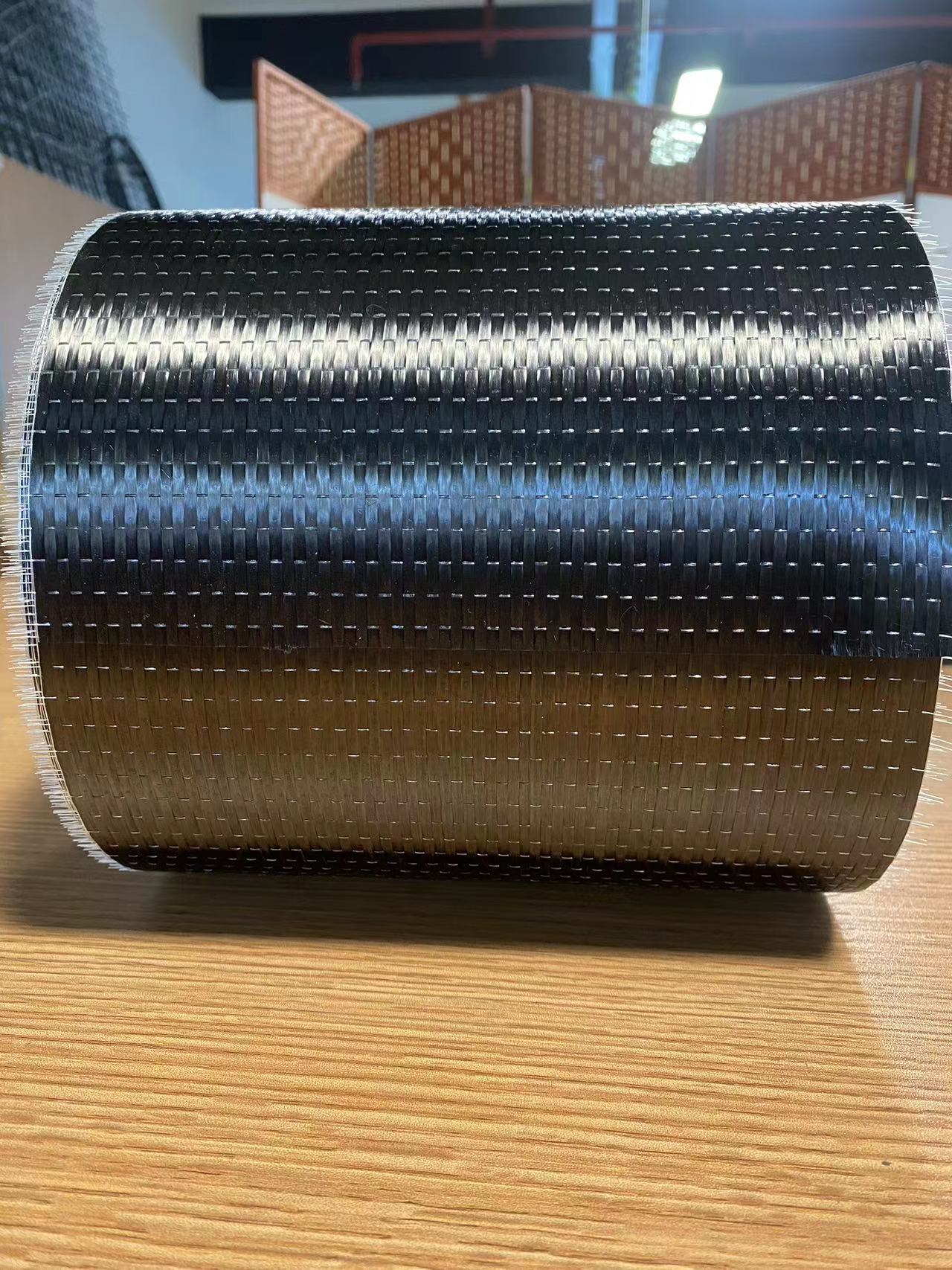
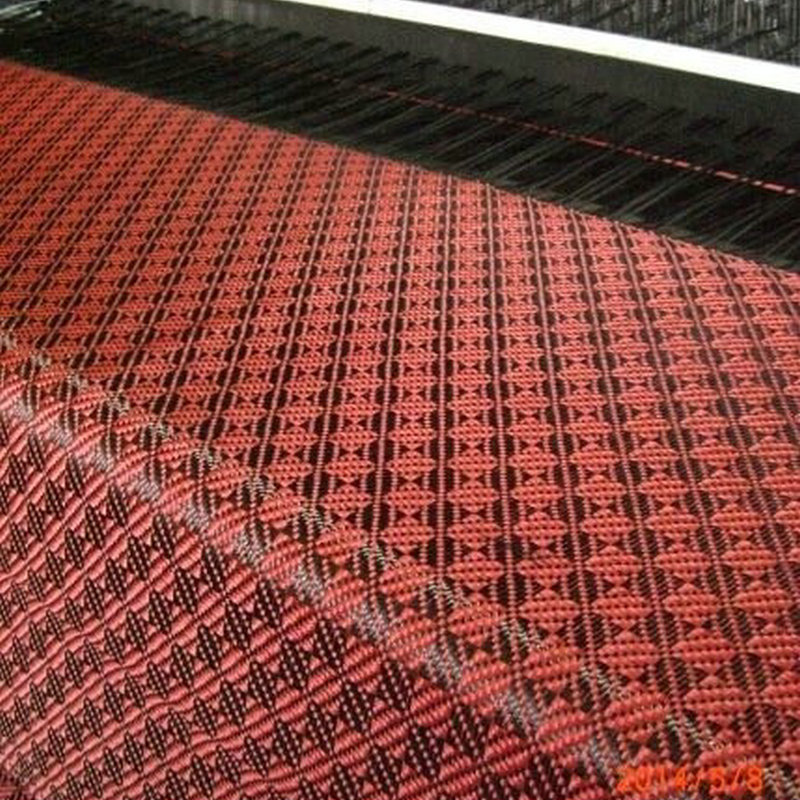
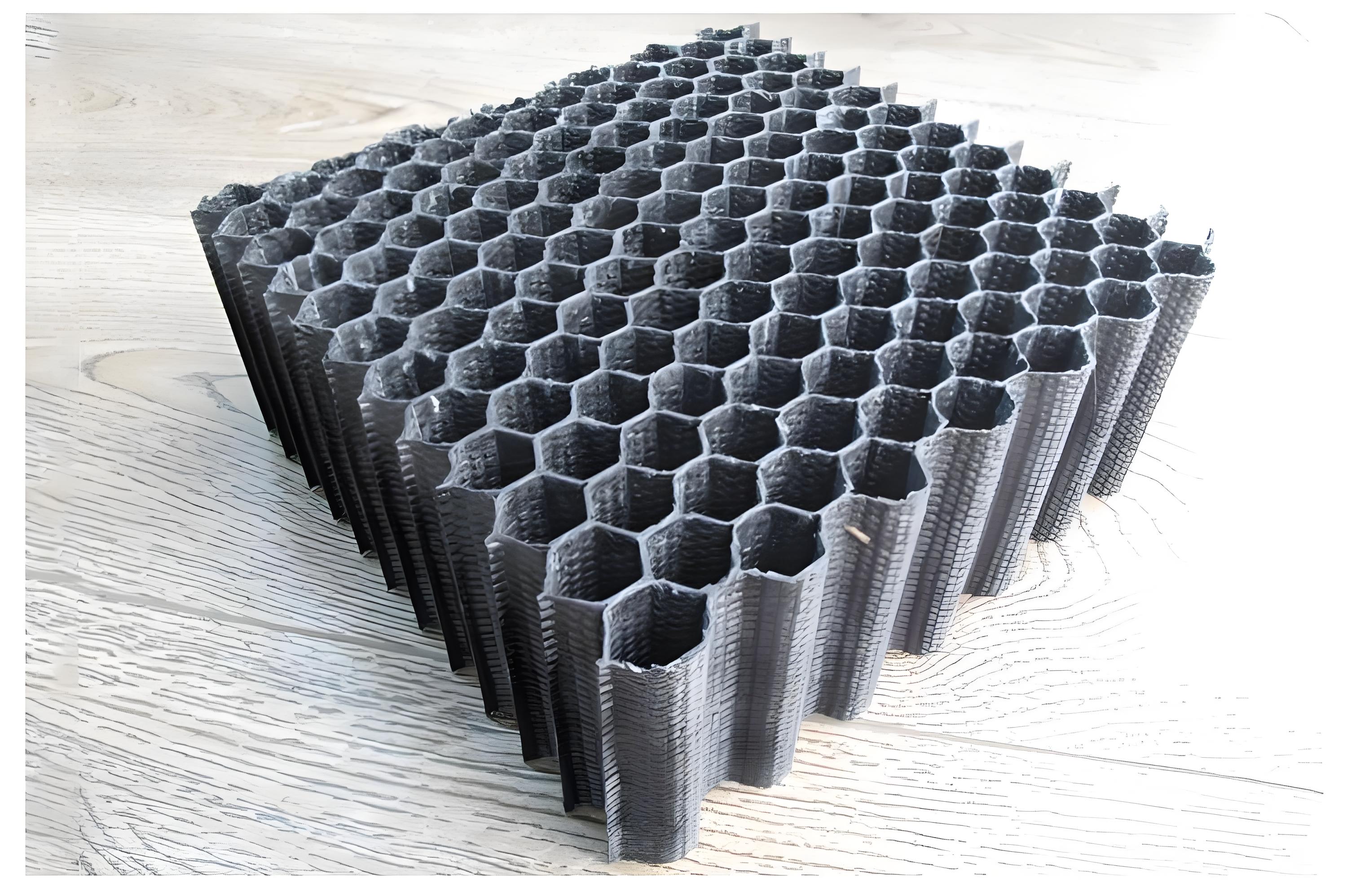
Woven roving fiberglass differs from woven fiberglass cloth in that it uses longer, thicker fibers. It is made by weaving large, continuous strands of fiberglass into a mesh. This type of material is more bulkier and is primarily used when a heavier, thicker material is needed for structural reinforcement. It is typically combined with resin in applications requiring extreme strength and durability, such as:
- Boat Building: To reinforce hulls or decks.
