+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!
What Is Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composite? A Deep Dive into Mian Carbon Fibre Products
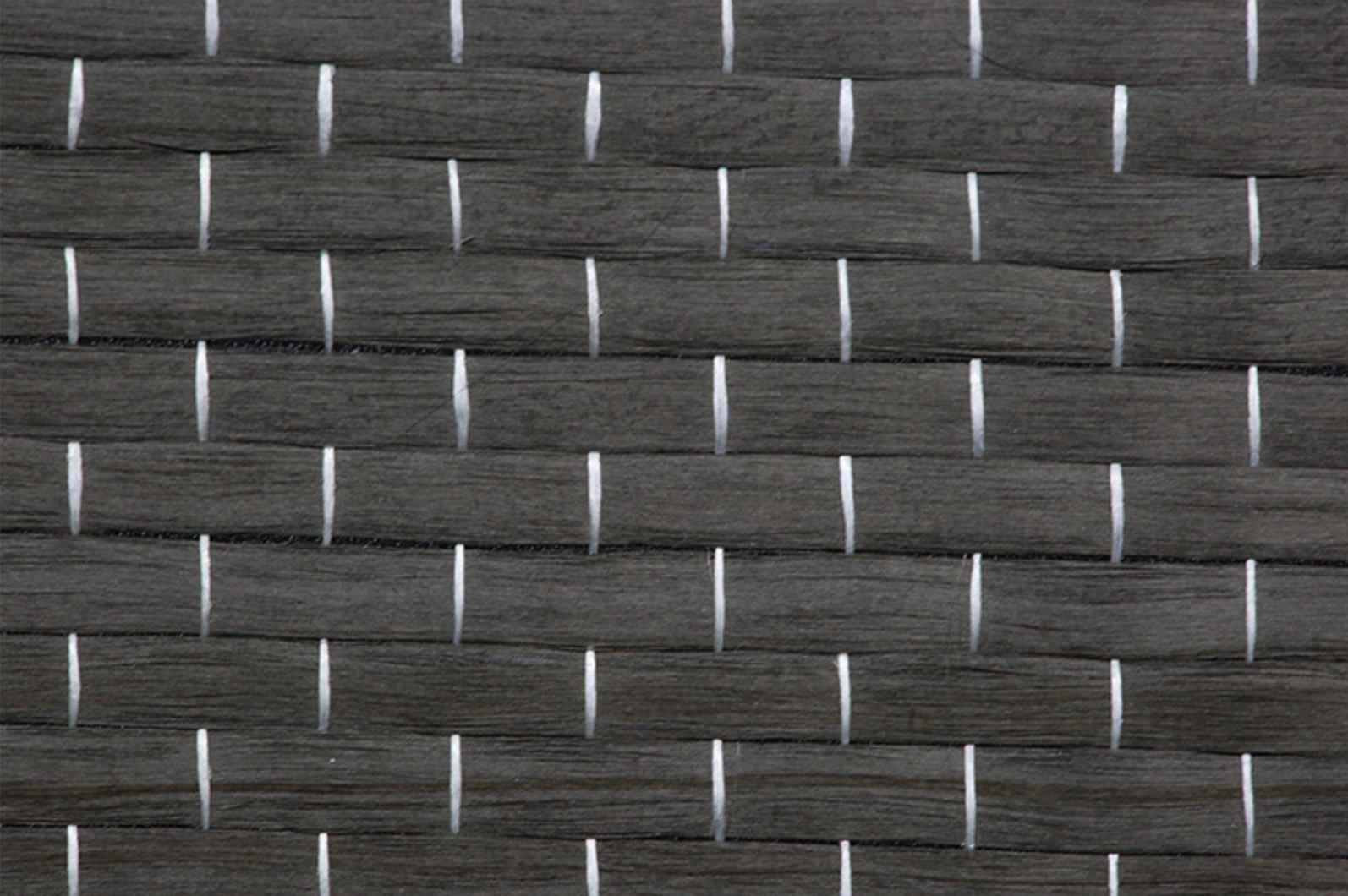
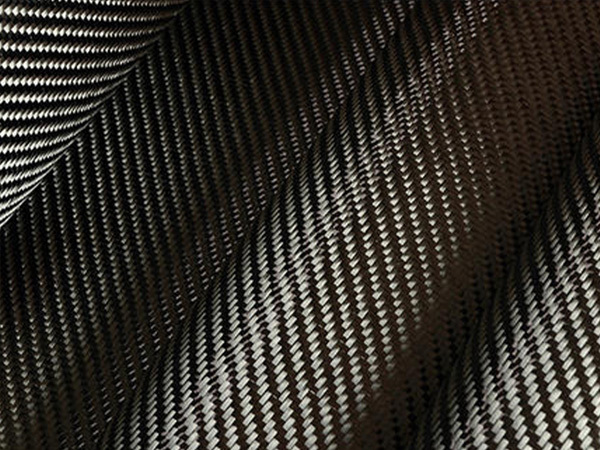
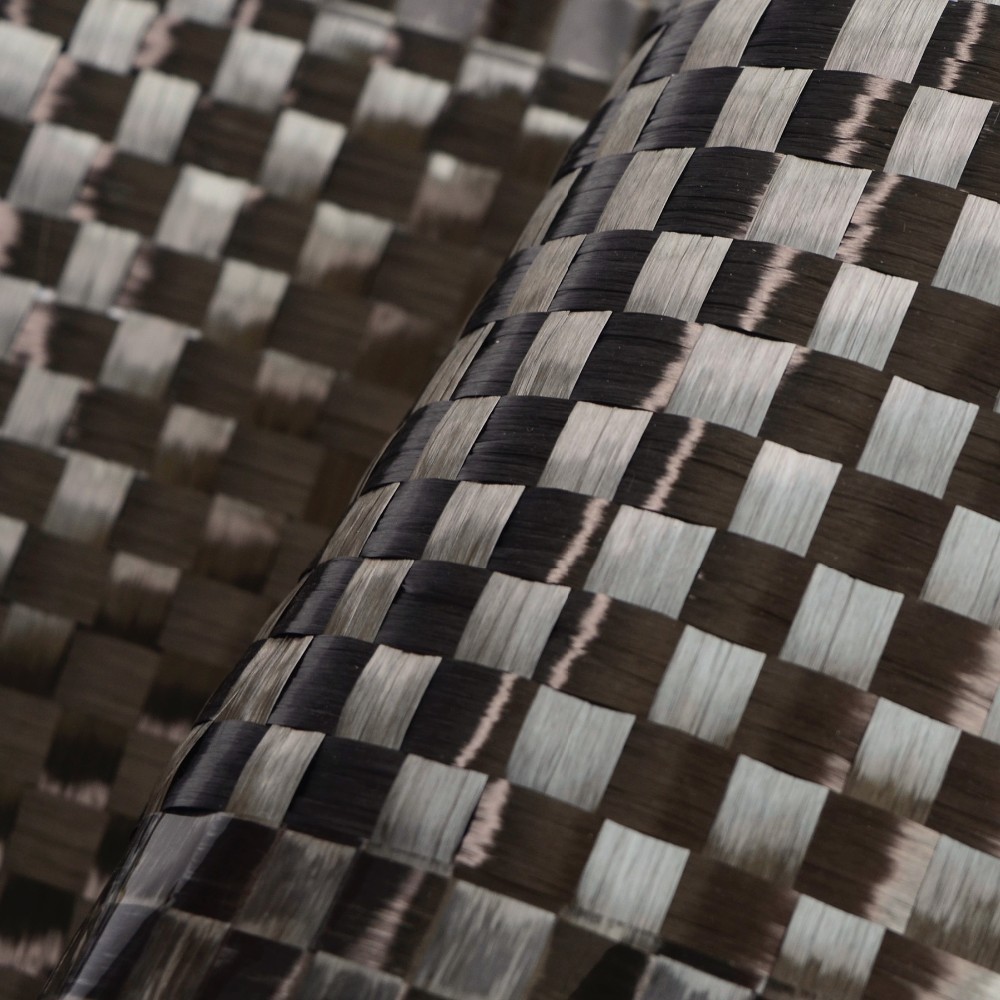
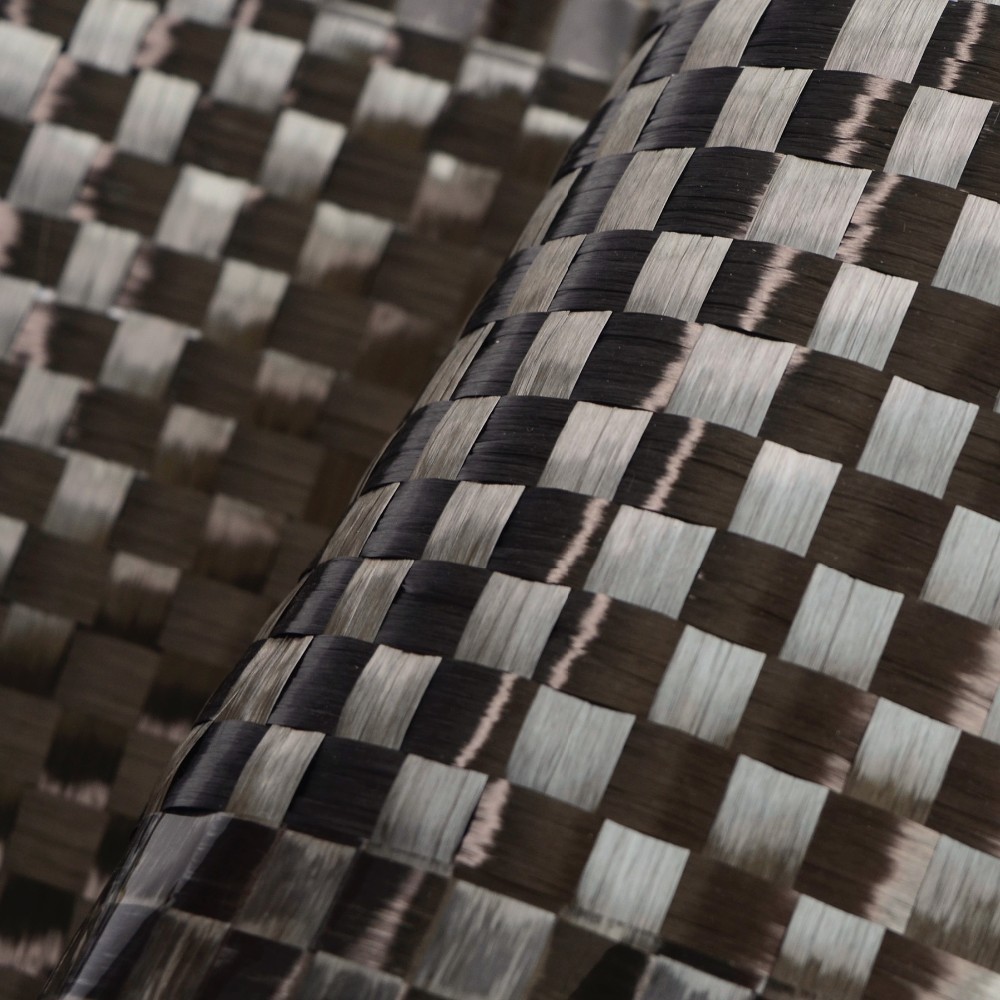
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composite (CFRC), also known as Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP), is