+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!
What is a Composite Material? Everything You Want to Know About Advanced Composites
Discover the world of composite materials and advanced composites. Explore their types, uses, benefits, properties, and future innovations in various industries, including aerospace and automotive. Learn how these materials enhance performance while addressing sustainability challenges.
What is a Composite Material?
Composite materials are engineered materials formed from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties. When these materials are combined, they create a composite that exhibits unique characteristics that cannot be achieved by any single material alone. For instance, combining a strong, rigid material with a lightweight, flexible one can result in a material that is both strong and light, making it ideal for a variety of applications.
Examples of Composite Materials
Some common examples of composite materials include:
-
Wood-Plastic Composites (WPCs): These materials are made from recycled wood fibers and plastic, making them durable and resistant to rot. They are widely used in outdoor decking, furniture, and fencing.
-
Fiberglass: Comprised of glass fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, fiberglass composite material is known for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. It is commonly used in boat hulls, pipelines, and storage tanks.
-
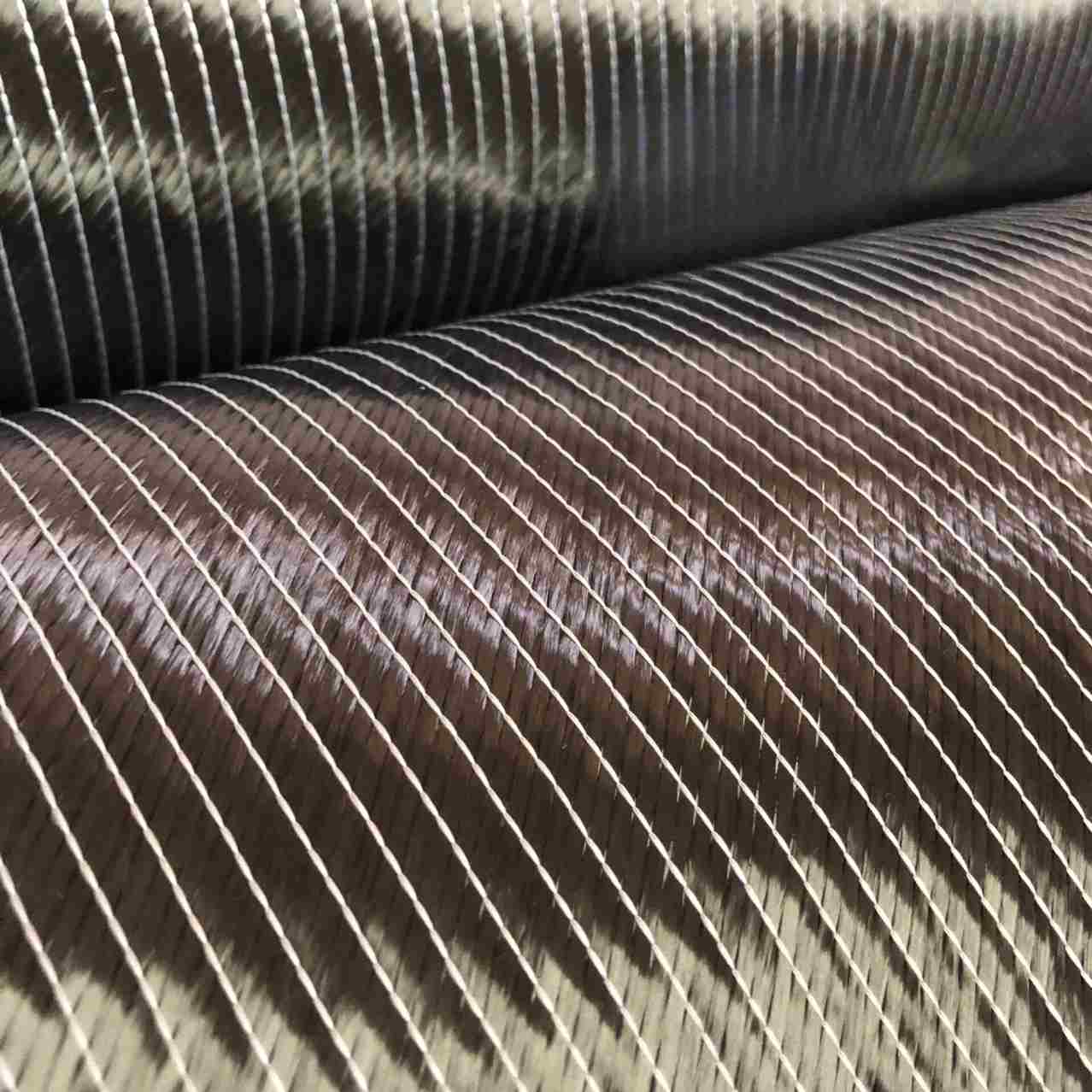
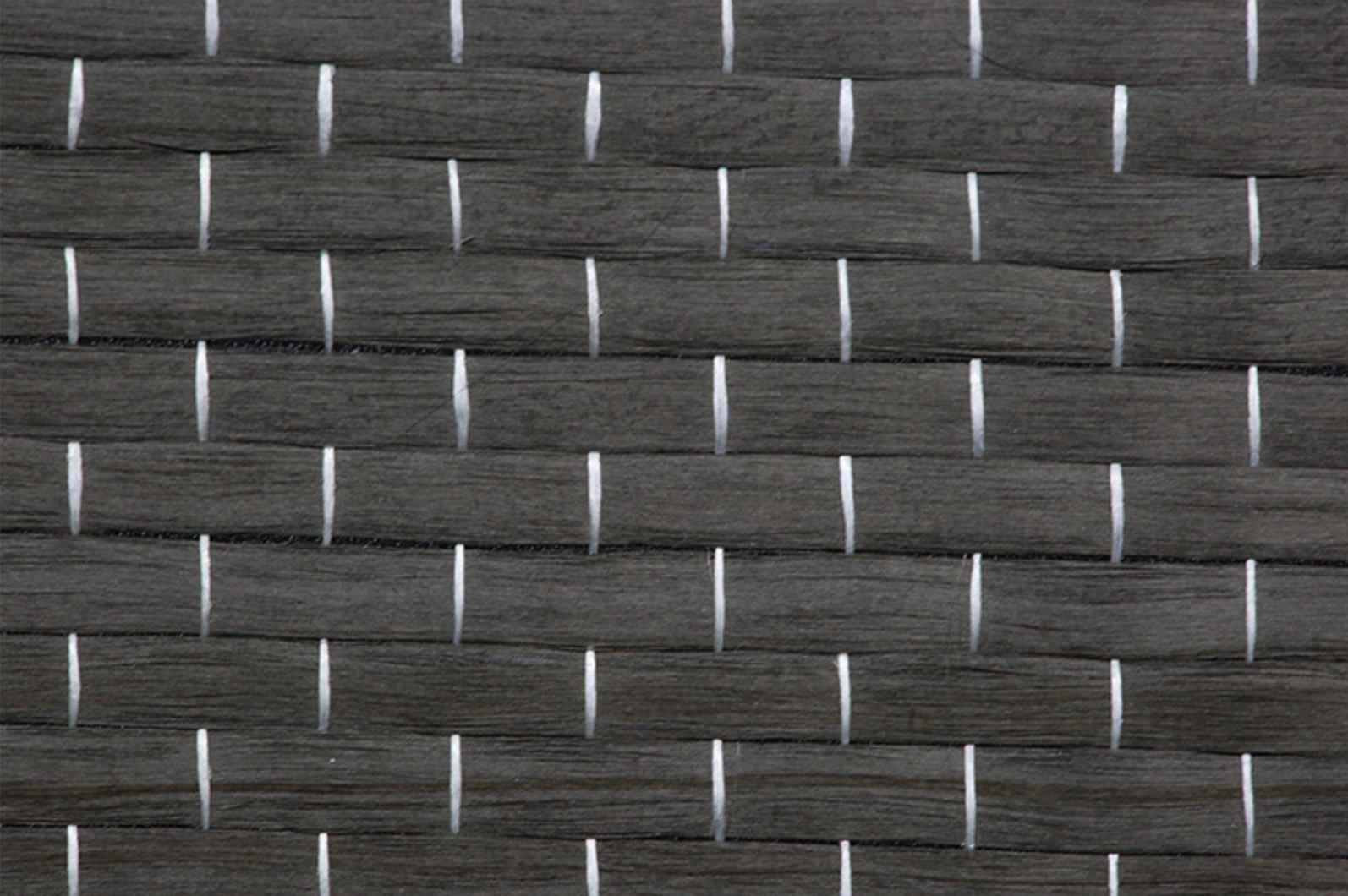
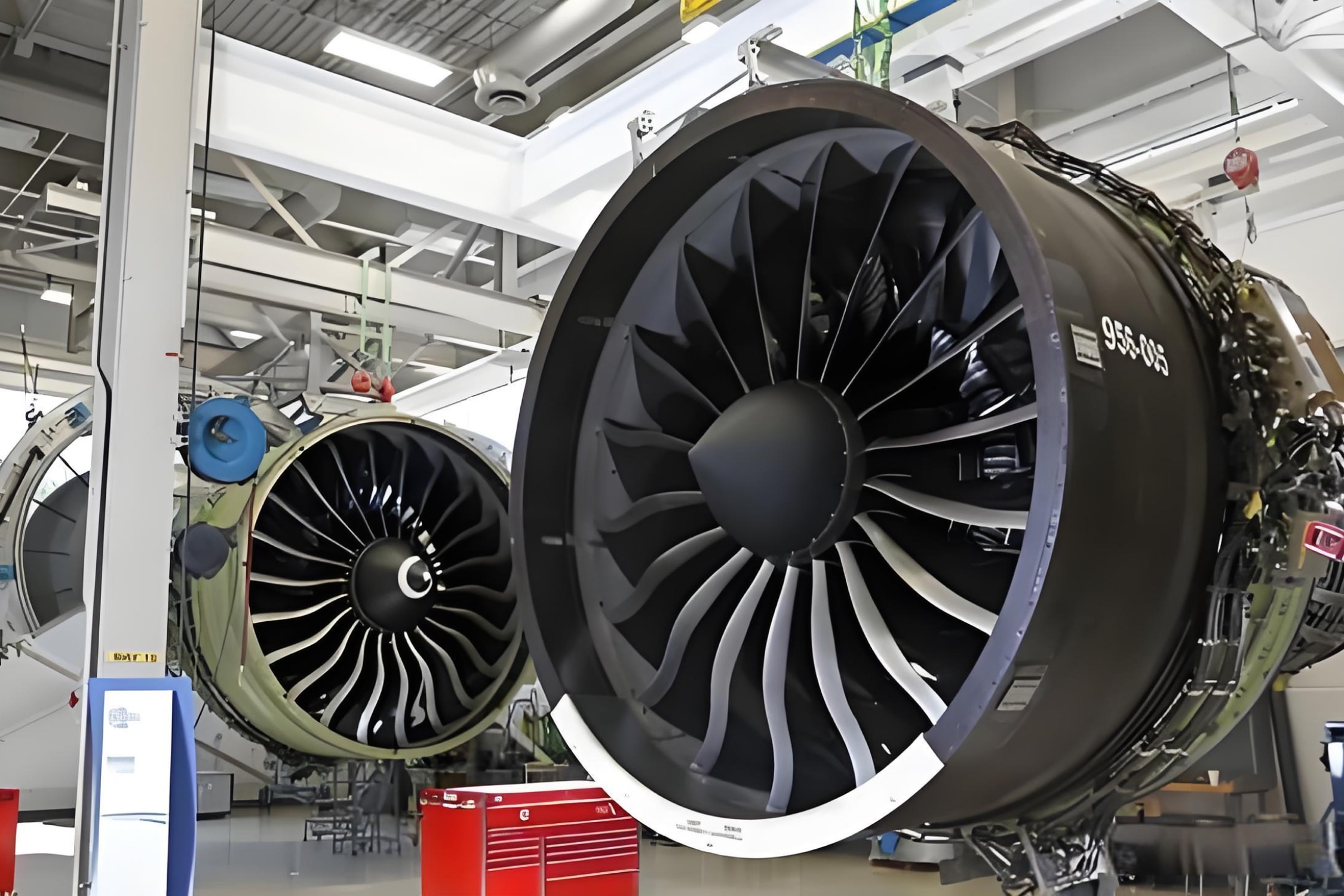
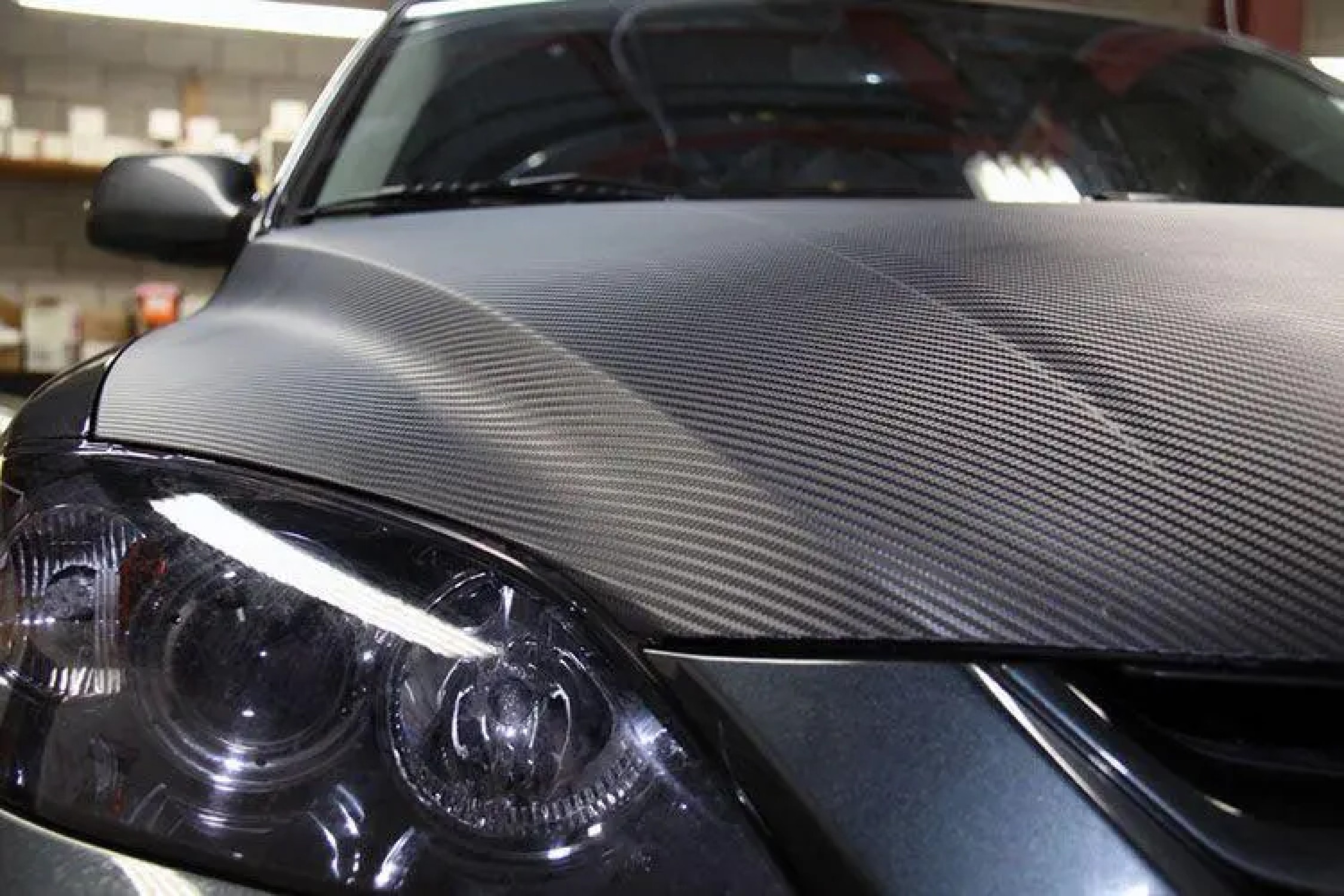
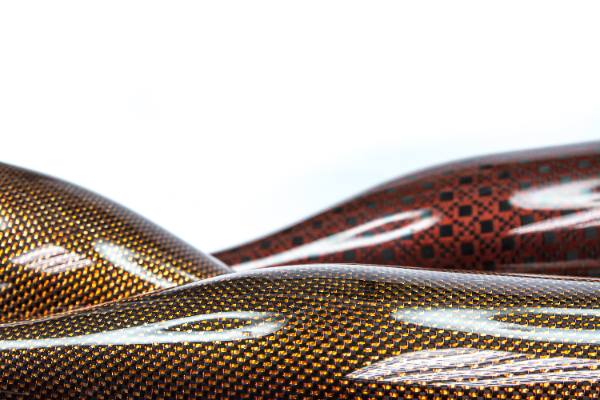
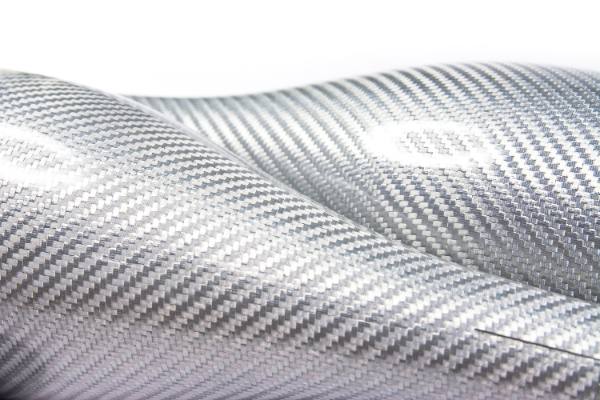
