+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!
What is Fiber Reinforced Material?
Fiber Reinforced Materials (FRM) are advanced composites that combine fibers with a matrix material to enhance strength, durability, and lightweight properties. Learn about their types, advantages, applications, and future trends in industries like aerospace, automotive, and construction. Discover why FRMs are the preferred choice for high-performance solutions.
Understanding Fiber Reinforced Materials (FRM)
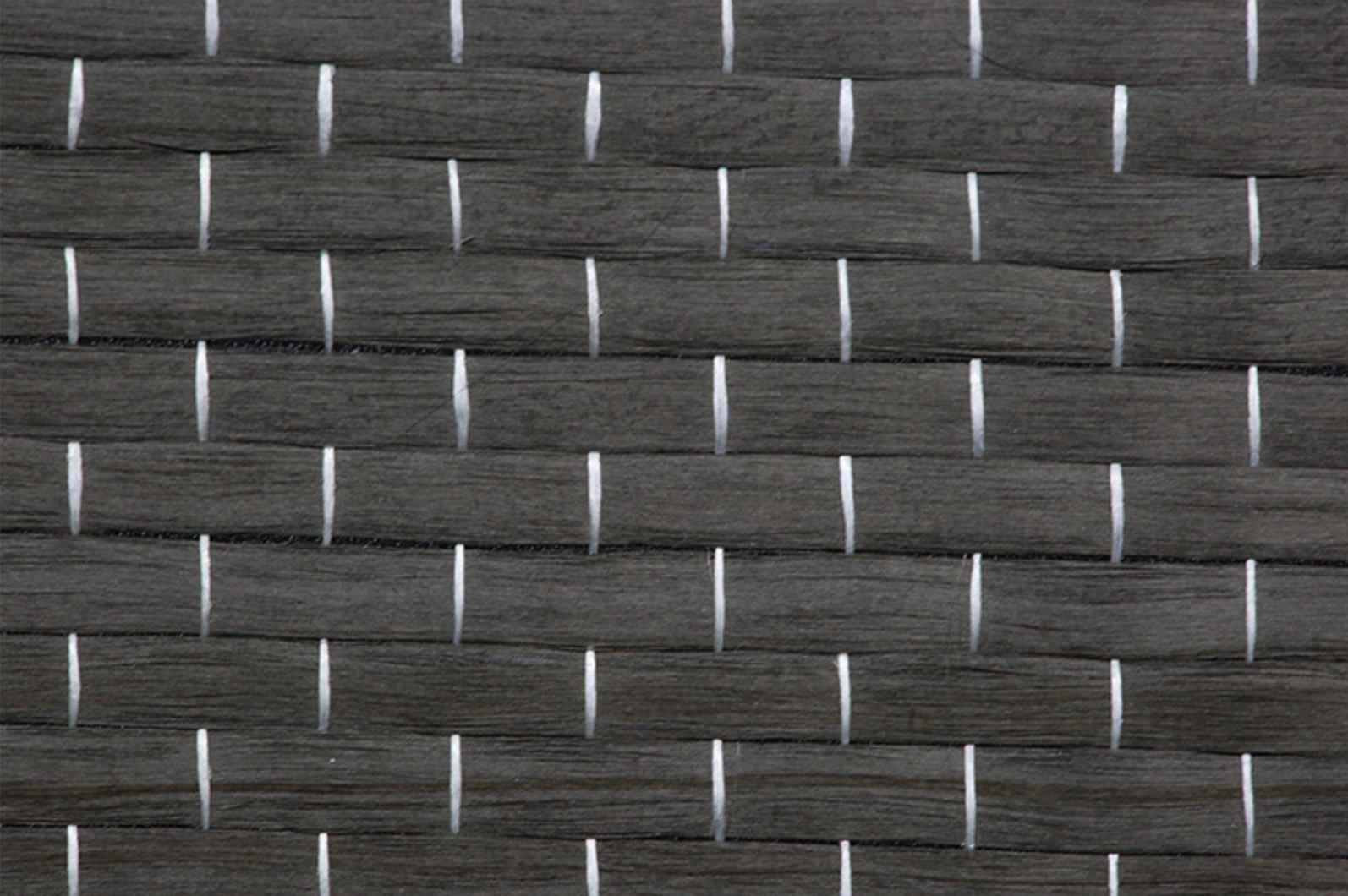
Fiber Reinforced Materials (FRM) are composite materials made by combining a matrix material, such as polymer, metal, or ceramic, with a reinforcing fiber component. The objective of incorporating fibers is to improve the mechanical properties of the base material, enhancing its strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials are widely used in industries ranging from aerospace and automotive to construction and sports equipment due to their exceptional performance characteristics.
What Makes Fiber Reinforced Materials Unique?
FRMs stand out from other materials due to the synergy between their two main components: the matrix and the fibers. The matrix binds the fibers together and protects them from environmental damage, while the fibers provide mechanical reinforcement, taking the load and improving structural stability. This unique combination creates a material that is stronger and lighter than conventional materials.