a high-performance material widely regarded for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and versatility. Combining the structural properties of carbon fibers with a polymer matrix, CFRC has become indispensable in industries ranging from aerospace and automotive to sports equipment and medical devices.
This article provides an in-depth exploration of what CFRC is, how it’s made, its unique characteristics, and its applications in modern engineering and manufacturing.
What Is Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composite?
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composite is a composite material composed of:
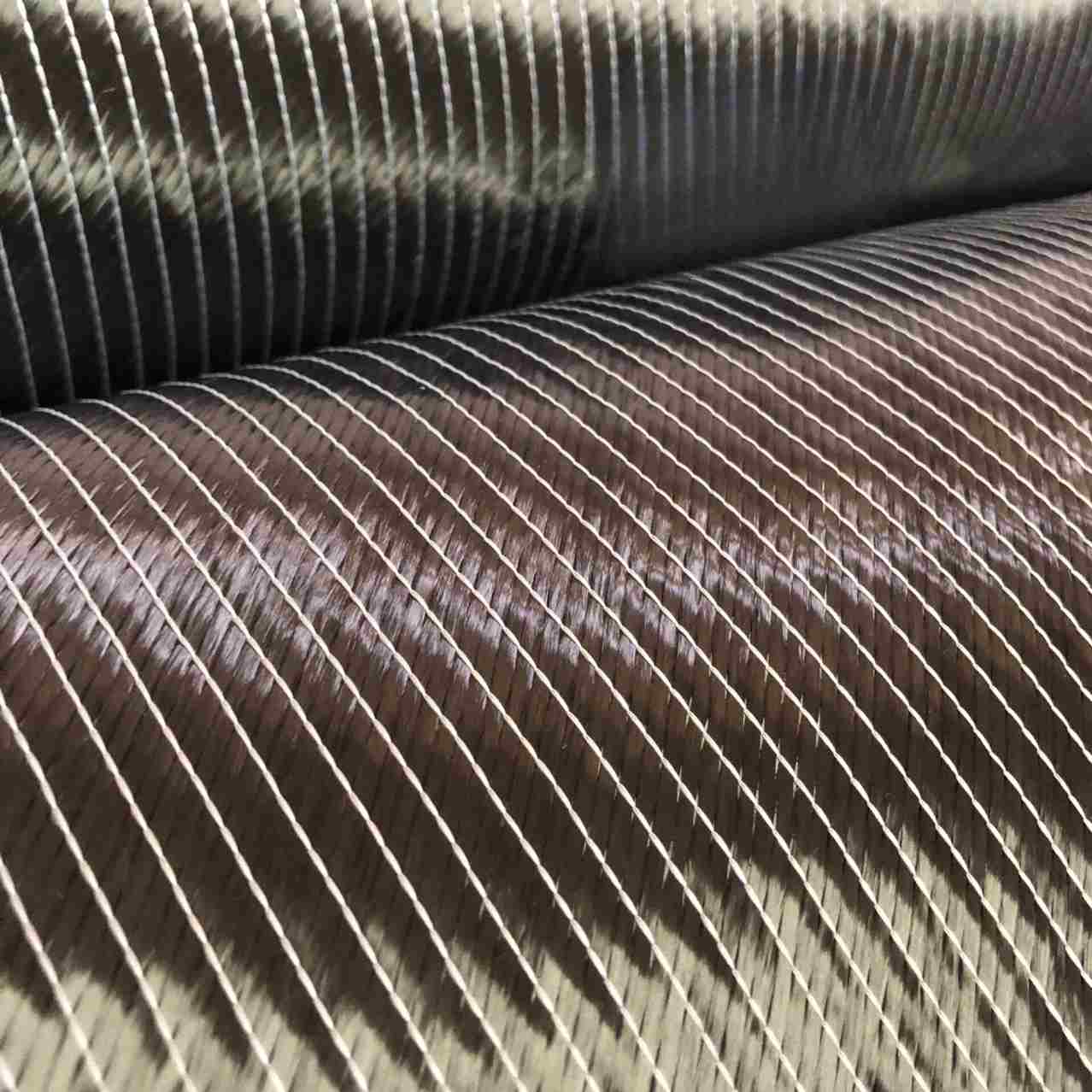
- Carbon Fibers: Thin, strong filaments made predominantly of carbon atoms arranged in a crystalline structure. These fibers provide high tensile strength and stiffness.
