+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!
Exploring Basalt Fiber Applications: The Ultimate Guide
Basalt fiber is rapidly emerging as a game-changing material across multiple industries due to its unique combination of strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and eco-friendliness. Extracted from natural volcanic rock, basalt fiber is a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to traditional materials such as steel, glass fiber, and carbon fiber.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various basalt fiber applications, its advantages, and its role in composite building materials and other high-performance products. Whether in construction, aerospace, automotive, marine, or renewable energy, basalt fiber is revolutionizing modern material science.

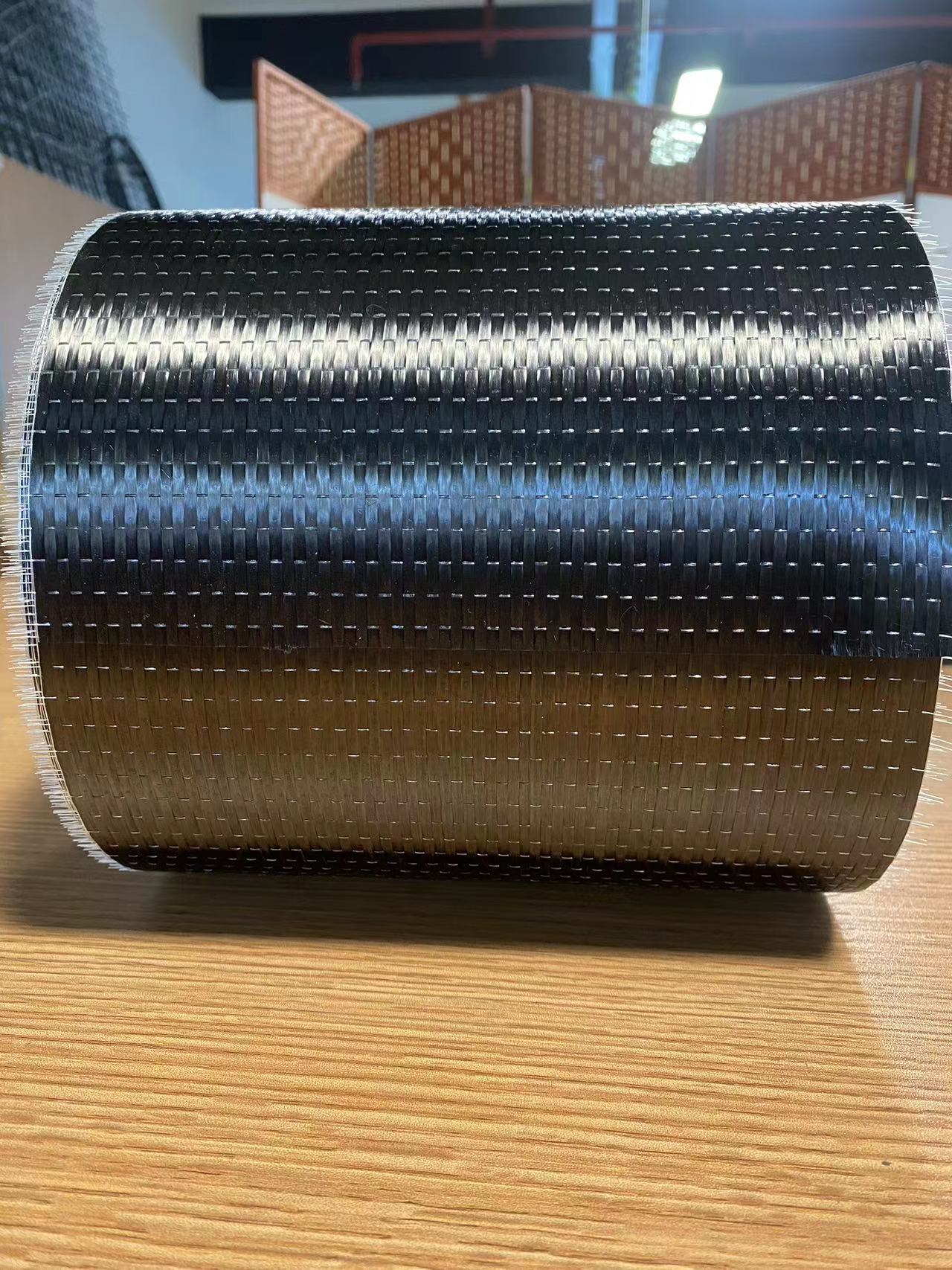
What is Basalt Fiber?