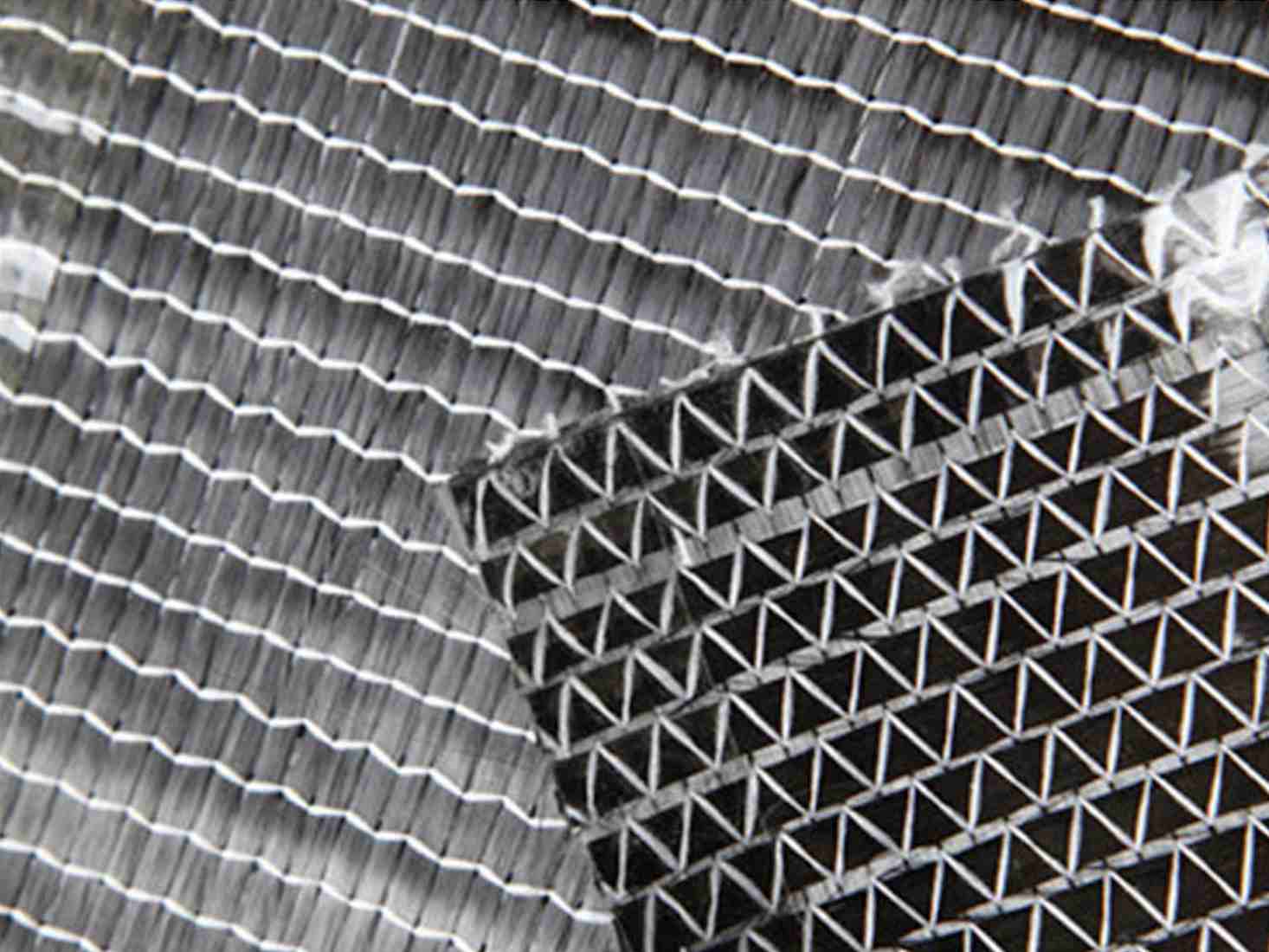
Types of Fiber Reinforced Materials
There are various types of fiber-reinforced materials, each offering unique properties suited to different applications. The most common classifications include:
1. Glass Fiber Reinforced Materials (GFRM)
Fiberglass reinforcements are among the most widely used reinforcing materials due to their cost-effectiveness and balanced properties. They offer high tensile strength, good chemical resistance, and are relatively lightweight. GFRM is commonly used in automotive body panels, boats, and construction.
