+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!

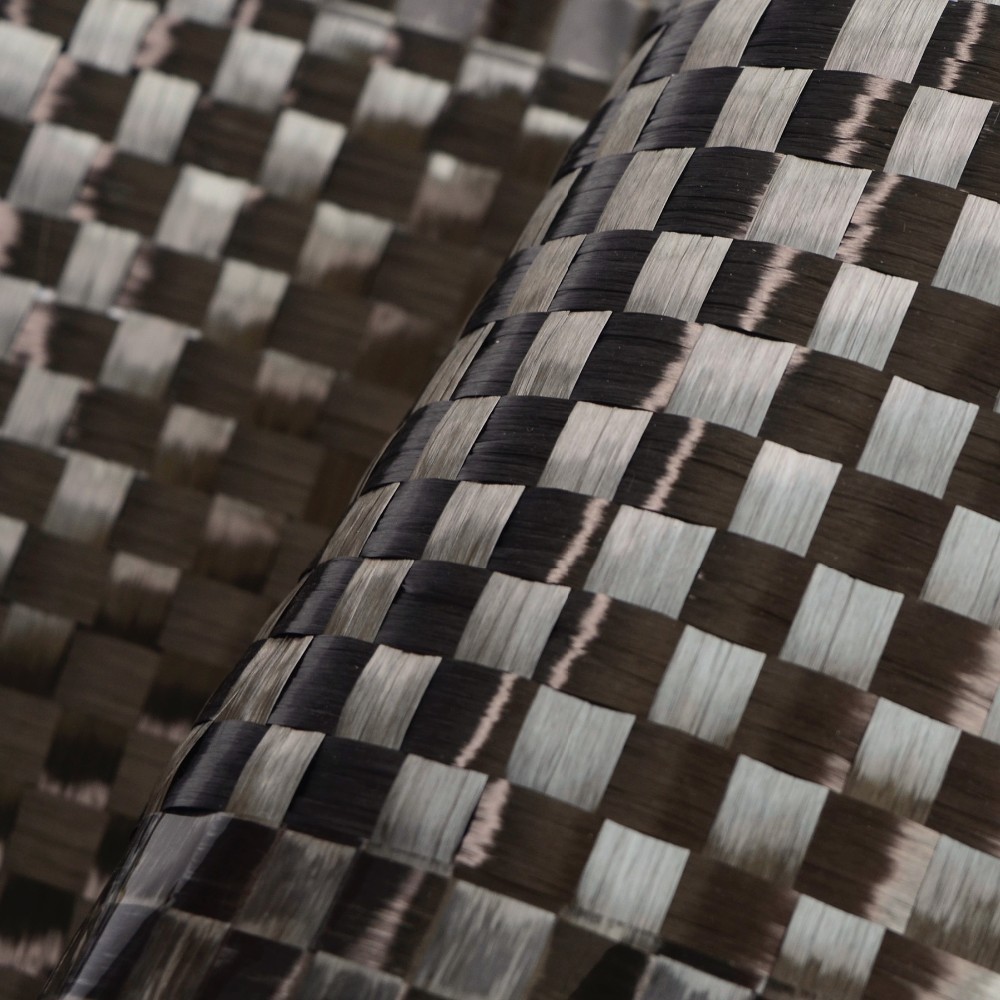
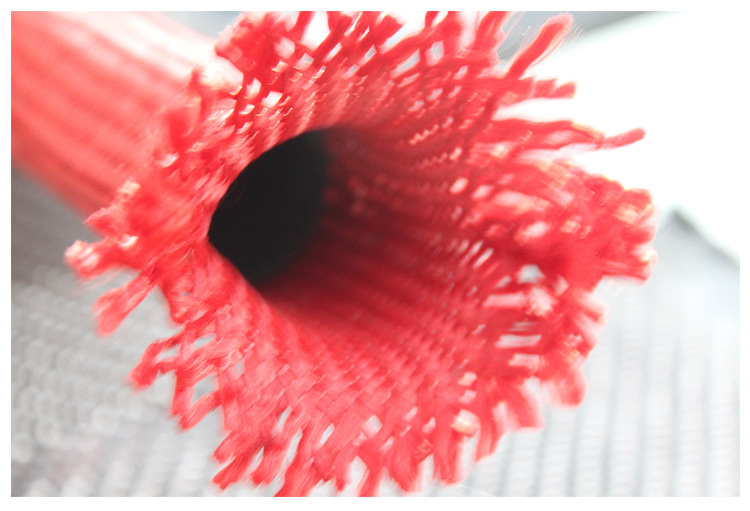
Carbon Fiber Multiaxial Fabric

Hybrid Woven Fabric
+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!
