+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!

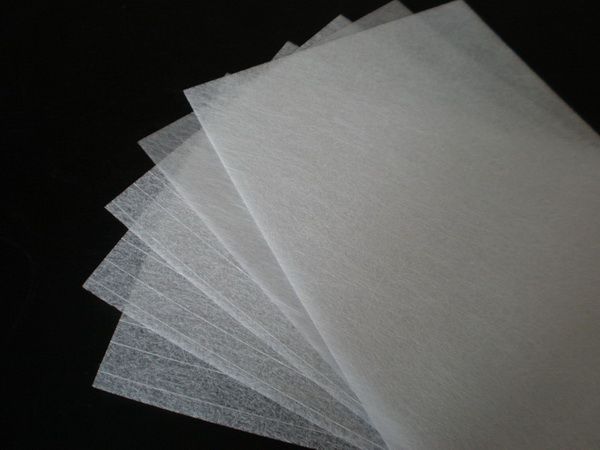
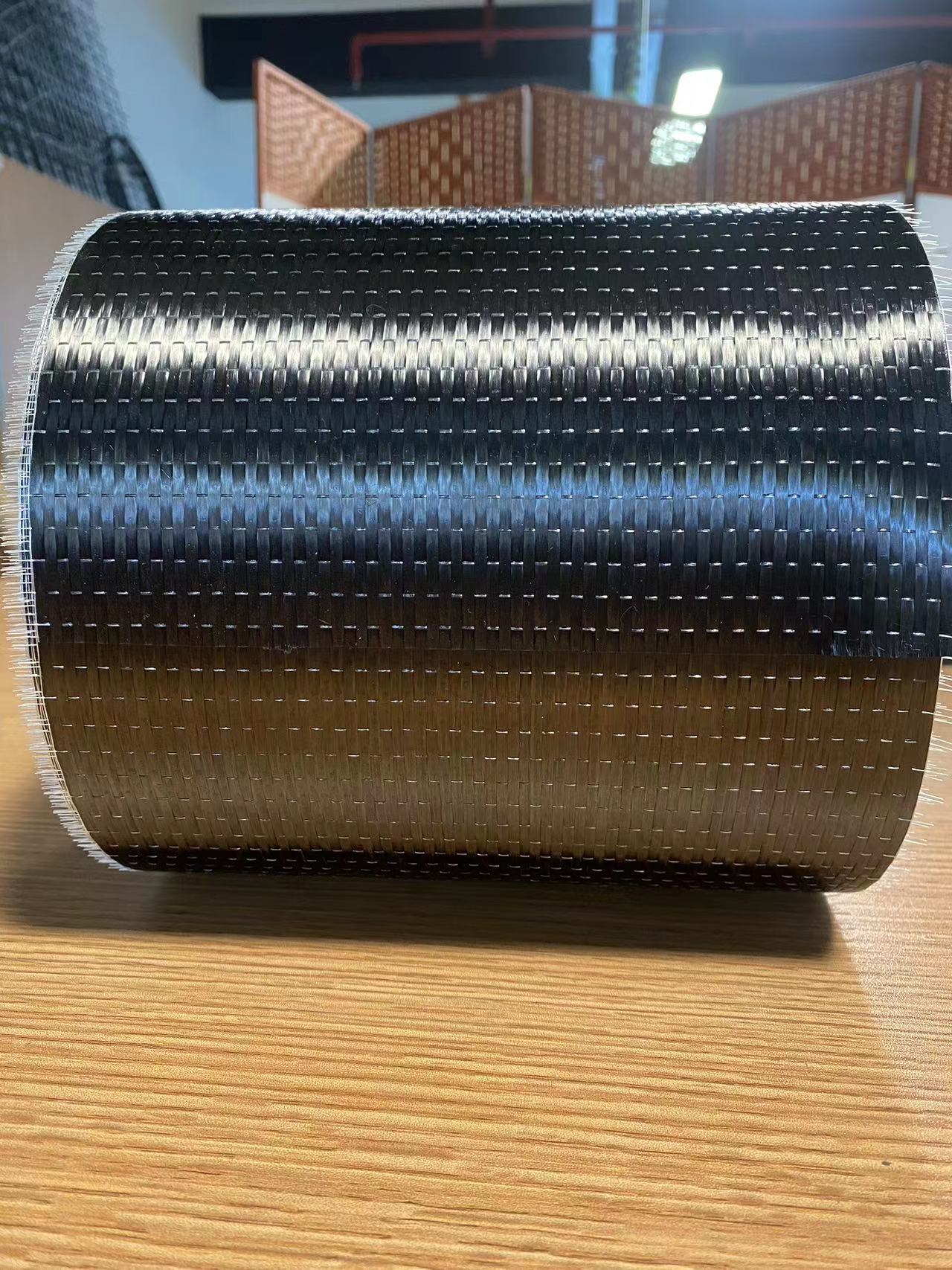
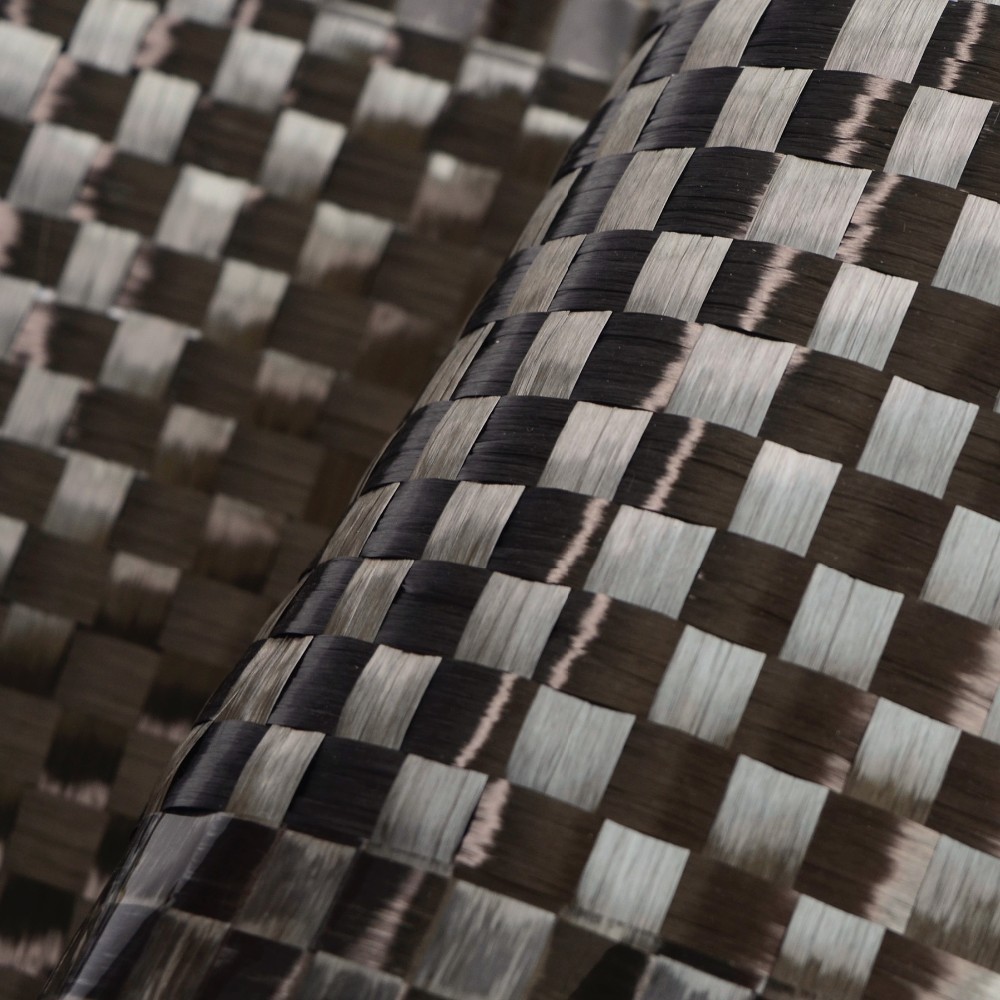
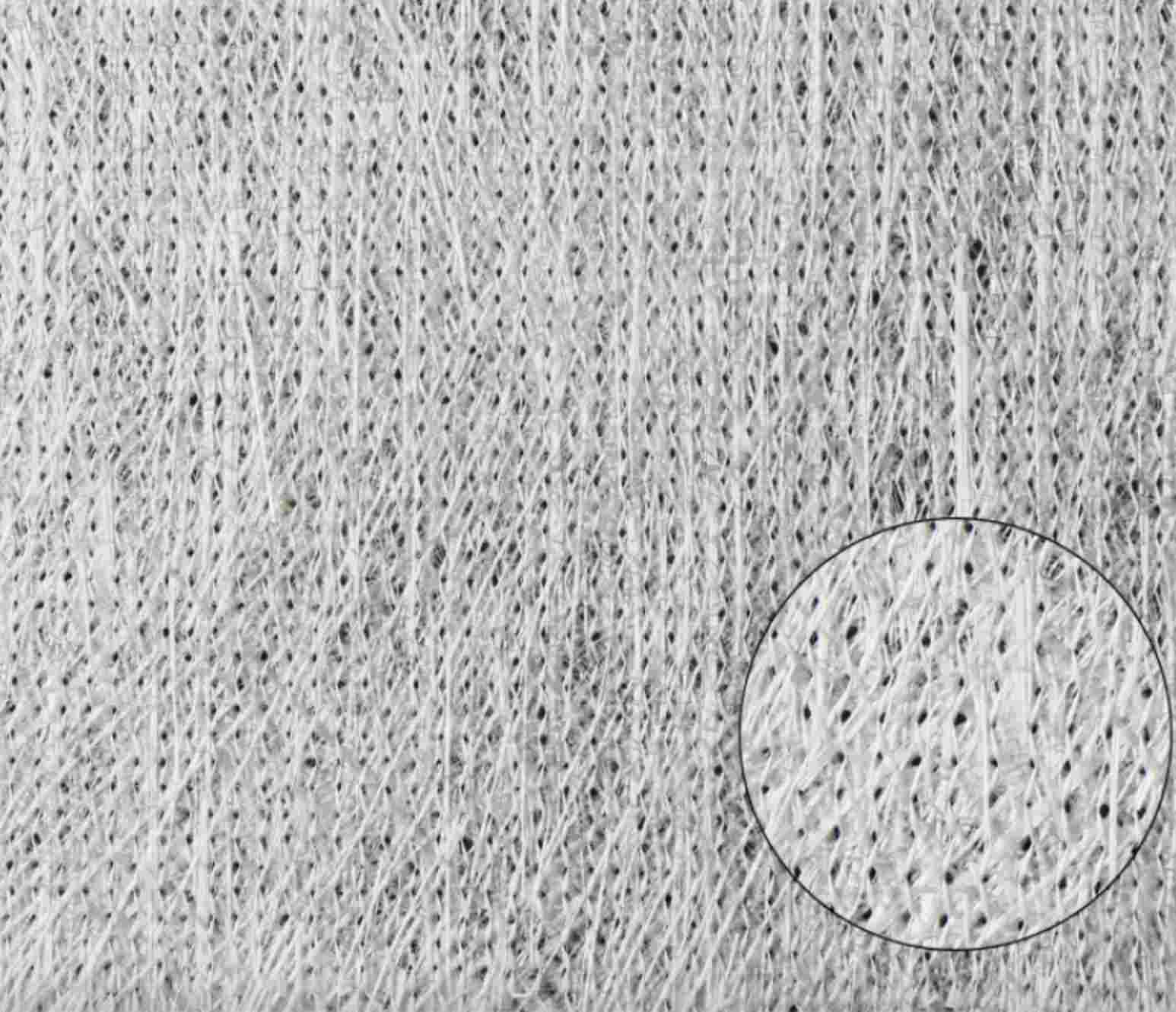
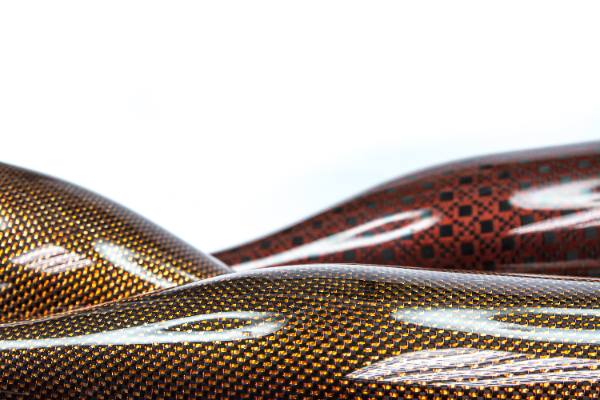
Carbon Fiber Multiaxial Fabric

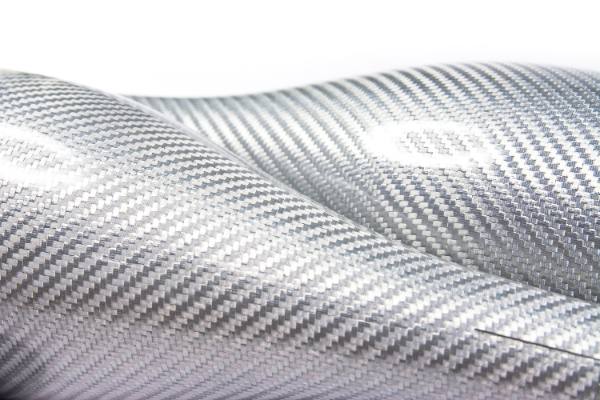
Hybrid Woven Fabric
+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!
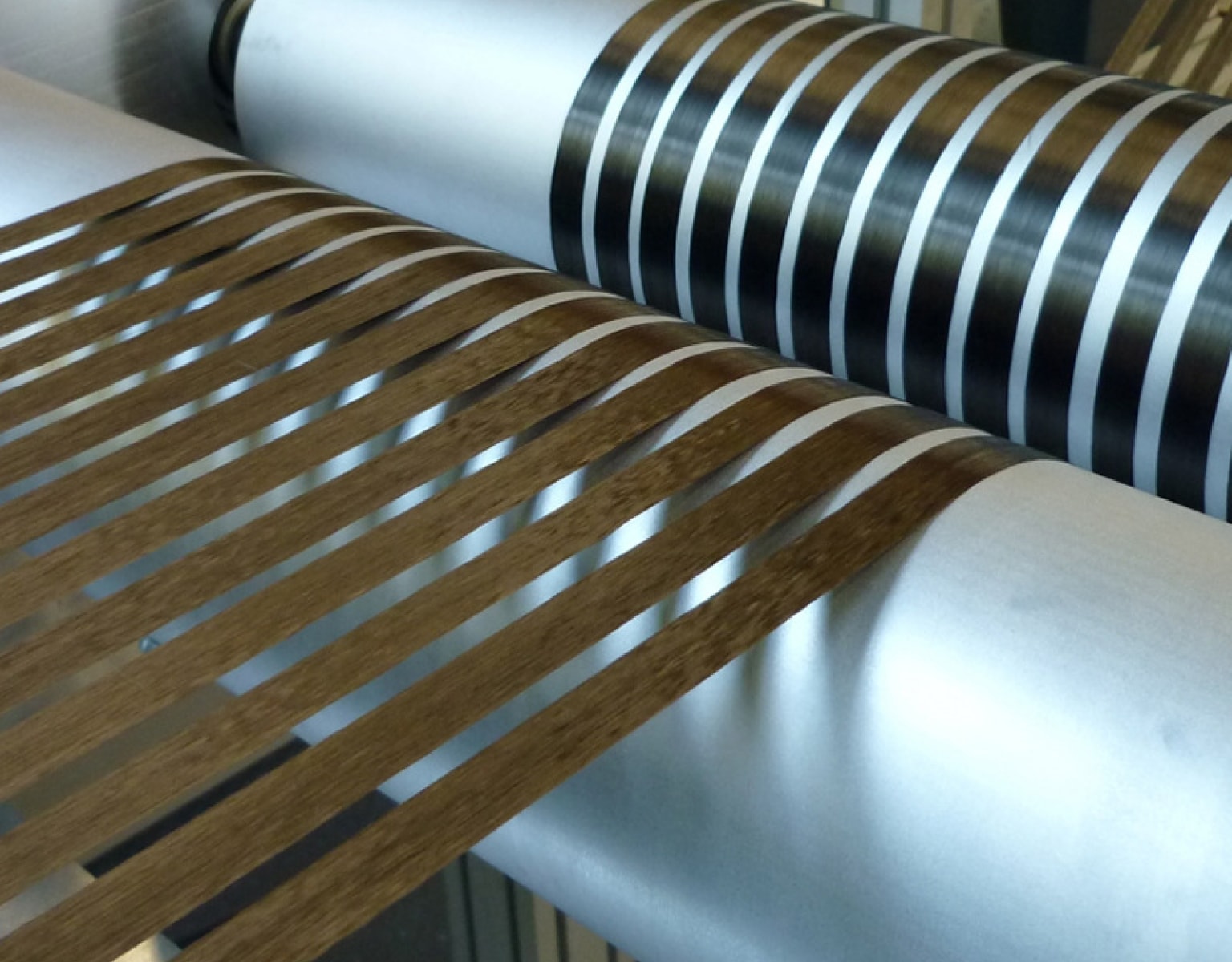


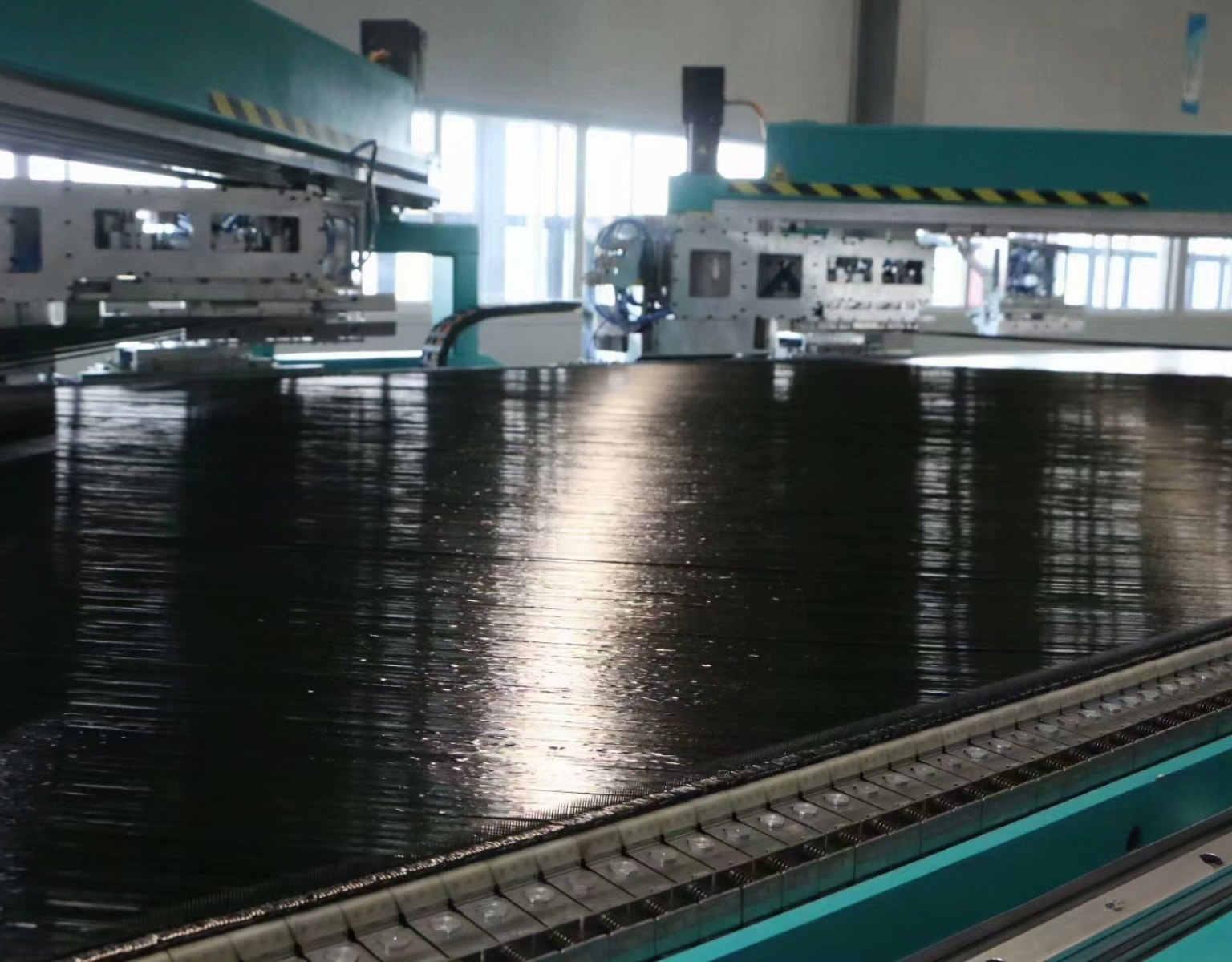