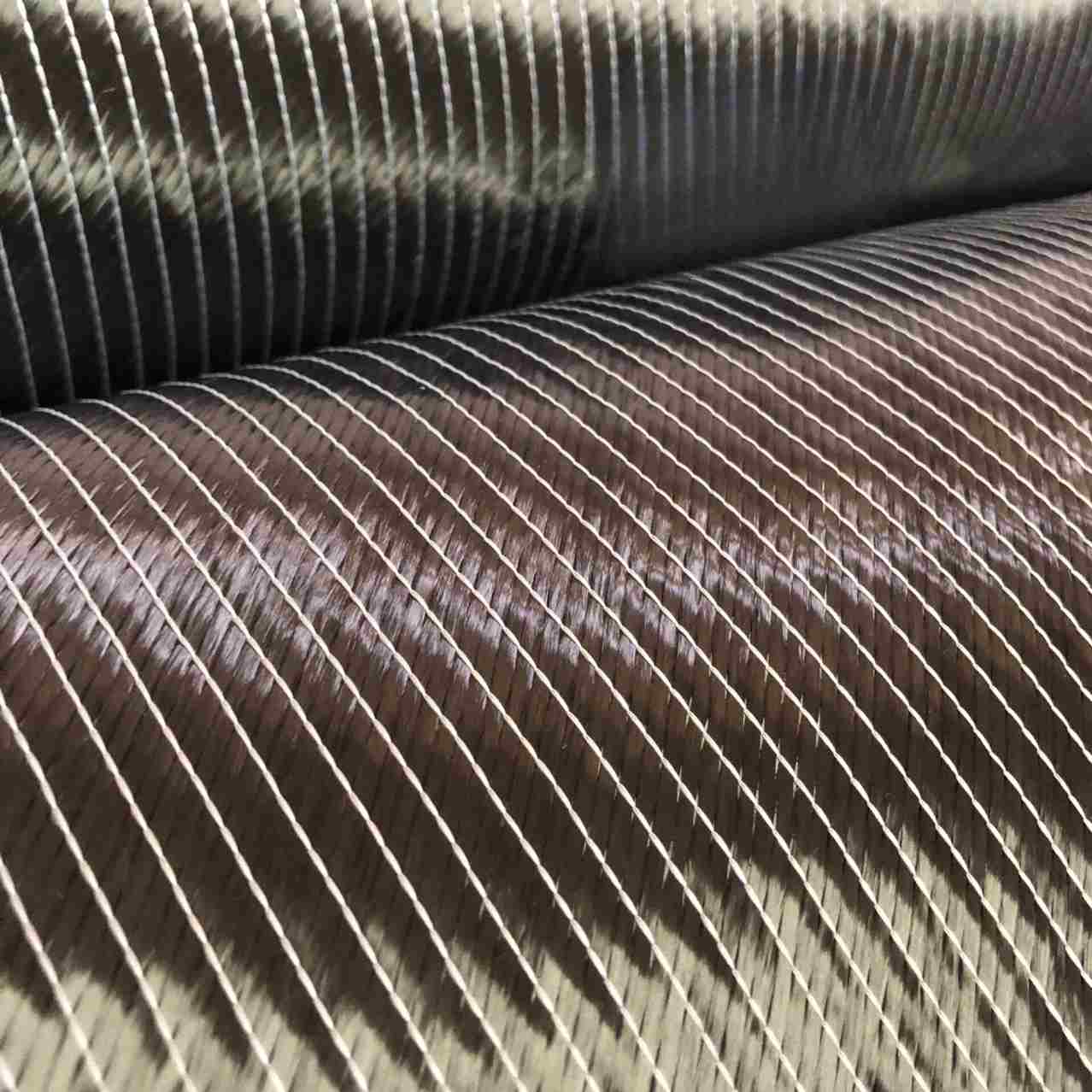
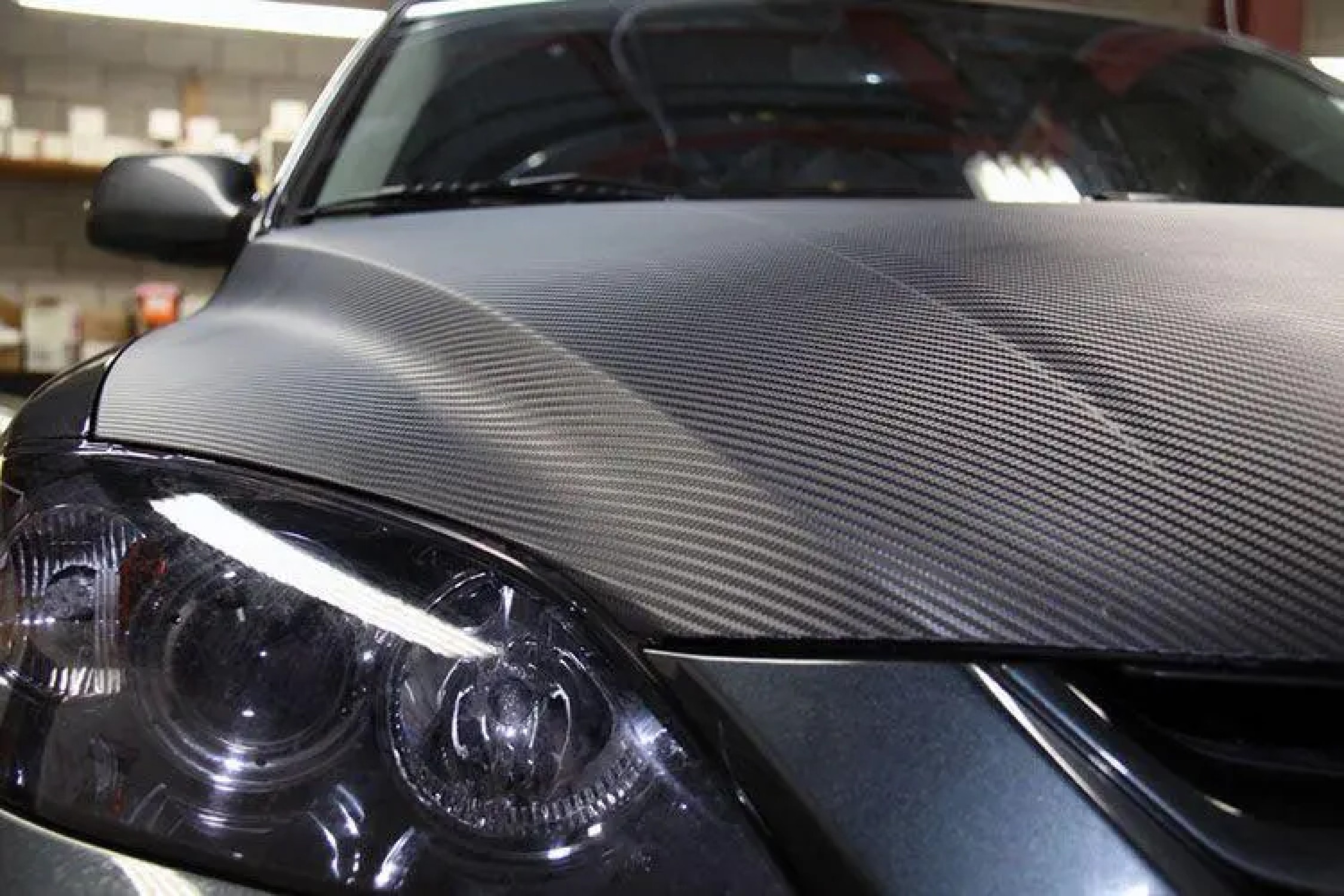
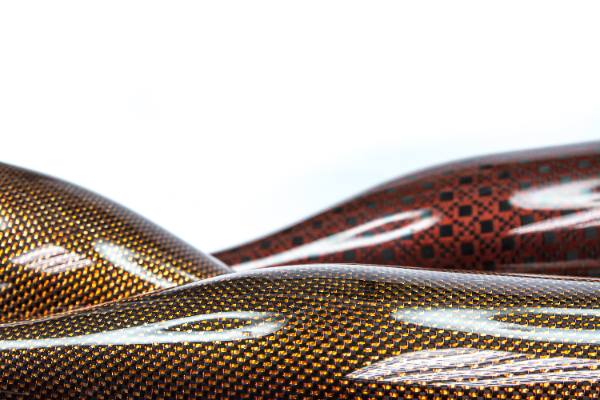
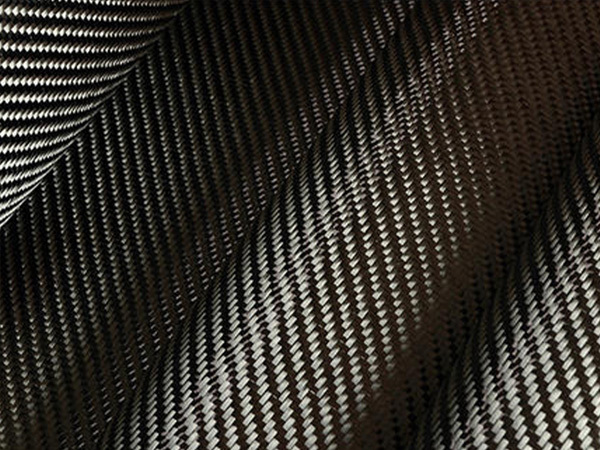
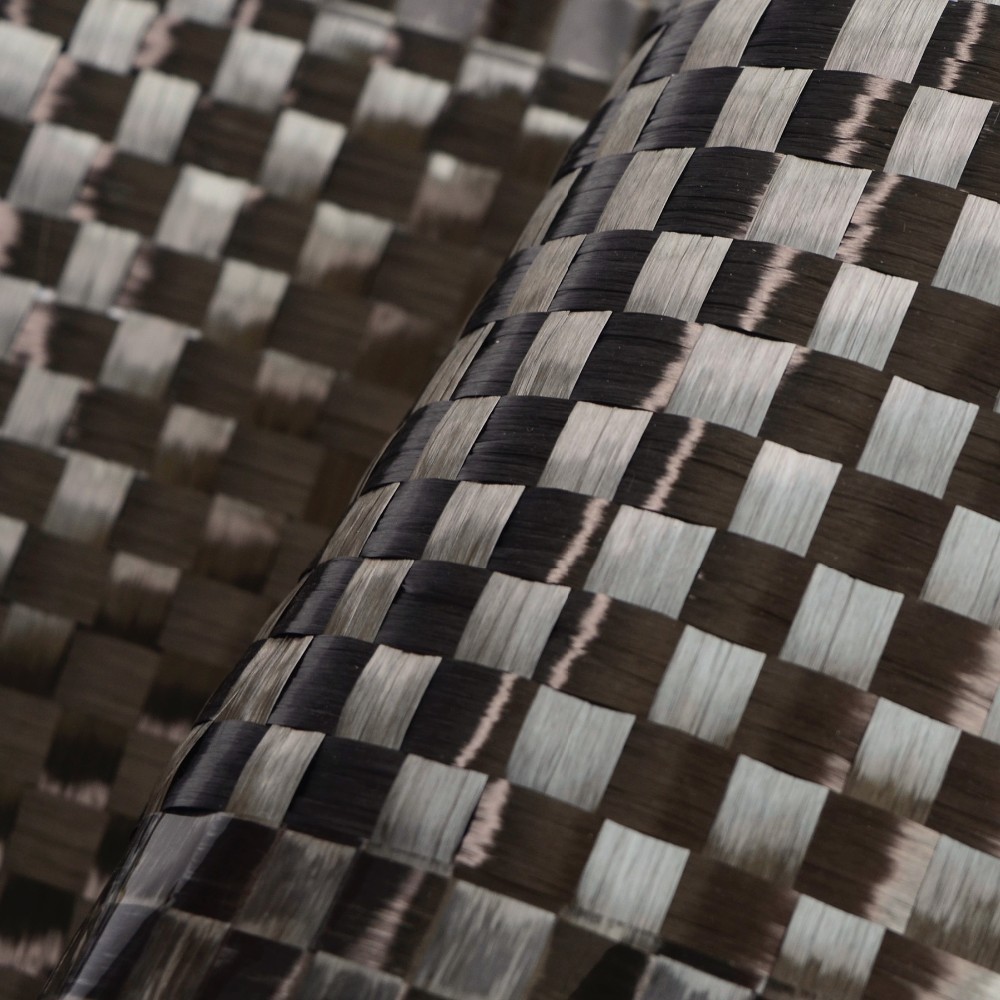
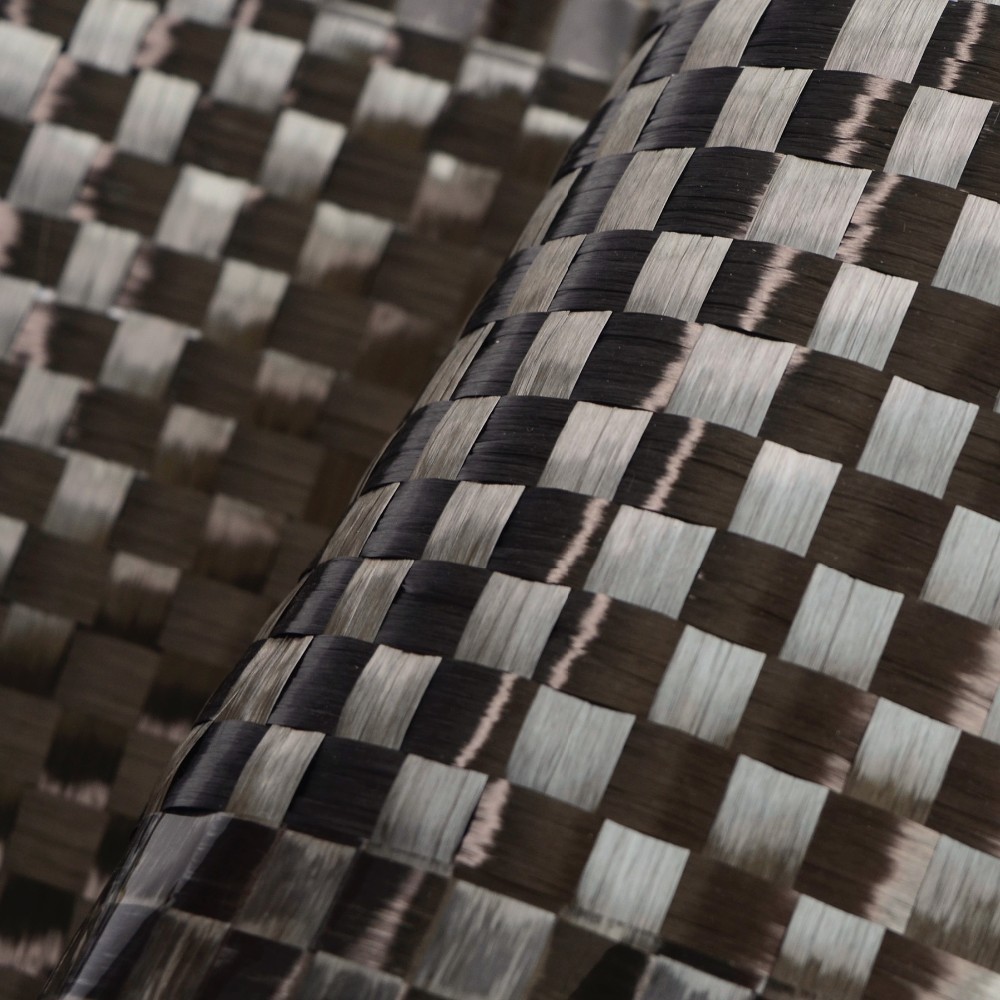
2. Carbon Fiber Reinforced Materials (CFRM)
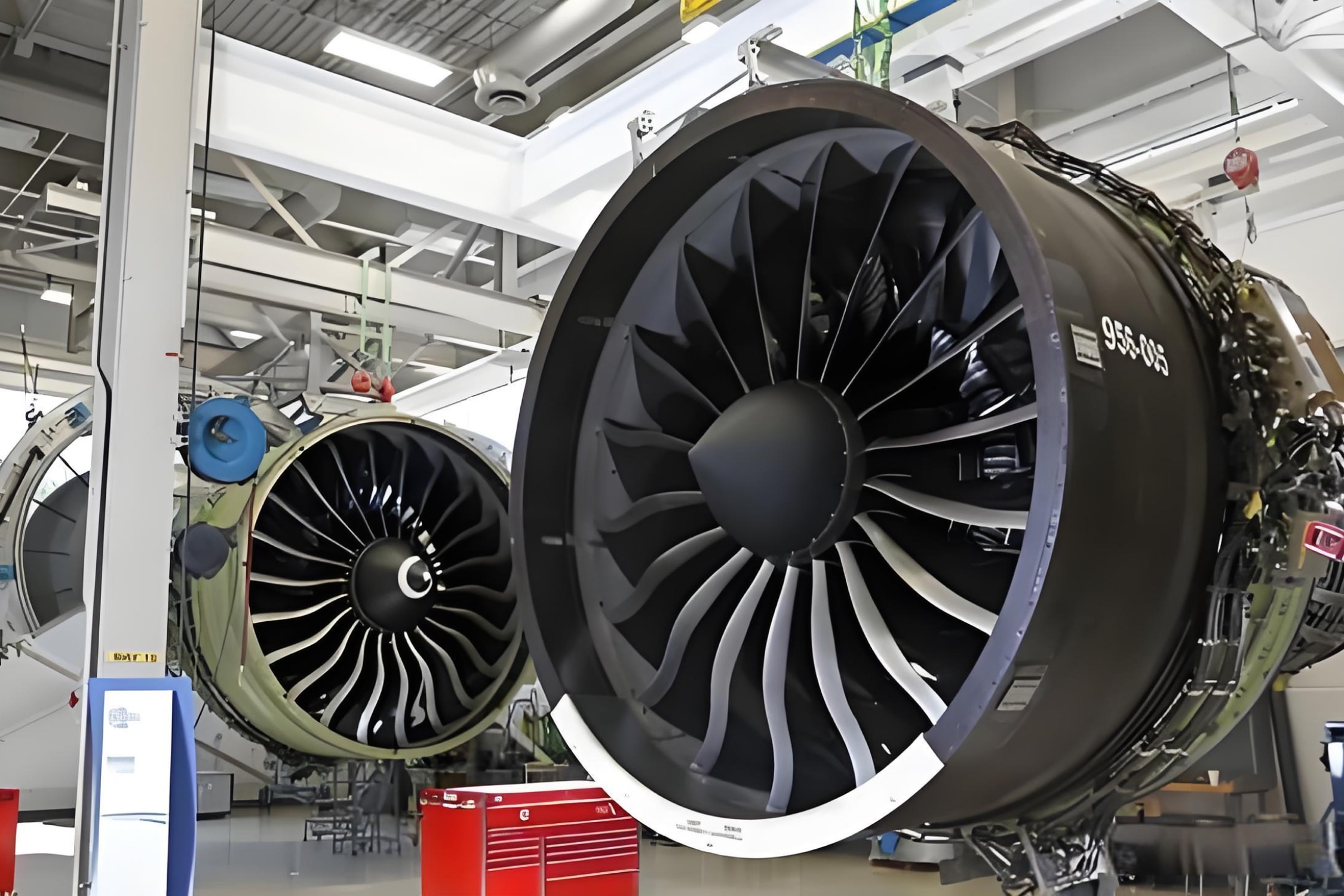
Carbon fiber reinforcement is known for their exceptional stiffness, low weight, and high resistance to heat and chemicals. They are more expensive than glass fibers, making them ideal for high-performance applications such as aerospace components, race car chassis, and sporting goods like tennis rackets.
3. Aramid Fiber Reinforced Materials (AFRM)
Aramid fibers, like Kevlar fiber, are famous for their outstanding impact resistance and strength-to-weight ratio. These properties make them suitable for bulletproof vests, protective clothing, and lightweight structural parts.
4. Natural Fiber Reinforced Materials