- Polymer Matrix: A resin, typically epoxy, polyester, or thermoplastic, that binds the carbon fibers together and transfers loads between them.
The resulting material combines the best properties of its constituents: the lightweight and strength of carbon fibers and the flexibility and durability of polymers.
How Is Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composite Made?
The production process involves several key steps:
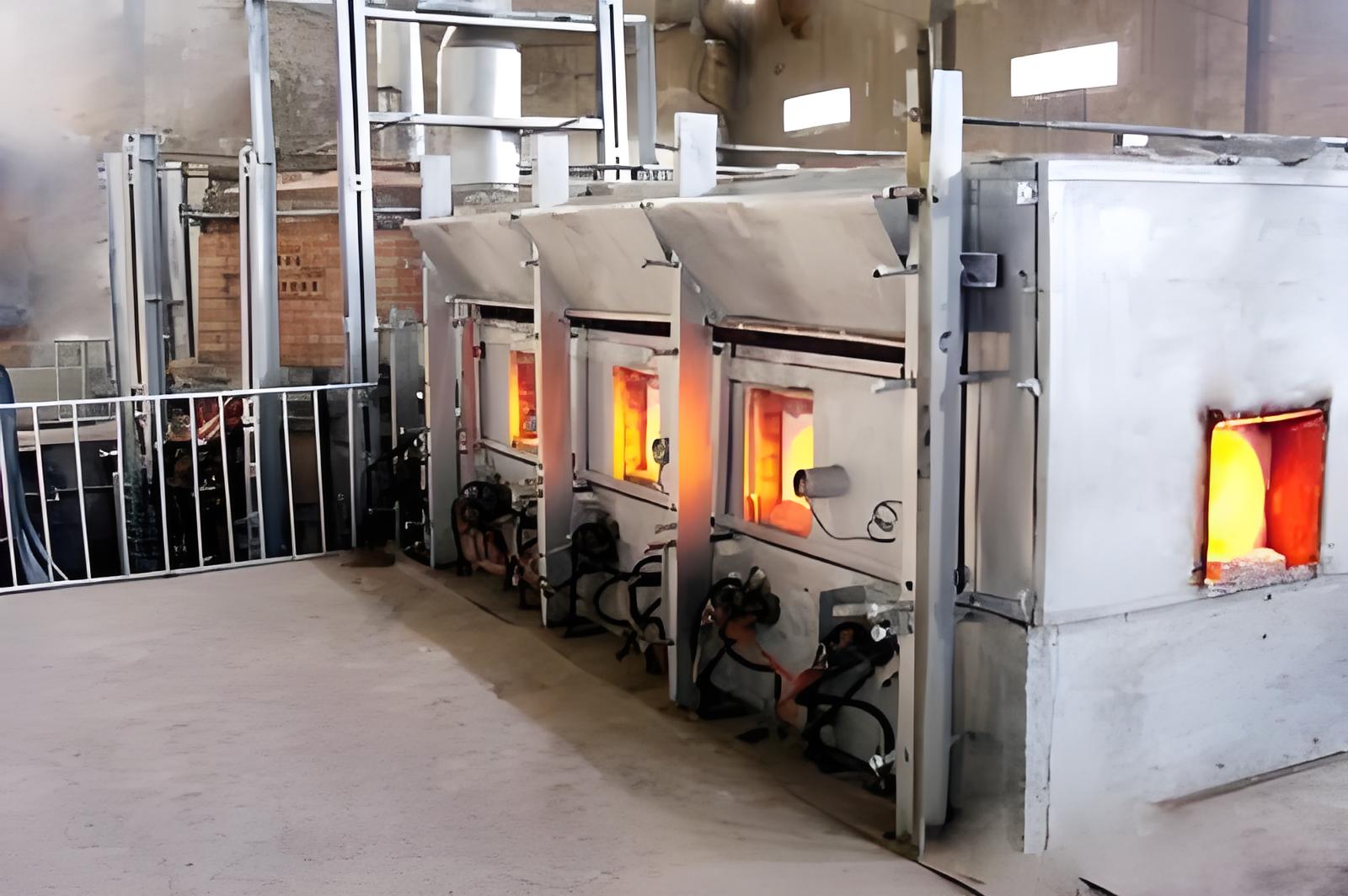
1. Carbon Fiber Production
Carbon fibers are created through a series of chemical and heat treatments:
- Raw material (precursor): Typically polyacrylonitrile (PAN), rayon, or pitch.