The development and Application of 2.5D Textile Composite Materials
Classified from an aerial structure perspective, textile composite materials can be divided into two major categories: two-dimensional textile composite materials and three-dimensional textile composite materials.
Textile structure composite materials refer to the composite materials that use textile processing methods to transform one-dimensional fibers (or yarns) into two-dimensional or three-dimensional fiber assemblies (commonly known as fabrics in the textile field) and use them as the reinforcing structure. Classified from an aerial structure perspective, textile composite materials can be divided into two major categories: two-dimensional textile composite materials and three-dimensional textile composite materials.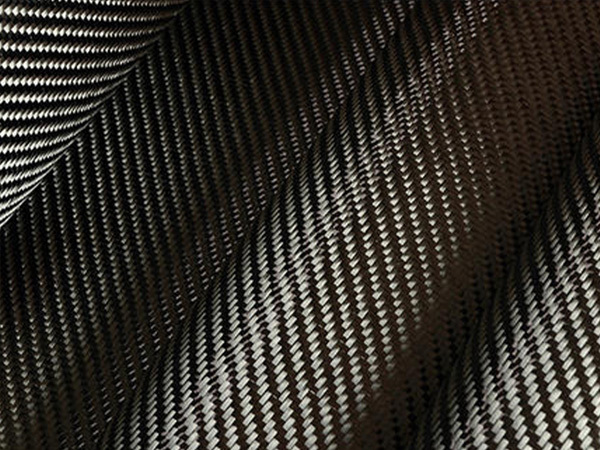 
In the early stages of the development of textile composite materials, the relatively backward textile weaving technology and equipment, combined with the superior performance compared to other composite materials, led to the widespread application of two-dimensional textile composite materials in various fields. However, the natural defects of two-dimensional textile composite materials restrict their application in key areas. The main reasons are twofold:
Two-dimensional textile composite material preforms are usually square samples, which cannot be directly made into tube-shaped fabrics according to actual usage requirements. So, actual use necessitates material cutting, layering, etc. Moreover, the thickness direction is mostly made by pressing a single layer of fiber cloth through the laminating process, most of which are manual operations. The process is complicated, labor-intensive, has poor working conditions, high costs, and expensive prices.
Two-dimensional textile composite materials typically exhibit low performance in the thickness direction, such as rigidity, strength, and fatigue resistance, making it difficult to withstand higher shear stress. This cannot meet the mechanical performance requirements of thicker parts in the thickness direction and has poor impact performance.
These two main reasons limit the actual application of two-dimensional textile composite materials. The major defect of insufficient strength in the thickness direction restricts its use in key parts and is generally used in auxiliary parts. To reduce production costs while addressing the natural defects of two-dimensional textile composite materials in terms of strength in the thickness direction, three-dimensional textile structure reinforced composite materials began to enter people's view from the 1960s.