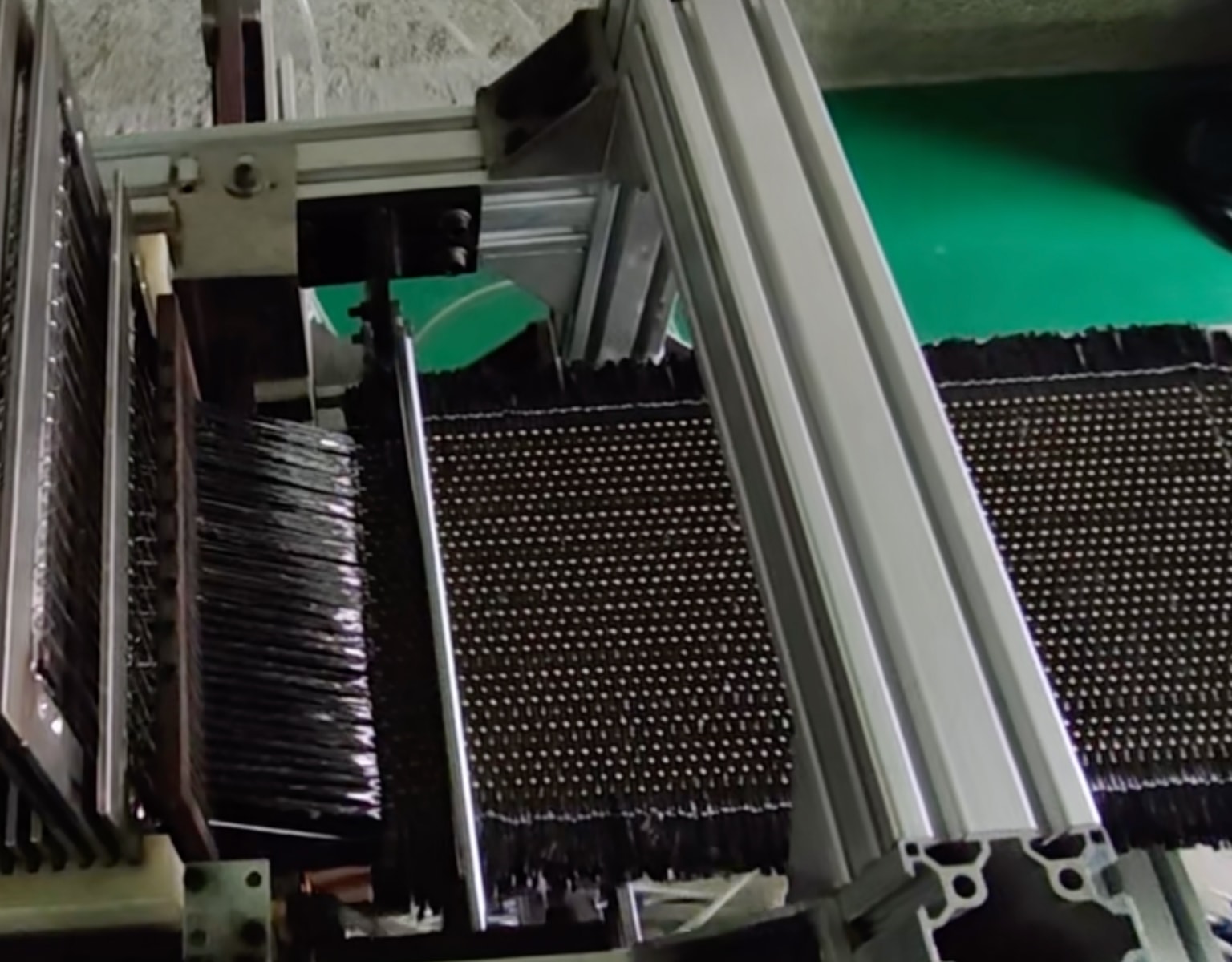
Prepregging
Thermoset and thermoplastic prepregs represent two major categories in the fabrication of composite materials. They differ fundamentally in their preparation methods, each presenting unique advantages and drawbacks while being suited for distinct applications.
The preparation methods for thermoset prepregs primarily include wet lay-up and dry lay-up techniques. Wet lay-up involves dissolving resin in a low-boiling solvent to form a solution, subsequently