- Stabilization: The precursor is heated to stabilize its structure.
- Carbonization: High temperatures (above 1000°C) remove non-carbon elements, leaving behind pure carbon filaments.
- Surface treatment: Fibers are treated to improve bonding with the matrix.
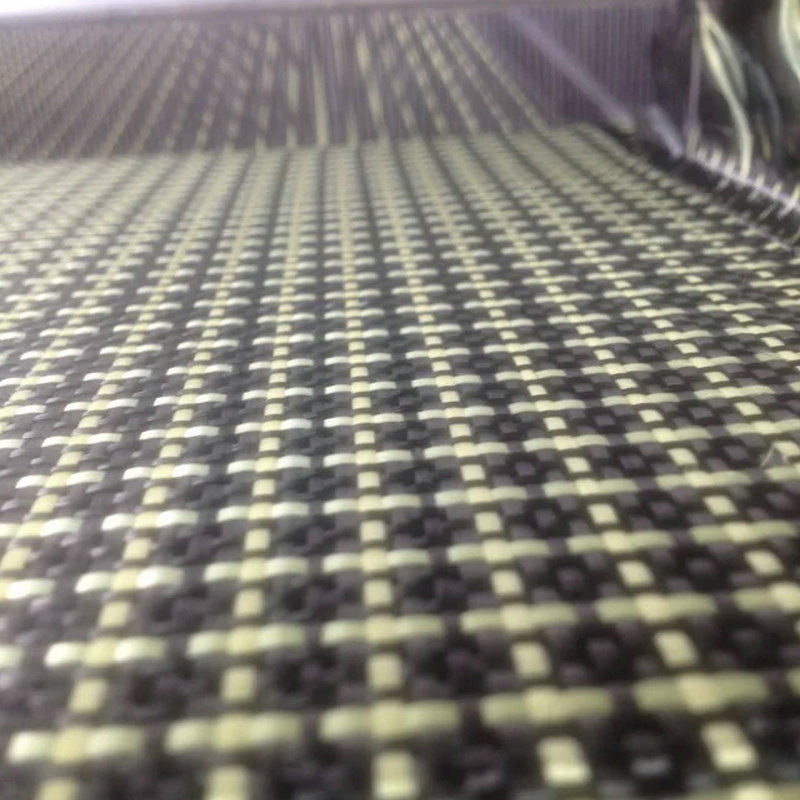
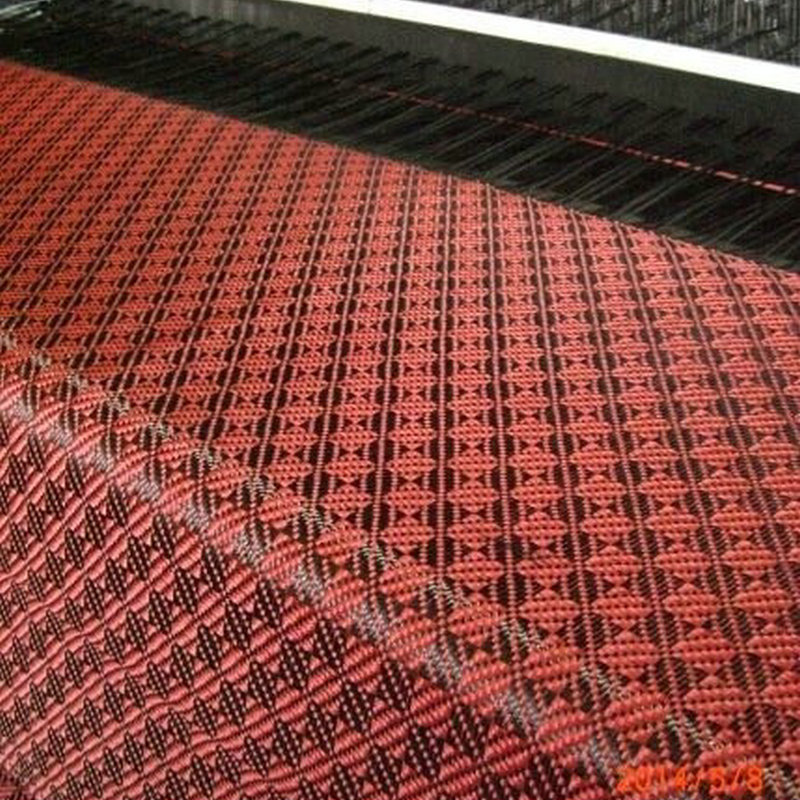
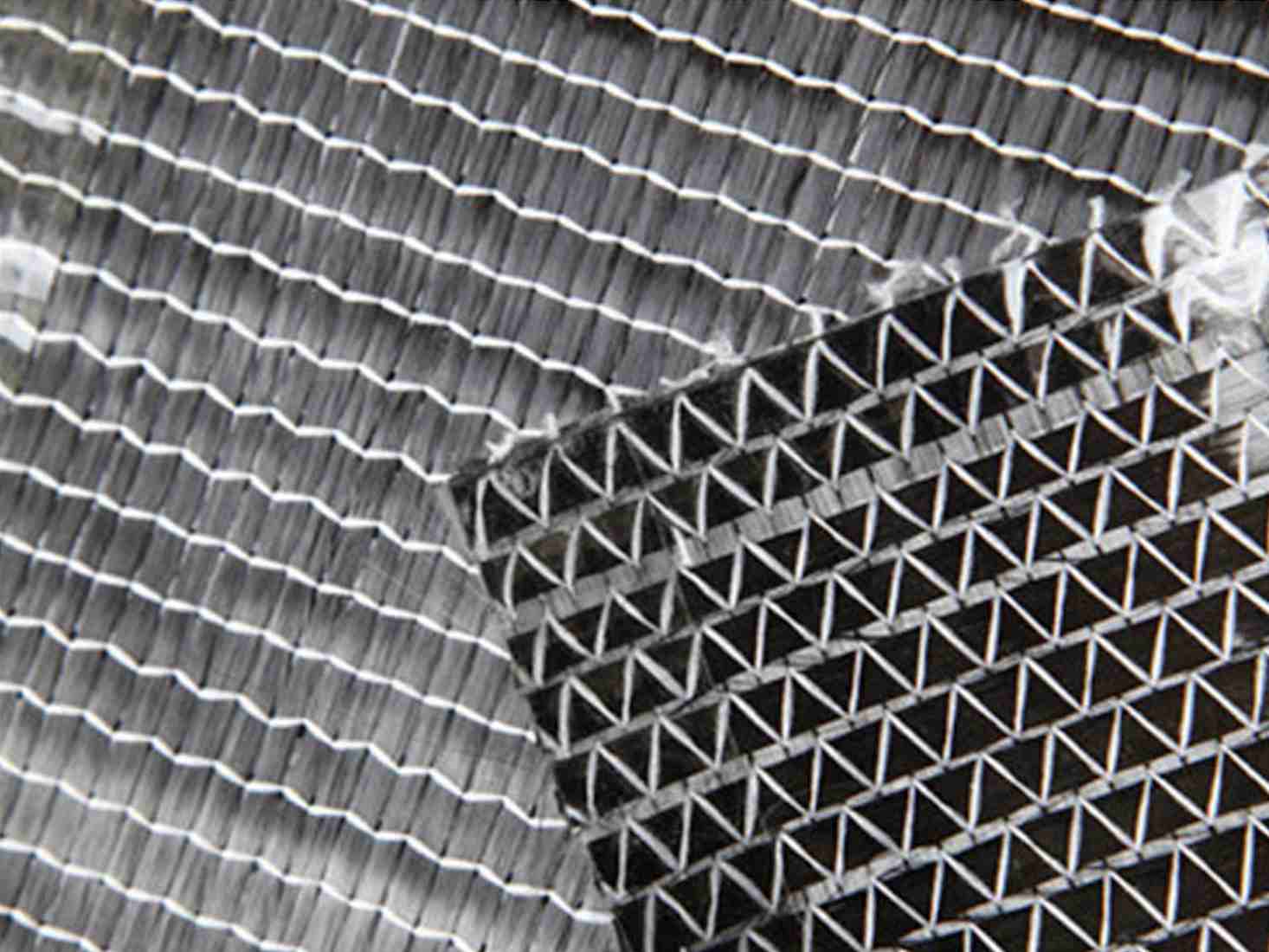
2. Composite Fabrication
Carbon fibers are integrated with a polymer matrix through one of the following methods:
- Hand Lay-Up: Layers of carbon fiber fabric are manually laid into a mold and impregnated with resin.
- Autoclave Curing: The composite is cured under heat and pressure in an autoclave, ensuring optimal strength and finish.
- Filament Winding: Fibers are wound around a mandrel in specific patterns, ideal for cylindrical shapes like pipes or tanks.