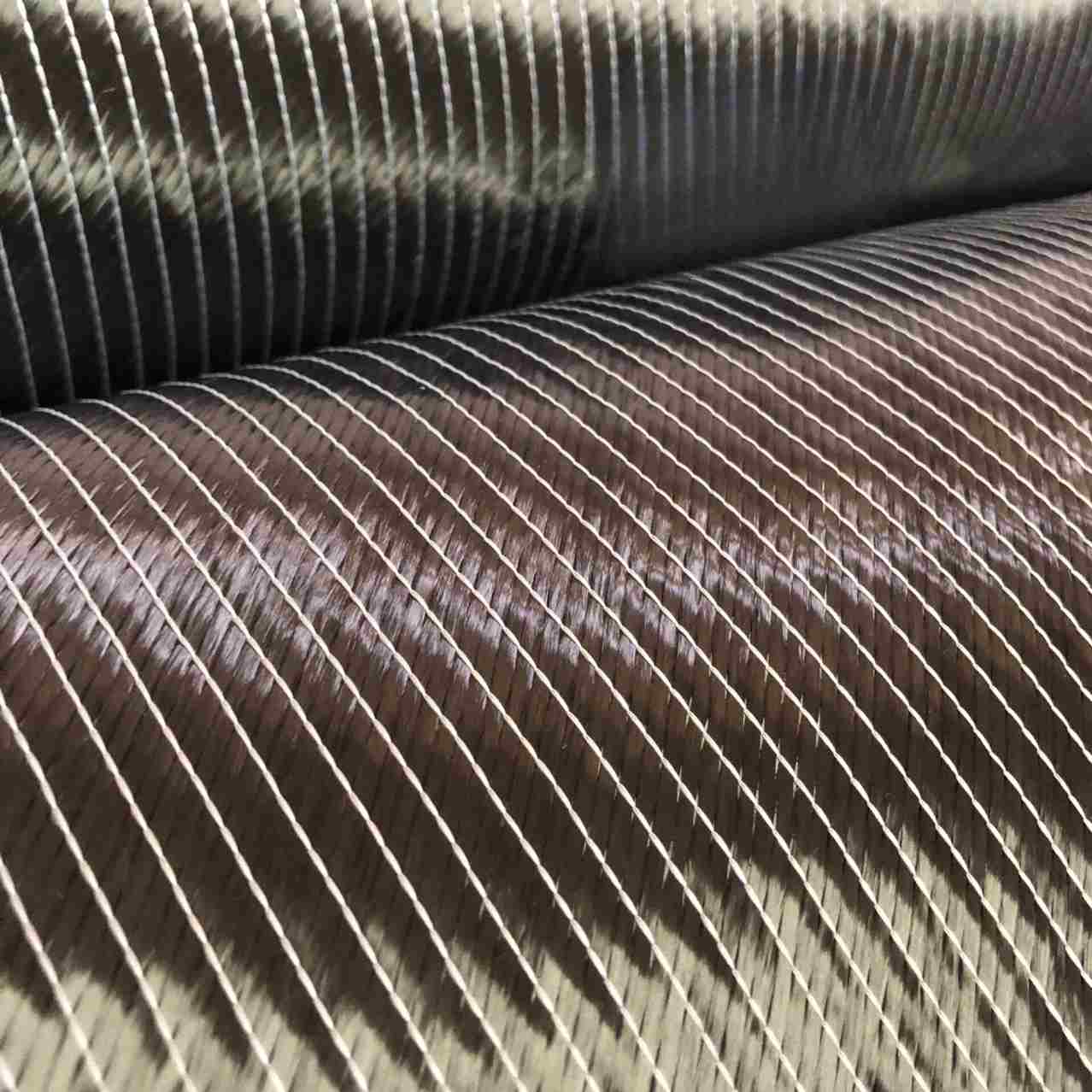
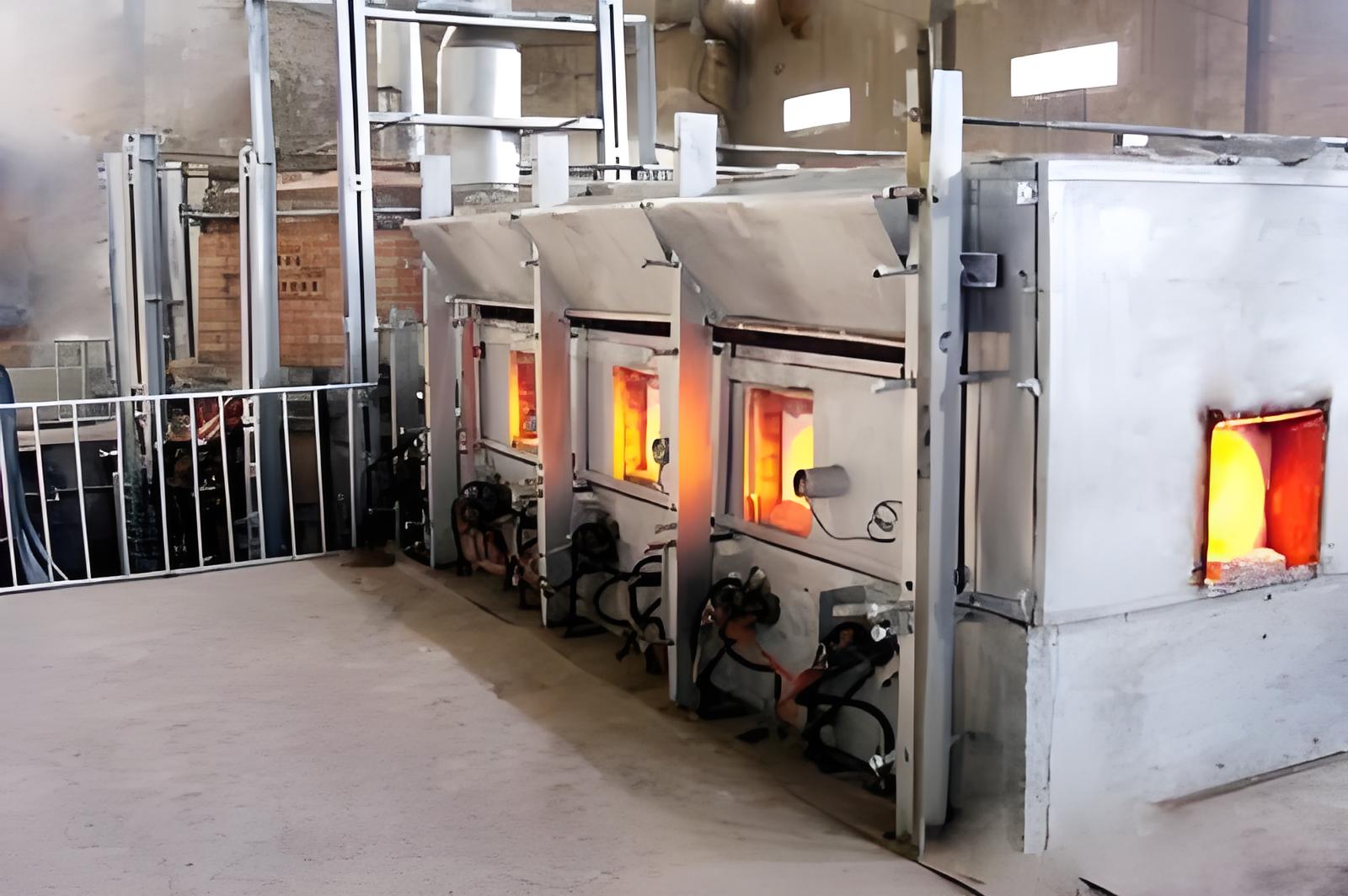
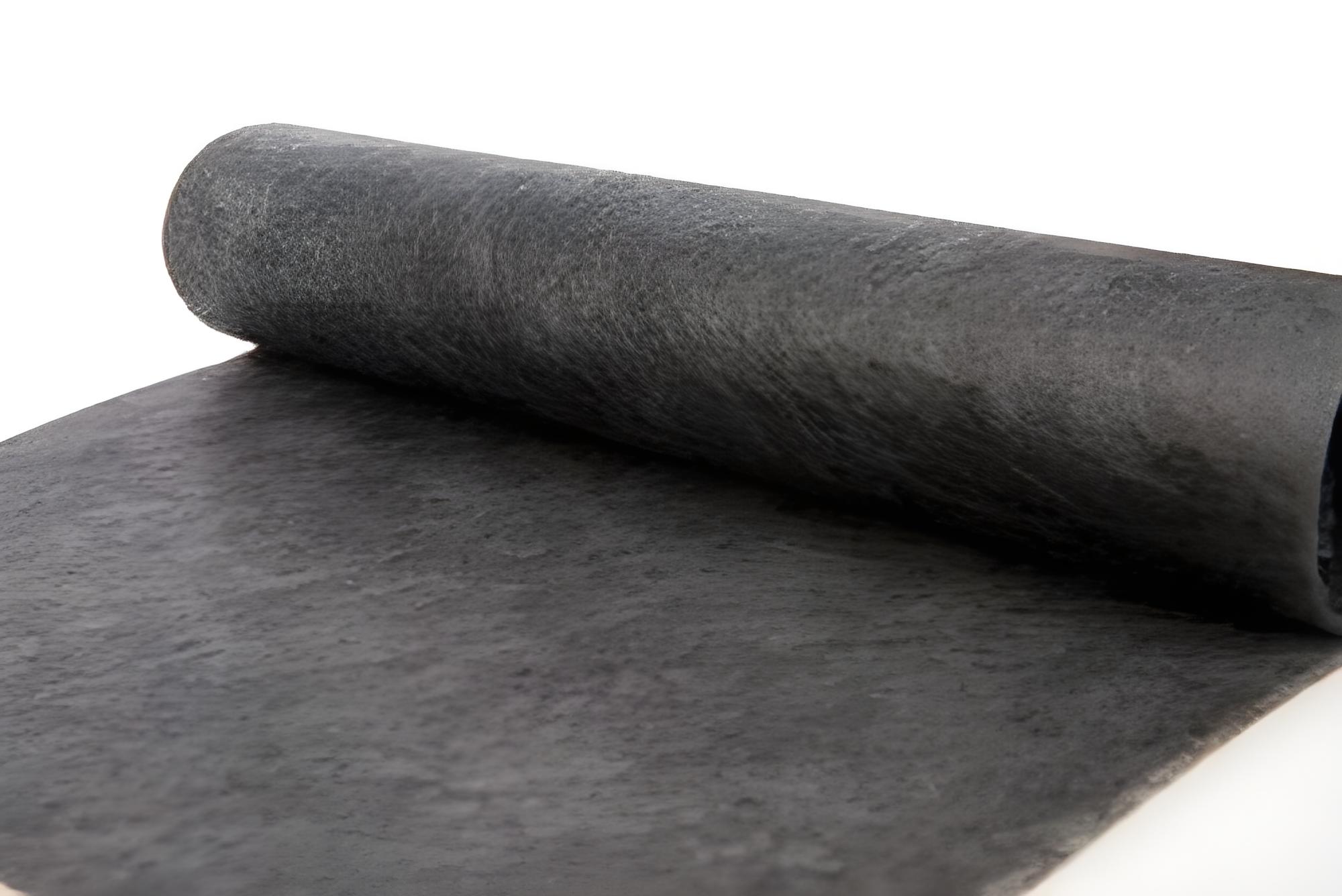
Basalt fiber is a continuous fiber made from basalt rock, a natural volcanic material. The process of producing basalt fiber involves:
- Melting the basalt rock at a temperature of around 1,400°C (2,552°F).
- Extruding the molten basalt through fine nozzles to create continuous filaments.
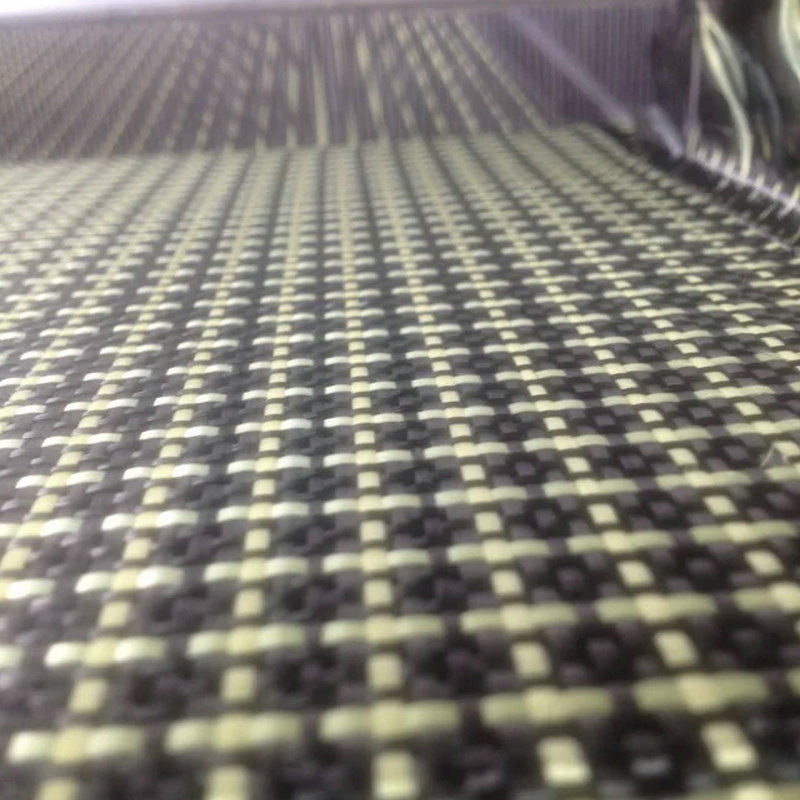
- Cooling and bundling the fibers to form rovings, yarns, or fabrics used in various applications.
Unlike synthetic fibers, basalt fiber does not require chemical additives, making it an environmentally friendly and non-toxic material.