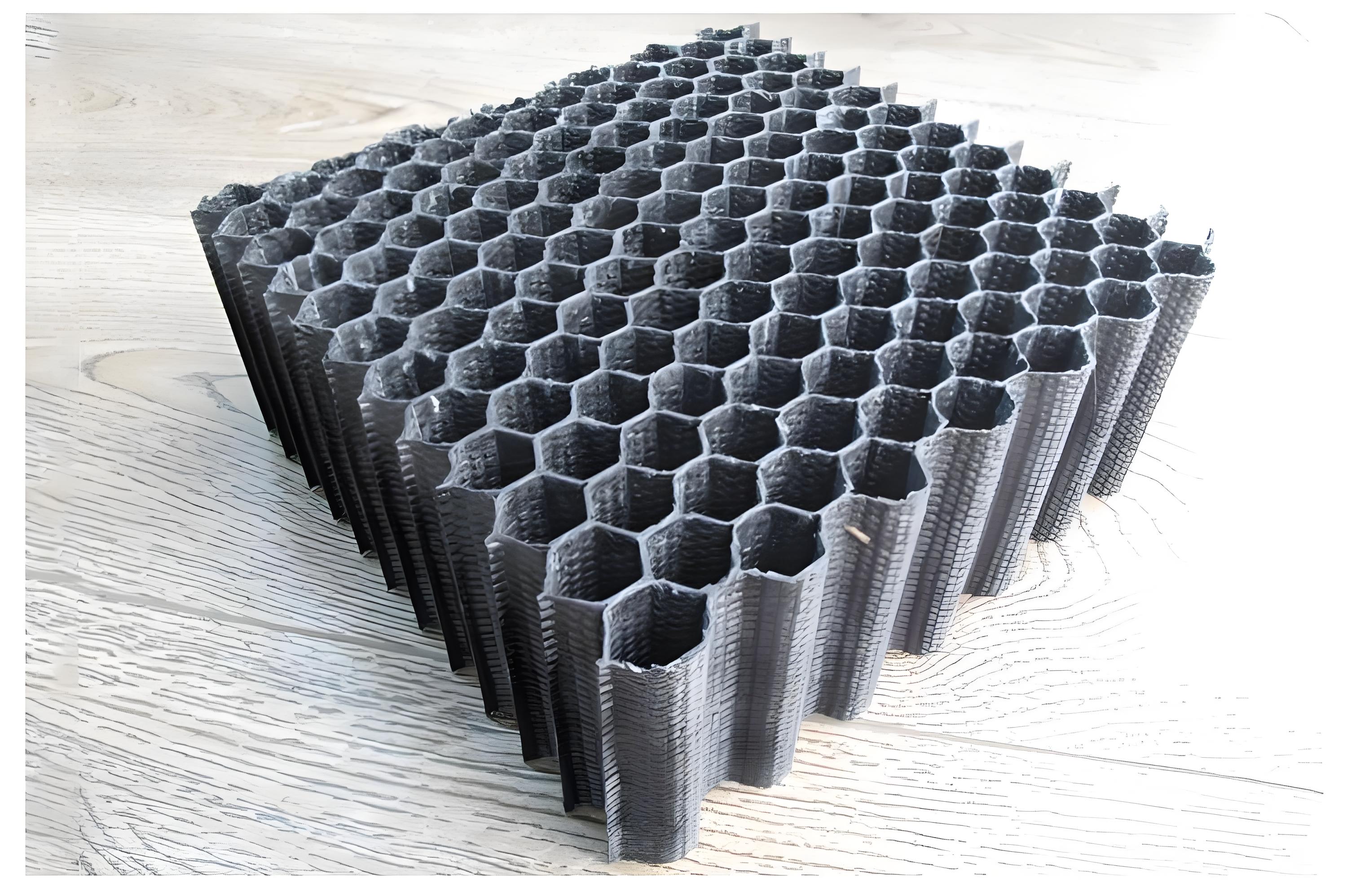
The most significant difference from two-dimensional laminated composite materials is that three-dimensional textile composite materials are woven into one piece, and there is no longer the concept of interlayers. The reinforcing fibers are continuous not only within the layer but also between the layers, significantly improving the strength and damage tolerance in the thickness direction, and providing the possibility for the overall forming of large structures.