Natural fibers such as jute, hemp, and flax are increasingly being used as environmentally-friendly reinforcement alternatives. These materials are gaining popularity in the automotive and construction industries for sustainable applications.
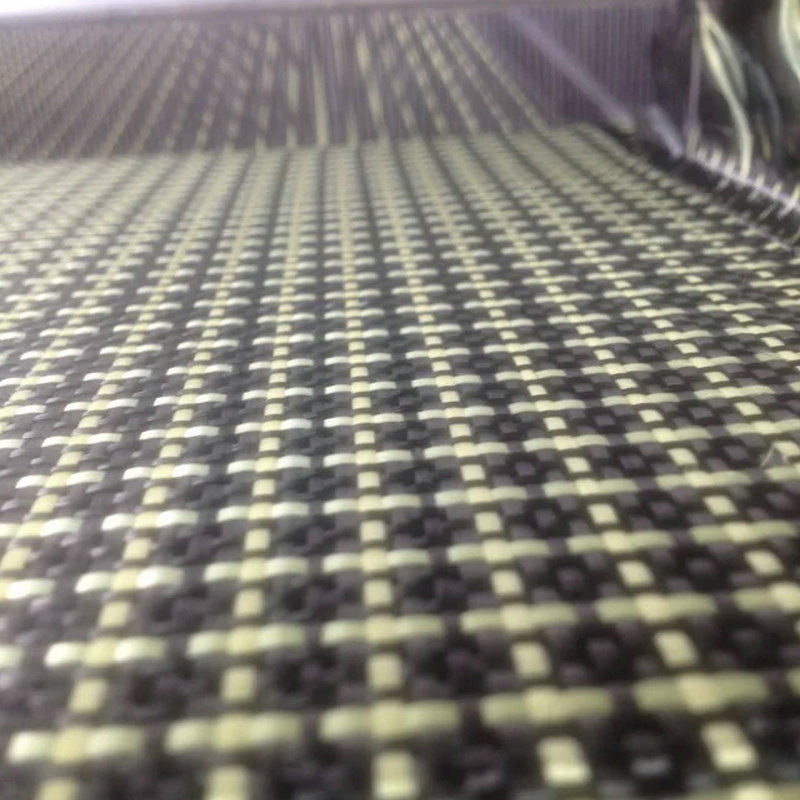
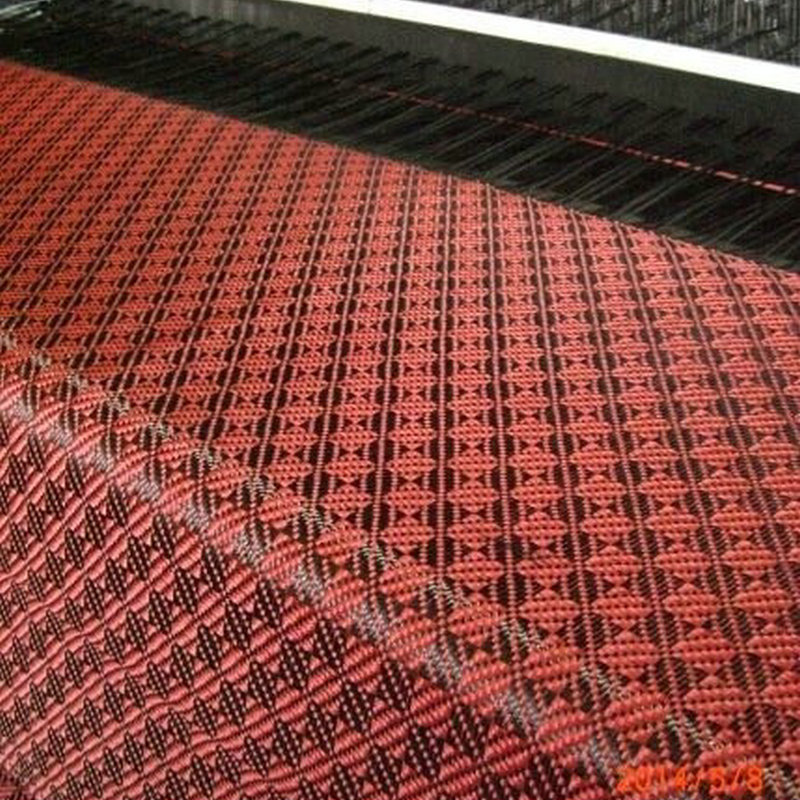
How Fiber Reinforced Materials Are Made
The process of creating fiber reinforced materials involves embedding the reinforcing fibers into the matrix material. Various manufacturing techniques are used depending on the type of fiber and matrix material. The most common methods include:
1. Hand Lay-Up Method
In this method, fibers are manually placed into a mold, and the matrix material (usually a liquid resin) is applied over them. Layers are built up until the desired thickness is achieved. It is a simple, cost-effective process used for producing low-volume, large-scale products like boat hulls and storage tanks.