Key Properties of Basalt Fiber:
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Stronger than glass fiber and close to carbon fiber in performance.
Superior Corrosion Resistance: Does not rust like steel, making it ideal for humid and chemically aggressive environments.
Excellent Thermal Stability: Withstands temperatures from -260°C to 700°C without losing its mechanical properties.
Eco-Friendly & Sustainable: Basalt is naturally abundant and requires minimal processing.
Low Water Absorption: Prevents degradation over time, ideal for marine and construction applications.
Given these properties, basalt fiber applications span across numerous industries, as we will explore in the following sections.
Basalt Fiber Applications in Construction & Infrastructure
One of the largest sectors benefiting from basalt fiber is the construction and infrastructure industry. The use of basalt fiber in composite building materials has led to increased durability, reduced maintenance, and improved sustainability.
1. Reinforced Concrete and Rebars
Traditional steel reinforcements in concrete structures are prone to rusting and deterioration over time, especially in humid and coastal regions. Basalt fiber is a superior alternative because:
Basalt Fiber Reinforced Polymer (BFRP) Rebars:
- Lighter than steel yet provides higher tensile strength.
- Completely resistant to rust and chemical corrosion.
- Increases the lifespan of bridges, tunnels, and dams.
Basalt Fiber in Concrete Mixtures:
- Reduces cracking by reinforcing the internal structure of concrete.
- Enhances impact resistance, making structures more durable.
- Decreases maintenance costs due to its superior longevity.
2. Basalt Fiber Composites for Roofing & Cladding
Basalt fiber-based panels and sheets are widely used in construction for:
- Roofing Materials: Fire-resistant and thermally insulating.
- Wall Cladding: Offers high weather resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Insulation Panels: Lightweight, durable, and highly energy-efficient.
3. Highway and Road Construction
- Asphalt Reinforcement: Adding basalt fibers to asphalt prevents cracks, improves flexibility, and extends road life.
- Geogrids and Geotextiles: Used for stabilizing roads, preventing soil erosion, and reinforcing embankments in highways and railway projects.
These advancements demonstrate why basalt fiber is becoming a preferred material in modern infrastructure projects.
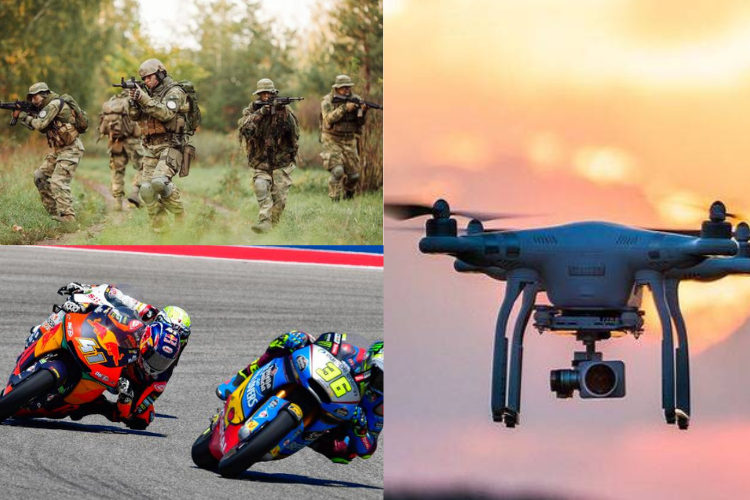
Automotive and Aerospace Applications
Basalt fiber’s combination of high strength, heat resistance, and lightweight properties makes it invaluable in automotive and aerospace engineering.
1. Automotive Industry
Car manufacturers increasingly use basalt fiber in composite building materials to improve fuel efficiency and vehicle durability.
- Lightweight Structural Components: Basalt fiber-reinforced plastics (BFRP) reduce vehicle weight, improving fuel economy and performance.
- Brake Pads & Clutches: Basalt fiber enhances friction and heat resistance, leading to longer-lasting brake systems.
- Heat Shields & Engine Components: Used in thermal barriers to protect engine parts from extreme temperatures.
Aircraft manufacturers utilize basalt fiber due to its low weight and exceptional strength. Some key applications include:
- Aircraft Structural Components: Used in fuselages, wings, and interior panels.
- Thermal and Acoustic Insulation: Basalt fiber provides excellent soundproofing and heat resistance inside aircraft cabins.