- Resin Transfer Molding (RTM): Resin is injected into a mold containing dry fiber preforms.
Key Properties of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composite
1. Strength-to-Weight Ratio
CFRC is significantly lighter than metals like steel and aluminum while offering superior strength and stiffness, making it ideal for weight-sensitive applications.
2. Corrosion Resistance
Unlike metals, CFRC does not rust or degrade when exposed to moisture or chemicals, making it highly durable in harsh environments.
3. Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Carbon fibers are excellent conductors of heat and electricity, making CFRC suitable for electronic components and heat dissipation applications.
4. Design Flexibility
CFRC can be molded into complex shapes, offering unparalleled design freedom for engineers and manufacturers.
5. Fatigue Resistance
CFRC demonstrates exceptional resistance to fatigue, maintaining its performance under repeated loading.
Types of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composites
CFRC can be classified based on the type of polymer matrix used:
1. Thermoset CFRC
- Matrix: Epoxy, polyester, or vinyl ester resins.
- Characteristics: High strength and thermal stability but non-recyclable.
- Applications: Aerospace, automotive, and structural components.
2. Thermoplastic CFRC
- Matrix: Polyetheretherketone (PEEK), polycarbonate (PC), or nylon.
- Characteristics: Recyclable, impact-resistant, and flexible.
- Applications: Consumer goods, medical devices, and lightweight components.
Mainstream Carbon Fibre Products: An Overview
Carbon fibre products have become synonymous with high performance, lightweight construction, and durability. From industrial applications to everyday goods, carbon fiber's unique properties have led to its widespread use across various fields. Below is an overview of the most mainstream carbon fibre products available today.
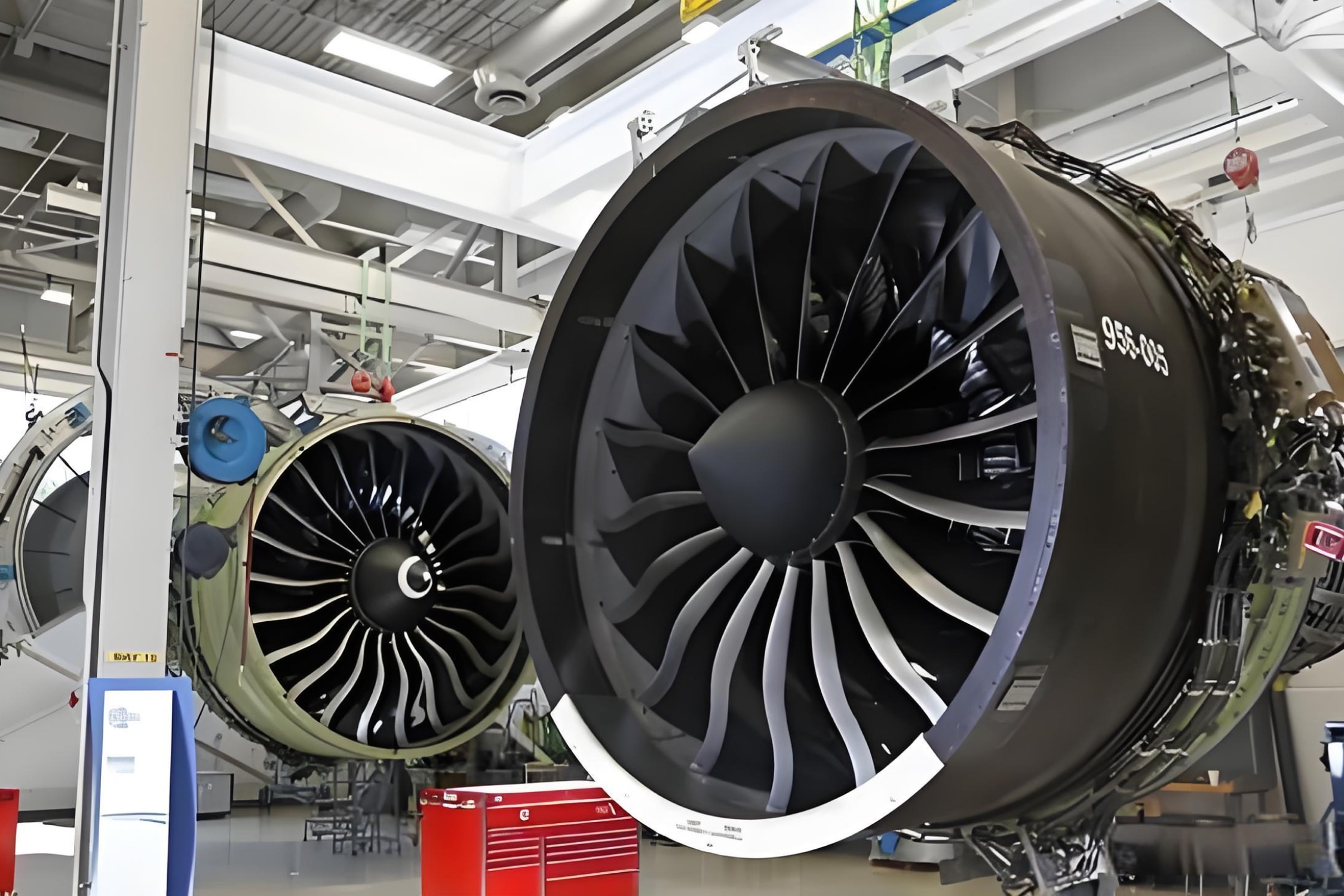
1. Aerospace Components
The aerospace industry has long been a pioneer in using carbon fiber due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to fatigue. Common products include:
- Aircraft fuselages: Lightweight yet strong materials for better fuel efficiency.