2. Filament Winding
This technique involves winding continuous fibers coated with resin around a rotating mandrel. The mandrel shape defines the final product's geometry, making this method suitable for producing cylindrical shapes such as pipes and pressure vessels.
3. Pultrusion
Pultrusion is a continuous process where fibers are pulled through a resin bath and then through a heated die to form long, straight profiles like rods, beams, and channels. It is widely used for producing structural elements in construction.
4. Resin Transfer Molding (RTM)
RTM involves placing dry fibers into a closed mold, and then injecting the resin under pressure. This method is ideal for producing complex shapes with high-quality surface finishes.
Advantages of Fiber Reinforced Materials
The use of fiber reinforced materials offers several benefits over traditional materials, including:
1. High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
FRMs are significantly stronger and lighter than metals like steel and aluminum, making them ideal for weight-sensitive applications such as aircraft and automotive components.
2. Corrosion Resistance
Many FRMs are resistant to environmental degradation, including corrosion, UV exposure, and chemical attacks. This makes them highly durable and suitable for outdoor applications.
3. Flexibility in Design
The ability to tailor the material’s properties by changing the type and orientation of fibers allows for a wide range of design possibilities. Engineers can optimize the material for specific applications, resulting in better performance and reduced material waste.
4. Reduced Maintenance
Due to their high durability and resistance to wear, FRMs require less maintenance compared to conventional materials, reducing the overall lifecycle costs.
Limitations of Fiber Reinforced Materials
Despite their advantages, FRMs also have some limitations:
1. High Production Costs
The manufacturing processes for some fiber reinforced materials, especially those involving carbon or aramid fibers, can be expensive due to the high cost of raw materials and processing.
2. Difficulty in Recycling
Recycling FRMs is a complex process because separating the matrix from the fibers without compromising the material’s integrity is challenging.
3. Anisotropy
FRMs are typically anisotropic, meaning their properties vary depending on the direction of the fibers. This requires careful design and analysis to ensure performance consistency.
Applications of Fiber Reinforced Materials
Fiber reinforced materials are used in a variety of applications across numerous industries. Some key examples include:
1. Aerospace and Aviation
CFRM is extensively used in aircraft structures, including fuselage and wings, to reduce weight while maintaining high strength and durability.