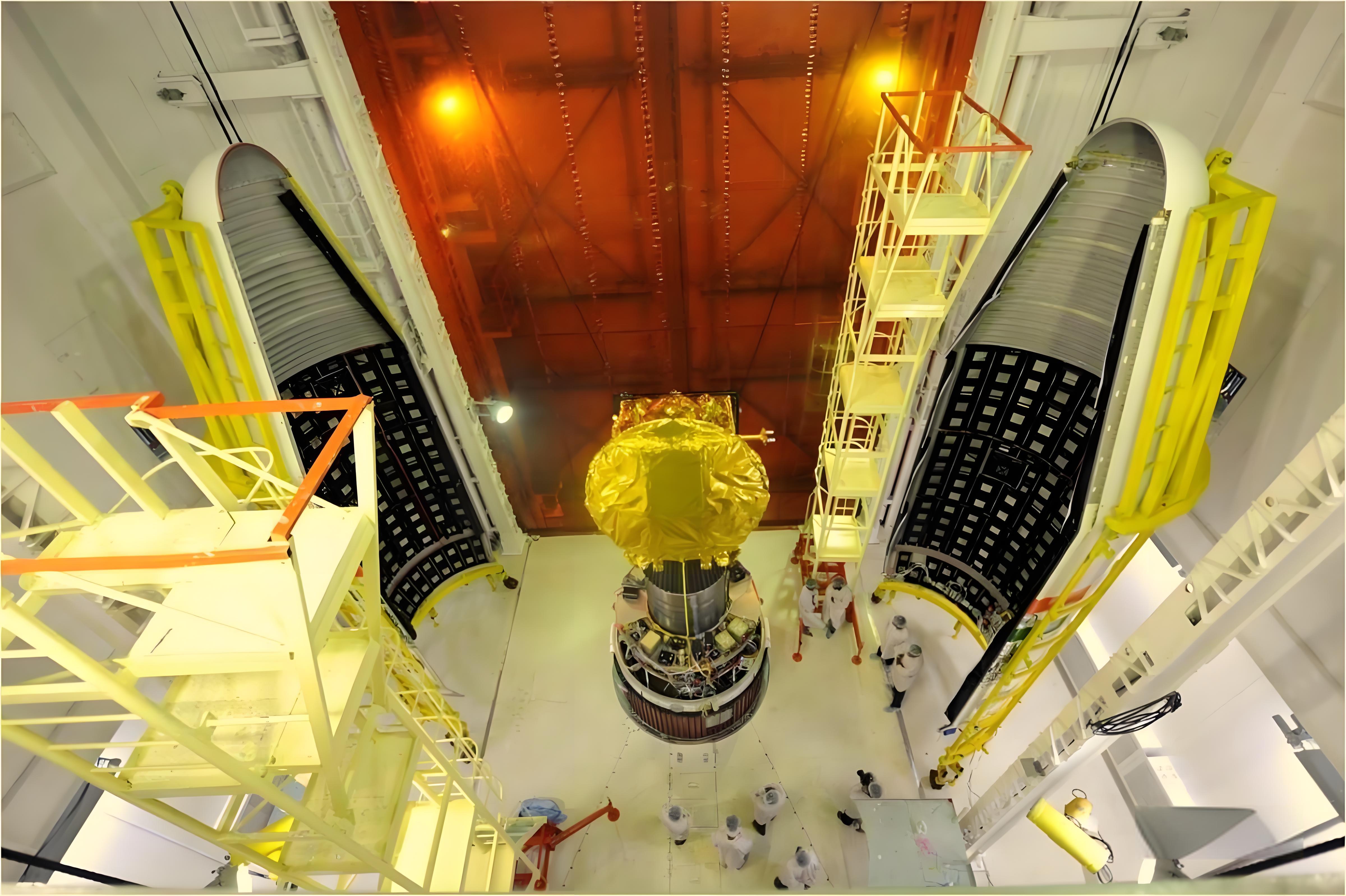
- Spacecraft and Rockets: NASA and other space agencies explore basalt fiber for shielding spacecraft from high temperatures and radiation in space missions.
By replacing heavier and more expensive materials, basalt fiber is driving innovations in both commercial and defense aviation.
Marine and Shipbuilding Industry
Basalt fiber is increasingly being adopted in the marine and shipbuilding industry due to its exceptional resistance to saltwater corrosion, high strength, and lightweight properties. Traditional materials like steel and glass fiber often suffer from rust, degradation, and high maintenance costs in marine environments. Basalt fiber, however, offers a durable, cost-effective, and sustainable alternative.
Applications in Shipbuilding:
- Hull Reinforcement: Basalt fiber-reinforced composites enhance structural integrity, providing high impact resistance, reduced weight, and superior durability, making vessels more fuel-efficient and long-lasting.
- Boat Decking & Interiors: Basalt fiber panels and laminates are used in flooring, walls, and furniture, offering water resistance, fireproofing, and an attractive finish without the risk of rust or decay.