- Large Composite Structures: For use in industries such as construction and wind turbine manufacturing.
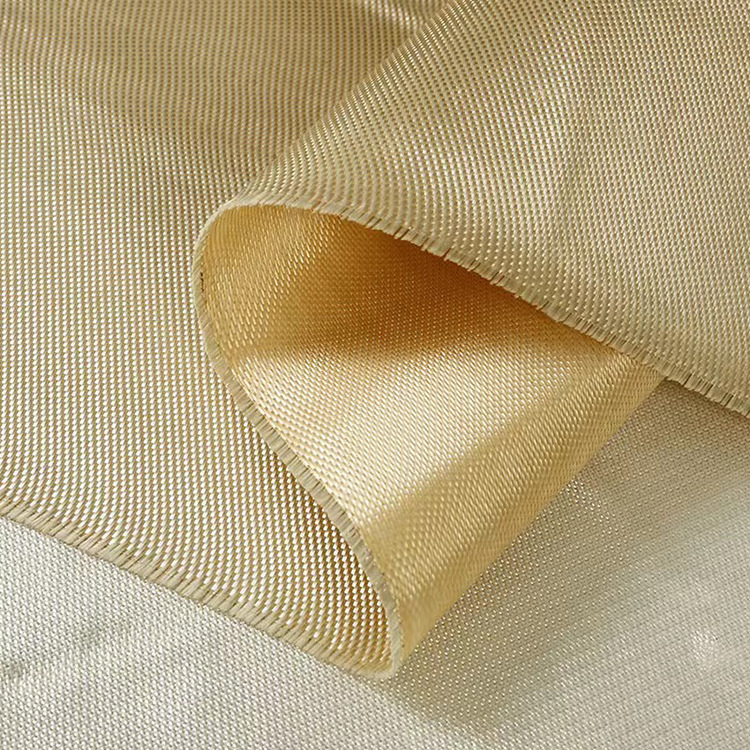

Understanding Woven Roving Fiberglass
Woven roving fiberglass is an alternative to traditional woven fiberglass cloth, featuring thicker glass fibers that are woven together in a less intricate pattern. Because of this, woven roving is typically bulkier and has a higher weight per square yard compared to woven fiberglass cloth. This gives it a higher load-bearing capacity, which is crucial in large composite structures.
In woven roving fiberglass, the fibers are not as tightly woven as in regular woven fiberglass cloth. Instead, they are organized into bundles or rovings, which are used to provide enhanced strength and thickness. The fibers are often used in heavy-duty applications, such as:
- Structural Reinforcement: When you need extra strength in large composite parts, woven roving fiberglass can provide the necessary load-bearing capacity.
- Marine Industry: For reinforced boat hulls, where impact resistance is essential.
- Automotive: For high-strength, lightweight automotive parts that must withstand heavy stress.
Differences Between Woven Fiberglass and Woven Roving Fiberglass
The primary difference between woven fiberglass and woven roving fiberglass is in the weight, fiber thickness, and intended use. Woven fiberglass cloth is lighter, more flexible, and easier to handle for detailed applications, while woven roving fiberglass is bulkier and designed for heavy-duty applications that require more strength and thickness.