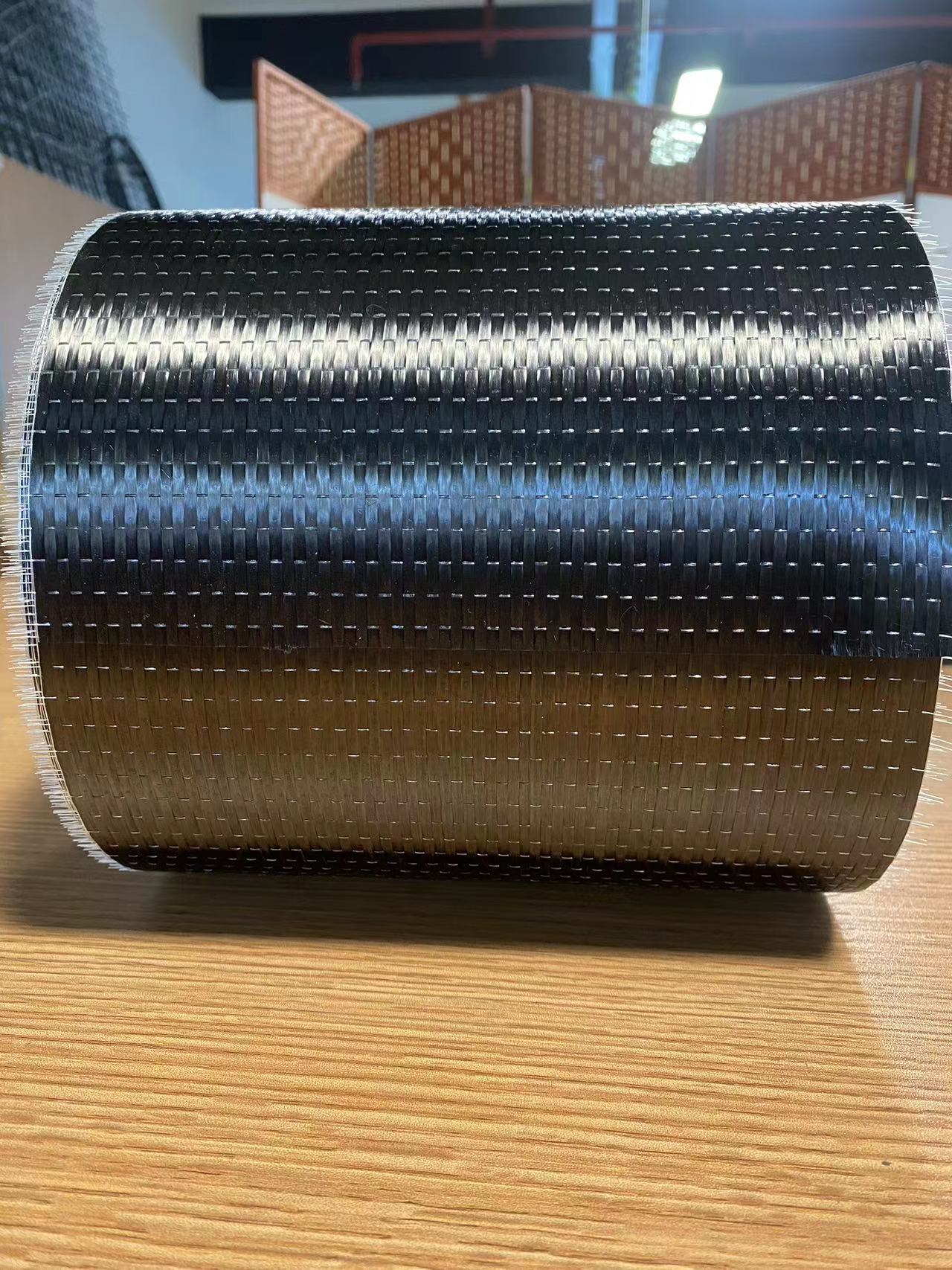
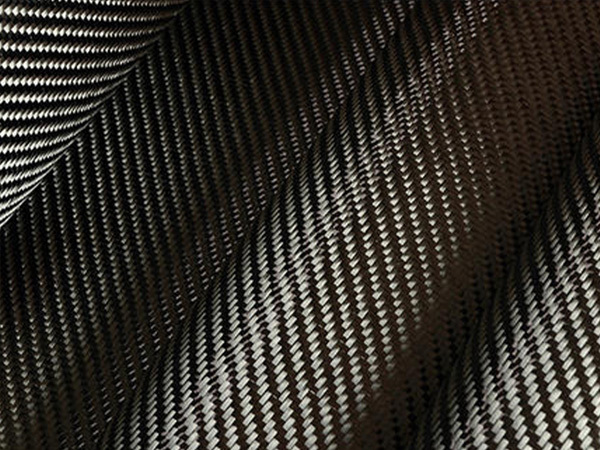
Carbon Fiber: This high-strength carbon fiber composite material consists of thin strands of carbon woven together and reinforced with resin. It is prized in aerospace composites and automotive industries for its superior strength-to-weight ratio.