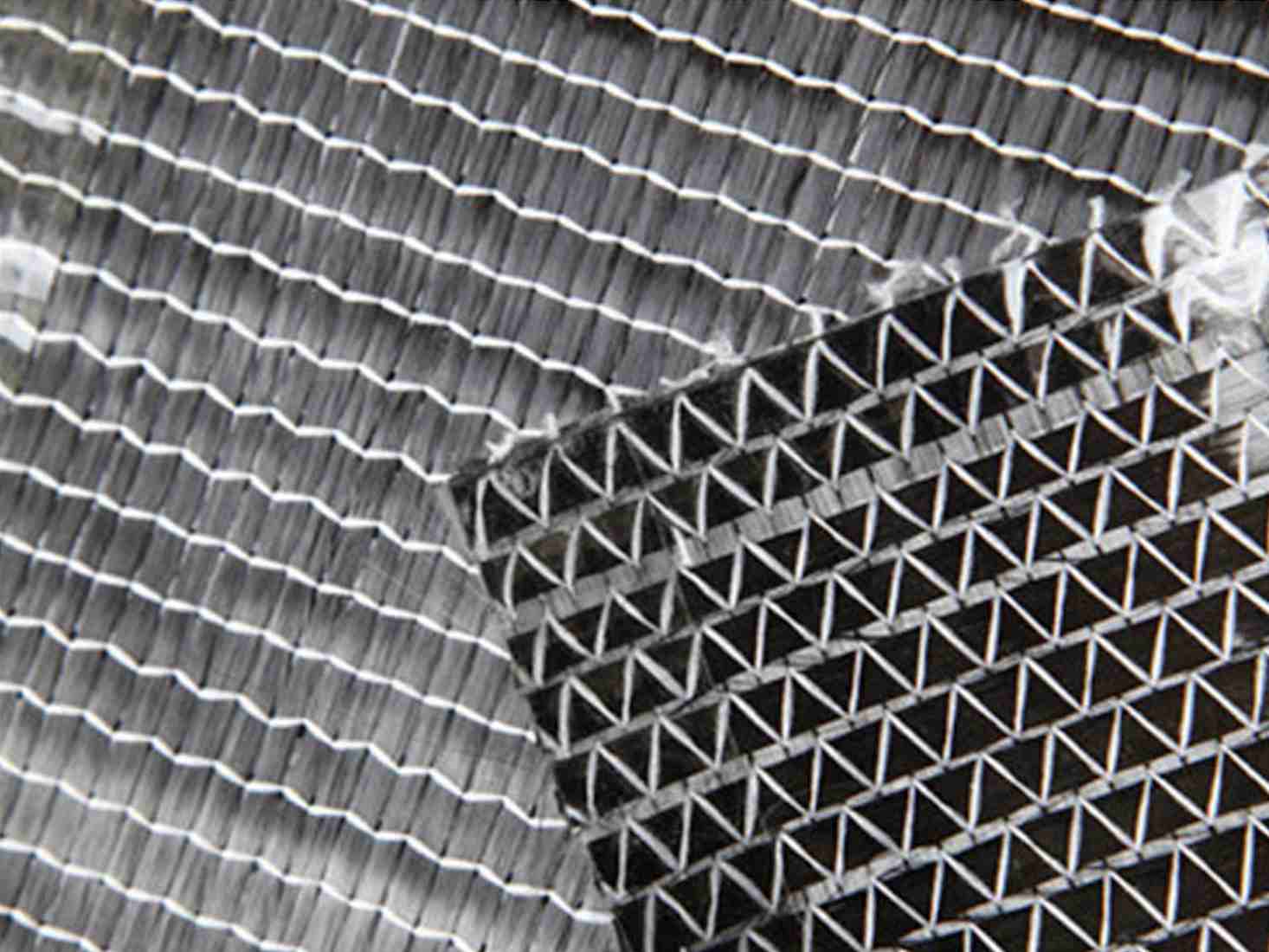
As a type of three-dimensional fabric, 2.5D textile structure reinforced composite materials have high structural integrity, high strength, high specific rigidity, corrosion resistance, fatigue resistance, and excellent designability. Compared with conventional three-dimensional textile composite materials, it avoids the complex forming process of three-dimensional textile composite materials, can effectively reduce production costs and shorten the production cycle, has excellent fabric design forming performance, is easy to design and weave complex structural parts, and realizes industrialization. It can better meet the widespread use in aerospace, military, and civil fields.
Popular Composite Materials
Popular Composite Materials








Composites Knowledge Hub
Composites Knowledge Hub




























Tel:
86-13732282311
E-mail:
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Copyright © Hangzhou Xcellent Composites Limited. All Rights Reserved.