- Pipelines & Tanks: Basalt fiber is extensively used for seawater pipelines, ballast tanks, and offshore drilling platforms, ensuring chemical resistance and a longer operational lifespan.
By improving the longevity of marine structures, basalt fiber reduces maintenance costs and promotes eco-friendly shipbuilding, making it a valuable material for the future of the industry.
Renewable Energy and Wind Power
1. Wind Turbine Blades
Higher Strength than Glass Fiber: Improves performance and extends the service life of wind turbines.
Weather-Resistant: Withstands high winds, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations.
2. Solar Panel Supports
Durable and Lightweight: Ensures long-lasting and reliable solar panel installations.
Eco-Friendly Alternative to Metals: Reduces environmental impact in renewable energy production.
By enhancing durability in renewable energy systems, basalt fiber contributes to a cleaner and more sustainable future.

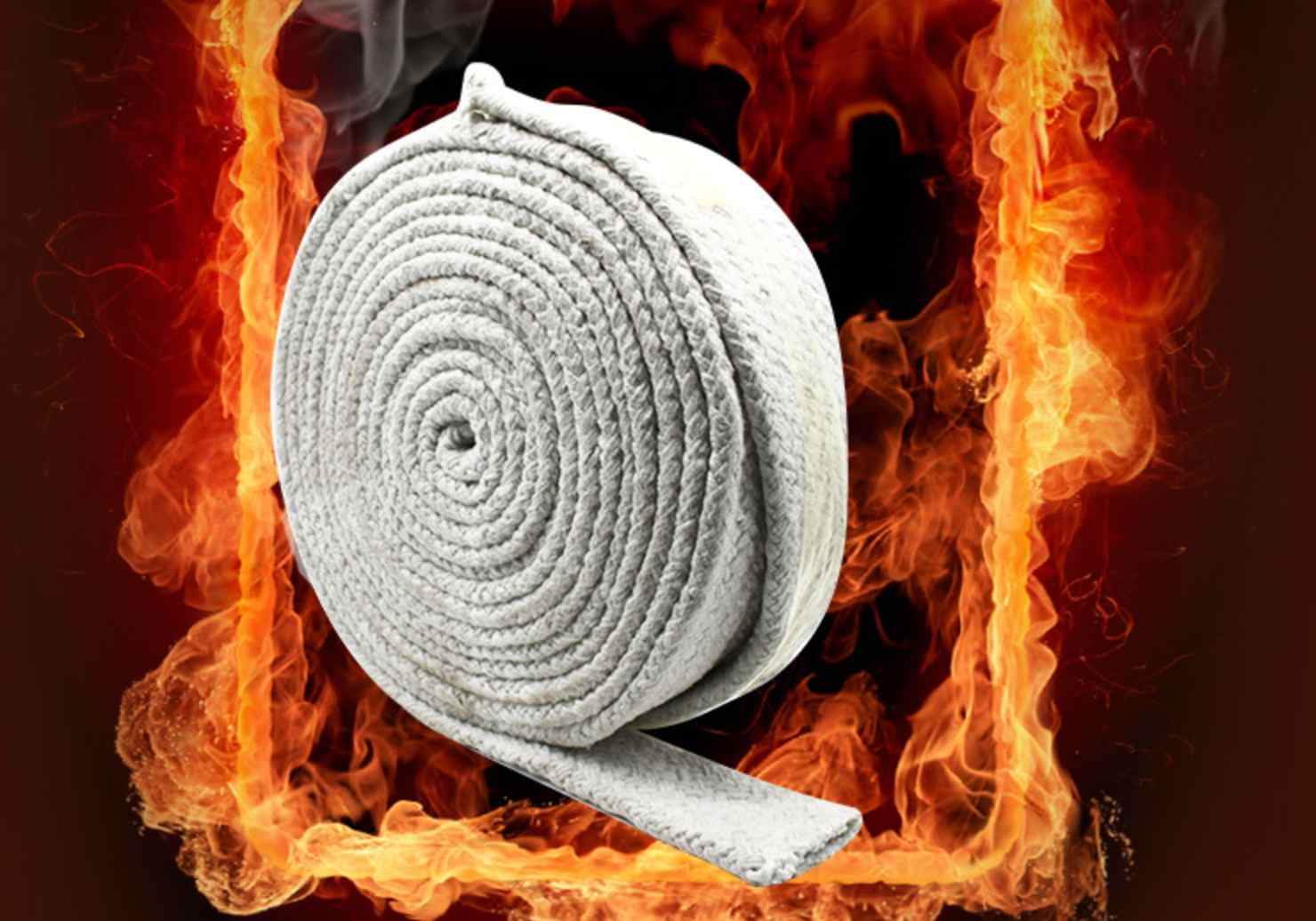
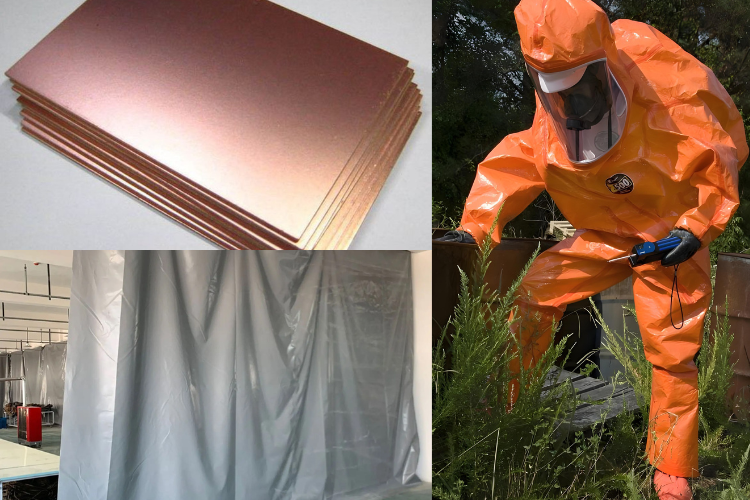
Protective Equipment and Industrial Applications
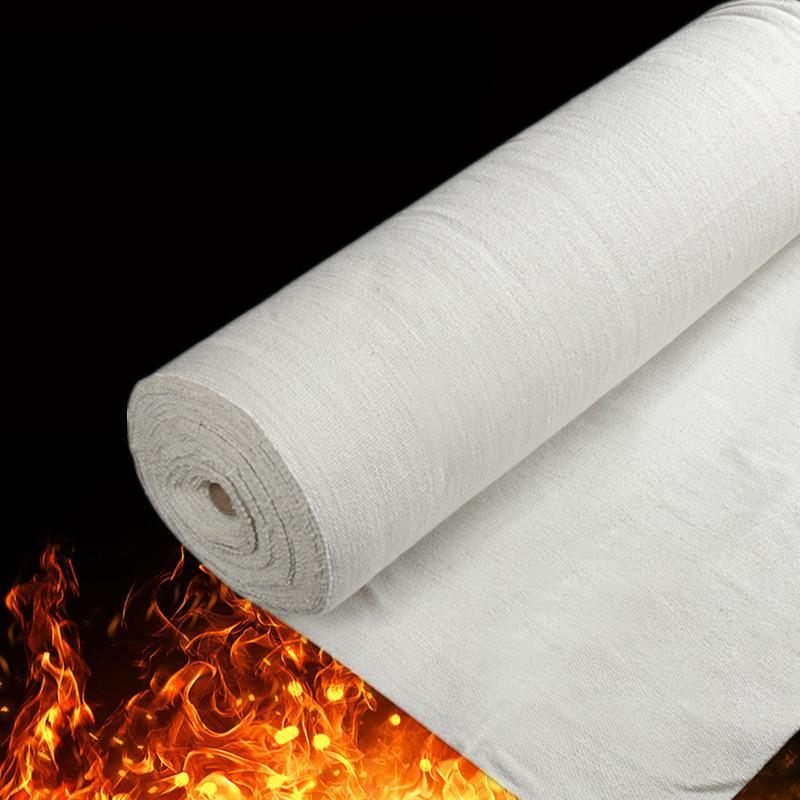
1. Fireproof Clothing & Protective Gear
Basalt Fiber Fabrics: Used in firefighter suits, welding protective clothing, and military body armor.
Thermal Insulation Materials: Applied in industrial heat shields and protective curtains.
2. Industrial Applications
High-Strength Ropes and Cables: Used in deep-sea exploration, construction, and rescue operations.
Molded Composite Parts: Helps manufacture lightweight yet strong industrial equipment.
Basalt fiber’s heat resistance and durability make it indispensable in industrial safety applications.
Conclusion: The Future of Basalt Fiber Applications
As industries seek sustainable, durable, and cost-effective materials, basalt fiber is emerging as a game-changer. From composite building materials in construction to high-performance aerospace and marine applications, its potential is vast.
Key Takeaways:
Basalt fiber is a high-performance, eco-friendly alternative to traditional materials.
Its applications include construction, automotive, aerospace, marine, and renewable energy.
Its superior properties make it one of the most promising materials of the future.
As research advances, basalt fiber applications will continue to expand, transforming industries and setting new benchmarks in material science.
Read More: Properties and Preparation of Ceramic Fiber
Popular Composite Materials
Popular Composite Materials
Composites Knowledge Hub
Composites Knowledge Hub