Applications of Woven Fiberglass Cloth
Fiberglass woven fabric is a versatile material that combines strength and flexibility, making it ideal for reinforcing composite structures in industries such as automotive, marine, and aerospace. Woven fiberglass cloth is incredibly versatile and used across numerous industries. Below, we explore some key applications:
1. Boat Building and Marine Industry
Fiberglass has been a preferred material in boat building due to its lightweight yet robust nature. Woven fiberglass cloth, when combined with a resin like epoxy, forms a highly durable composite material ideal for creating boat hulls, decks, and other marine components. The woven structure of fiberglass provides an optimal balance between strength and flexibility, ensuring boats can withstand the stress of waves and impacts.
- Boat Hulls: Fiberglass boats are known for their excellent resistance to water, corrosion, and impacts, making them long-lasting.
- Repair Work: Woven fiberglass cloth is often used to patch or reinforce existing boats. Its ability to mold to curves and provide a smooth finish makes it perfect for repairs.
2. Automotive Manufacturing
In automotive applications, woven fiberglass cloth is used for creating lightweight yet strong components. These include body panels, hoods, fenders, and interior parts. Fiberglass cloth’s high strength-to-weight ratio is crucial for improving fuel efficiency, reducing overall vehicle weight, and ensuring safety during high-stress conditions such as crashes.
- Body Panels: Reinforcing body panels to provide better structural integrity while reducing weight.
- Component Manufacturing: Components like bumpers, hoods, and dashboard parts are often made using woven fiberglass cloth for strength and aesthetic appeal.
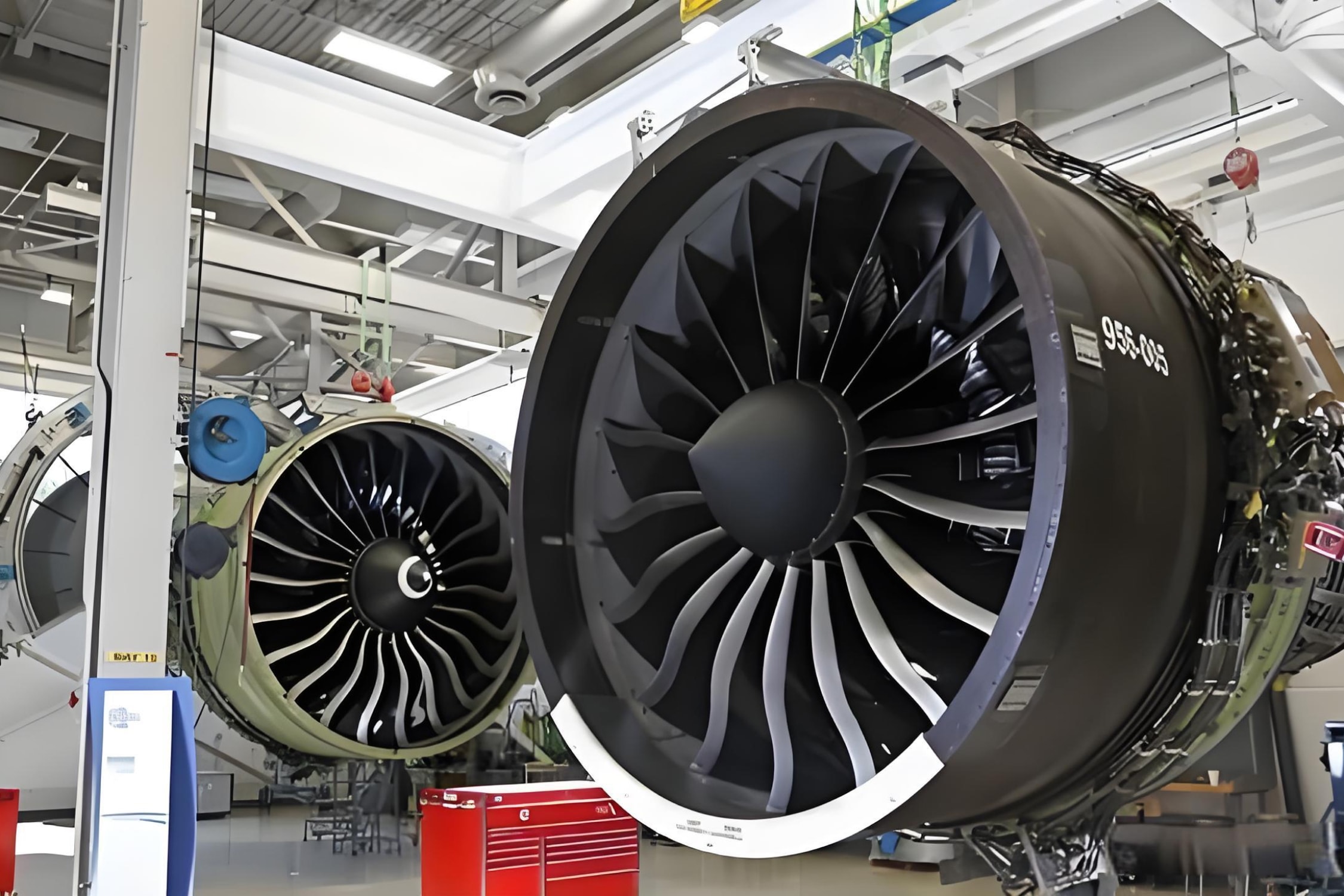
3. Aerospace and Aviation
Woven fiberglass cloth plays an essential role in the aerospace industry, where weight and strength are of paramount importance. Aircraft components such as wings, fuselage panels, and internal structures are often made from fiberglass-reinforced composites due to their low weight, high strength, and durability.