Different Types of Composite Materials
Composite materials can be classified into several categories based on their matrix and reinforcement types:
-
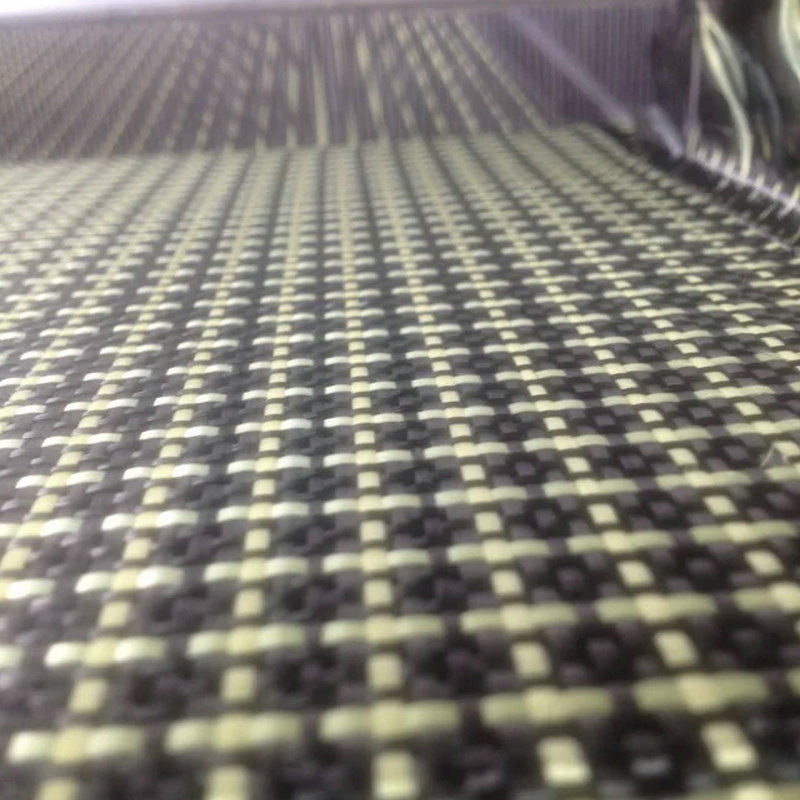
Polymer Matrix Composites (PMCs): These composites are the most prevalent and are characterized by a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers (e.g., glass, carbon). PMCs are lightweight, versatile, and often used in consumer goods and automotive applications.
-
Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs): These composites combine metals with ceramic or polymer fibers to improve strength and thermal properties. They are used in aerospace applications and automotive components requiring higher thermal resistance.
-
Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs): Comprising ceramic fibers in a ceramic matrix, these materials are designed for high-temperature applications, such as turbine engines and thermal protection systems in aerospace.
What Are Some Composite Materials?
Beyond the common examples, numerous other composite materials serve specialized functions:
-
Concrete: Reinforced concrete, which incorporates steel bars or fibers, is essential for constructing strong buildings and infrastructure. The combination enhances tensile strength, making it suitable for heavy loads.
-
Kevlar: A type of aramid fiber, Kevlar is used in personal protective equipment like bulletproof vests and helmets due to its high strength and impact resistance.
Uses of Composite Materials
Composite materials are renowned for their versatility, with applications spanning various industries:
-
Aerospace: In the aerospace sector, composites are critical for creating lightweight structures, improving fuel efficiency, and enhancing performance. Aircraft wings and fuselages often utilize advanced composites, which significantly reduce weight without sacrificing strength.
-
Automotive: In the automotive industry, composite materials are used to manufacture parts such as body panels, bumpers, and structural components. Their lightweight nature helps improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
-
Construction: Composites are employed in constructing bridges, railways, and buildings, thanks to their resistance to environmental degradation, such as corrosion and rot. Fiberglass-reinforced polymers are particularly popular for infrastructure applications.
What is Composite Used For?
The applications of composite materials are vast and diverse, including:
-
Aerospace Components: Composites are extensively used in modern aircraft for wings, fuselage sections, and interiors, contributing to significant weight reductions and improved aerodynamic performance.
-
Sports Equipment: High-performance sports gear, such as bicycles, tennis rackets, and golf clubs, often incorporate advanced composites to enhance performance while minimizing weight.
-
Infrastructure: Composites are increasingly used in civil engineering for building bridges and structures, especially in areas prone to corrosion.
Advantages of Composite Materials
Composite materials offer numerous advantages, making them a preferred choice across industries:
-
Lightweight: Composites can be significantly lighter than traditional materials, enhancing transport efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
-
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: The superior strength of composites compared to their weight allows for innovative designs and applications, particularly in aerospace and automotive sectors.