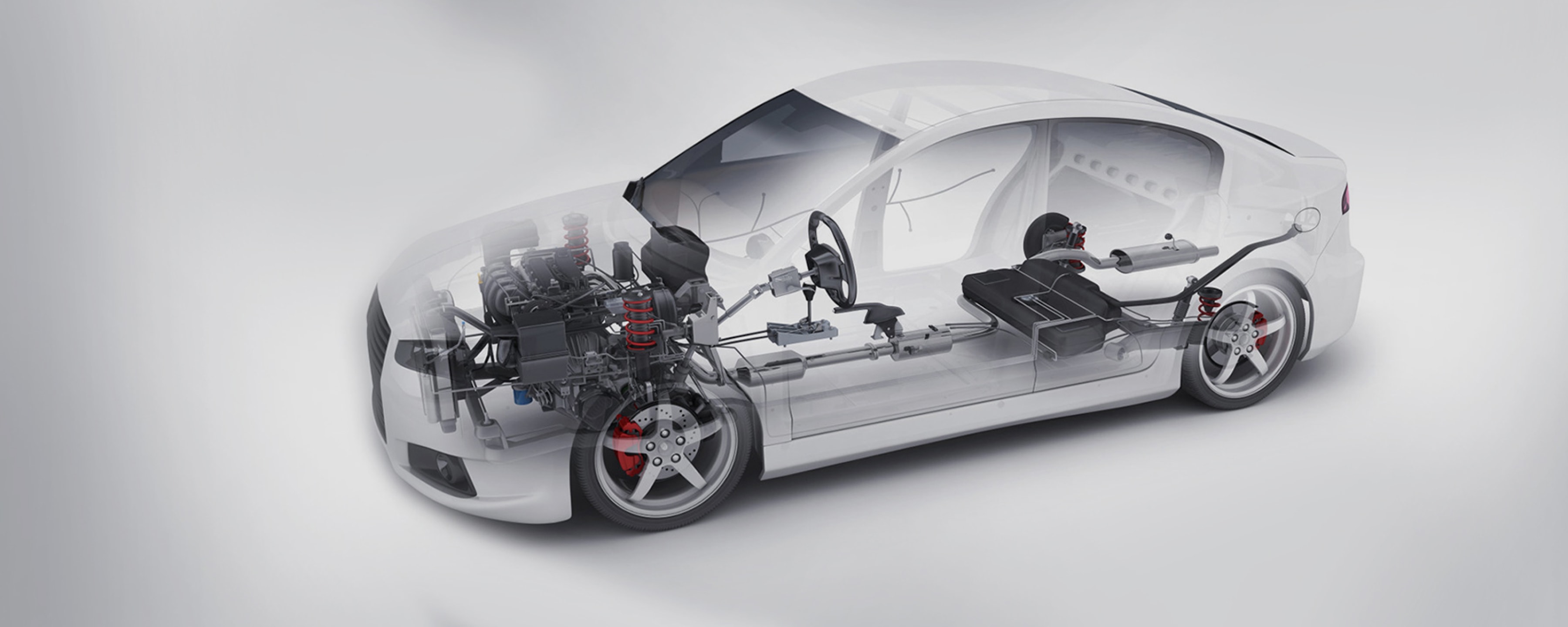
2. Automotive
GFRM and CFRM are used in car bodies, interior components, and high-performance parts to enhance fuel efficiency and safety.
3. Construction
FRMs are utilized in construction for making lightweight, durable structures such as bridge decks, rebar for concrete reinforcement, and architectural elements.
4. Sporting Goods
From bicycles to golf clubs, FRMs are favored in the sports industry for their ability to provide high strength without compromising weight.
Future Trends in Fiber Reinforced Materials
The demand for lightweight and high-performance materials is driving innovation in the FRM industry. Key trends include:
1. Sustainable Reinforcement Options
The focus is shifting towards eco-friendly materials, including biodegradable matrices and natural fibers, to address environmental concerns.
2. Enhanced Manufacturing Techniques
Advancements in 3D printing and automated fiber placement are enabling more complex and precise fabrication of FRMs, reducing production time and costs.
3. Smart Fiber Reinforced Composites
The integration of sensors and conductive fibers into composites is paving the way for "smart" materials that can monitor structural health and respond to changes in their environment.
Conclusion
Fiber reinforced materials have revolutionized engineering by offering an exceptional combination of strength, lightweight, and durability. From aerospace and automotive to sports and construction, these materials provide unparalleled performance, making them an essential part of modern technological advancements. As innovation continues, FRMs are expected to play an even more prominent role in developing sustainable and high-performance solutions across industries.
FAQs
1. What are fiber reinforced materials? Fiber Reinforced Materials are composite materials made by combining fibers such as glass, carbon, or aramid with a matrix material to enhance mechanical properties like strength and stiffness.
2. What are the common types of fiber reinforced materials? The main types include Glass Fiber Reinforced Materials (GFRM), Carbon Fiber Reinforced Materials (CFRM), Aramid Fiber Reinforced Materials (AFRM), and Natural Fiber Reinforced Materials.
3. What are the advantages of using fiber reinforced materials? The primary benefits include high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, flexibility in design, and reduced maintenance costs.
4. What industries use fiber reinforced materials? FRMs are widely used in aerospace, automotive, construction, and sports equipment industries.
5. What are the future trends in fiber reinforced materials? Future trends include the development of sustainable materials, advancements in manufacturing techniques, and the creation of smart composites with embedded sensors for monitoring structural health.
Popular Composite Materials
Popular Composite Materials
Composites Knowledge Hub
Composites Knowledge Hub