- Aircraft Parts: High-strength parts that require precise control over their weight-to-strength ratio are manufactured using woven fiberglass cloth.
- Insulation: Woven fiberglass is also used for thermal and electrical insulation in aircraft systems.
4. Electrical Insulation
Fiberglass is a non-conductive material, making it perfect for electrical insulation. Woven fiberglass cloth is used to cover wires and cables to prevent short circuits or damage caused by electrical faults. It can withstand high temperatures and resist electrical conductivity, ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical systems.
- Insulation for Wiring: Used in industries where electrical components need to be shielded from high temperatures and external damage.
- Thermal Insulation: Protects wires from extreme heat in industrial settings, ensuring long-term functionality of electrical systems.
5. Construction and Roofing
Fiberglass cloth is also used in construction materials such as roofing, insulation, and reinforcing concrete. Its resistance to water, weather, and chemicals makes it ideal for both exterior and interior applications. Fiberglass can be integrated with concrete to reinforce structural integrity without adding excessive weight.
- Reinforced Roofing: Provides strength to roofing materials, especially in areas prone to extreme weather conditions.
- Wall Panels and Insulation: Lightweight but strong insulation materials used in the construction of both residential and commercial buildings.

How to Work with Woven Fiberglass Cloth
Working with woven fiberglass cloth involves a few important steps that ensure proper handling, application, and safety.
1. Choosing the Right Type of Woven Fiberglass Cloth
Before you begin, it’s essential to select the appropriate type of woven fiberglass cloth for your project. Consider factors such as the intended application, the weight of the cloth, and whether you need additional strength, flexibility, or aesthetic appeal. For example, if you’re working on a boat hull, plain weave or twill weave will likely work best. For complex, intricate parts like vehicle body panels, satin weave may be the better option.
2. Cutting the Fiberglass Cloth
Cutting woven fiberglass cloth requires precision to ensure that the fabric fits correctly into the mold or area where it will be applied. Use sharp scissors or a rotary cutter to minimize fraying at the edges, and always wear gloves to protect your hands from the sharp fibers that can cause irritation.
3. Applying Resin
Once the cloth is cut to the desired shape, it’s time to apply resin to bond the cloth together and harden the material. There are various types of resins, with epoxy resin being the most popular due to its strong bonding properties and resistance to environmental factors.
- Epoxy Resin: Ideal for most fiberglass applications, especially where high strength is needed.
- Polyester Resin: Suitable for lighter applications and more cost-effective projects.
To apply the resin, use a brush or roller to evenly coat the woven fiberglass cloth. Ensure that the cloth is saturated without excess resin pooling. This step is critical for achieving the desired strength and durability of the finished piece.
4. Curing the Fiberglass
After applying resin, the fiberglass needs to cure to harden into its final form. This curing process can take several hours or even days, depending on the type of resin used. It’s essential to allow the material to fully cure before sanding, trimming, or applying additional layers of fiberglass cloth.
Conclusion
Woven fiberglass cloth is an essential material with a wide range of applications. Whether you're building a boat, repairing a car, or crafting aerospace components, its strength, flexibility, and versatility make it a top choice. By understanding its different types, applications, and how to properly work with it, you can ensure that your projects benefit from the full potential of this remarkable material.
Read More: Exploring Aramid Fiber Applications: Everything You Need to Know
Popular Composite Materials
Popular Composite Materials
Composites Knowledge Hub
Composites Knowledge Hub