impregnating fibers and drying them in an oven to yield prepregs. This method is straightforward and versatile, yet struggles with precise control over the fiber-to-resin ratio, while the volatility of solvents may lead to environmental pollution. Dry lay-up, on the other hand, entails combining resin with fibers at high temperatures, either through a one-step direct impregnation or a two-step process involving initial film formation before fiber integration. Dry lay-up allows for precise resin content control but necessitates specific resin melting points and involves complex equipment.
Methods for preparing thermoplastic prepregs encompass melt impregnation, powder impregnation, solution impregnation, fiber blending, and film laminating. Melt impregnation utilizes extrusion to combine molten resin with fibers, offering easy regulation and environmental friendliness, albeit demanding high resin viscosity. Powder impregnation involves depositing resin powder with static electricity onto fibers, followed by high-temperature treatment, ideal for rapid continuous production. Solution impregnation binds dissolved resin with fibers, suitable for manufacturing thick prepregs but possibly posing environmental contamination concerns. Fiber blending intertwines resin fibers with reinforcement fibers for weaving, enabling straightforward resin content control but potentially resulting in uneven fiber infiltration. Film laminating is a simplistic method but may yield composite materials with lower performance.
Compared to thermoset prepregs, thermoplastic prepregs boast advantages such as recyclability, elimination of low-temperature storage requirements, and shorter molding cycles. Thermoplastic materials can be reshaped after reaching a specific temperature, unlike thermoset materials that remain fixed once cured. These properties of thermoplastic materials render them more convenient and efficient during storage and molding processes. Nonetheless, owing to their unique performance attributes and cost-effectiveness, thermoset prepregs continue to hold an irreplaceable position in numerous applications.
Popular Composite Materials
Popular Composite Materials
Related Composite Materials Capabilities
Related Composite Materials Capabilities
Composites Knowledge Hub
Composites Knowledge Hub




























Tel:
86-13732282311
E-mail:
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Copyright © Hangzhou Xcellent Composites Limited. All Rights Reserved.