-
Corrosion Resistance: Many composites resist environmental factors, leading to lower maintenance costs and longer lifespans.
Properties of Composite Materials
Key properties that define composite materials include:
-
Stiffness: The ability to resist deformation under load, important for structural applications.
-
Strength: High tensile and compressive strength make composites suitable for demanding applications.
-
Thermal Stability: Composites often maintain their properties at elevated temperatures, making them ideal for various high-performance applications.
What are Composite Material Properties
The mechanical properties of composite materials vary widely based on their composition and structure. Notable properties include:
-
Impact Resistance: Composites can absorb significant energy without fracturing, making them ideal for protective applications.
-
Fatigue Resistance: Composites are designed to withstand repeated loading cycles without degrading, crucial for automotive and aerospace components.
What is Classification of Composites
Composites can be classified using several systems:
-
By Matrix Type: Composites can be categorized as polymer, metal, or ceramic matrix composites.
-
By Fiber Type: The classification can also be based on fiber types such as glass, carbon, or natural fibers.
What is Advanced Composites
Advanced composites refer to high-performance materials engineered for specific applications that require enhanced properties. They often include sophisticated reinforcement methods and are typically used in demanding environments.
Types of Advanced Composites
Key types of advanced composites include:
-
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers (CFRPs): These composites are increasingly popular in industries where performance is critical. CFRPs are used in aircraft, sporting goods, and automotive parts, thanks to their outstanding strength and stiffness.
-
Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs): Designed for high-temperature applications, CMCs are crucial in the aerospace industry, particularly for jet engines where they withstand extreme conditions.
Benefits of Advanced Composites
The benefits of advanced composites include:
-
Enhanced Performance: Advanced composites provide exceptional performance characteristics, including high strength, light weight, and resistance to extreme environments, making them suitable for specialized applications.
-
Weight Savings: Their lightweight nature can lead to significant fuel savings in transportation industries, reducing operational costs.
-
Design Flexibility: Advanced composites can be tailored to meet specific performance criteria, allowing for innovative designs.
Disadvantages of Composites
Despite their advantages, composite materials also have some disadvantages:
-
Cost: The manufacturing processes for advanced composites can be expensive, making them less accessible for some applications.
-
Manufacturing Complexity: Producing composites often requires specialized equipment and techniques, leading to increased production times and costs.
-
Recycling Challenges: Many composite materials are difficult to recycle due to their heterogeneous nature, posing environmental concerns.
Future of Composite Materials
The future of composite materials looks promising, with ongoing research focusing on sustainability, recycling methods, and the development of bio-based composites. Innovations such as 3D printing with composite materials are expected to revolutionize manufacturing processes, providing greater design freedom and efficiency.
Conclusion
Composite materials and advanced composites are integral to modern engineering and manufacturing. Their unique properties and advantages make them indispensable in various industries, from aerospace to construction. As technology continues to evolve, the applications and performance of these materials will only expand, paving the way for new possibilities in material science.
FAQs for Advanced Composite Materials
-
What are the most common composite materials?
- Common composites include fiberglass, carbon fiber, and wood-plastic composites, each serving specific applications.
-
How are advanced composites different from regular composites?
- Advanced composites are designed for high-performance applications, offering enhanced properties like strength, weight savings, and thermal stability.
-
What industries benefit from composite materials?
- Industries such as aerospace, automotive, sports, and construction heavily rely on composite materials for their unique properties.
-
Are composite materials recyclable?
- Recycling composite materials is challenging, but ongoing research aims to develop more effective recycling methods.
-
What are the primary disadvantages of composite materials?
- Key disadvantages include high cost, manufacturing complexity, and difficulties in recycling.
-
What future developments can we expect in composite materials?
- Innovations in sustainable materials, recycling processes, and advanced manufacturing techniques are expected to drive future advancements.
Popular Composite Materials
Popular Composite Materials
Composites Knowledge Hub
Composites Knowledge Hub