- Wing structures: Improved aerodynamic performance with reduced weight.
- Satellite components: Durable, lightweight materials suited for space environments.
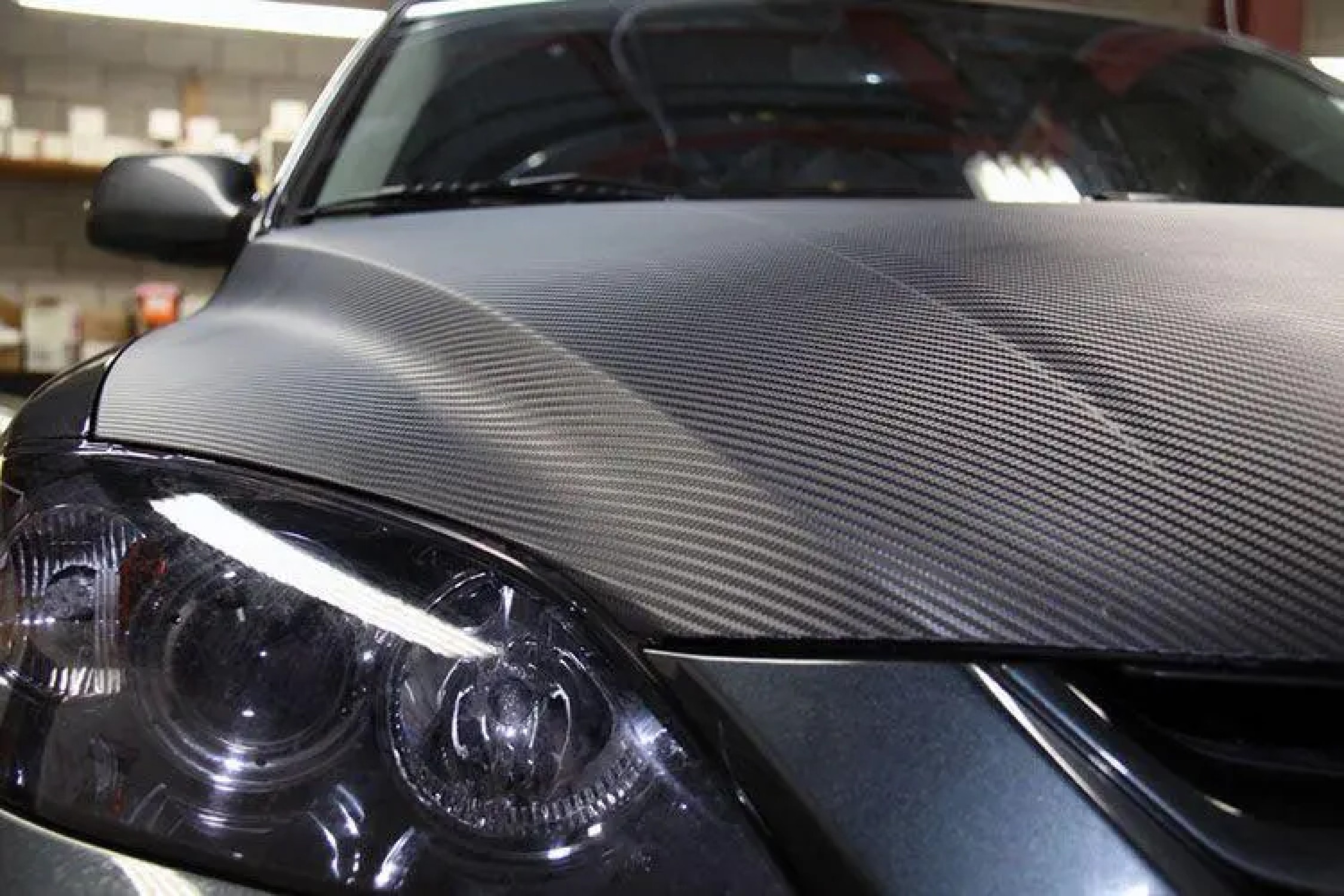
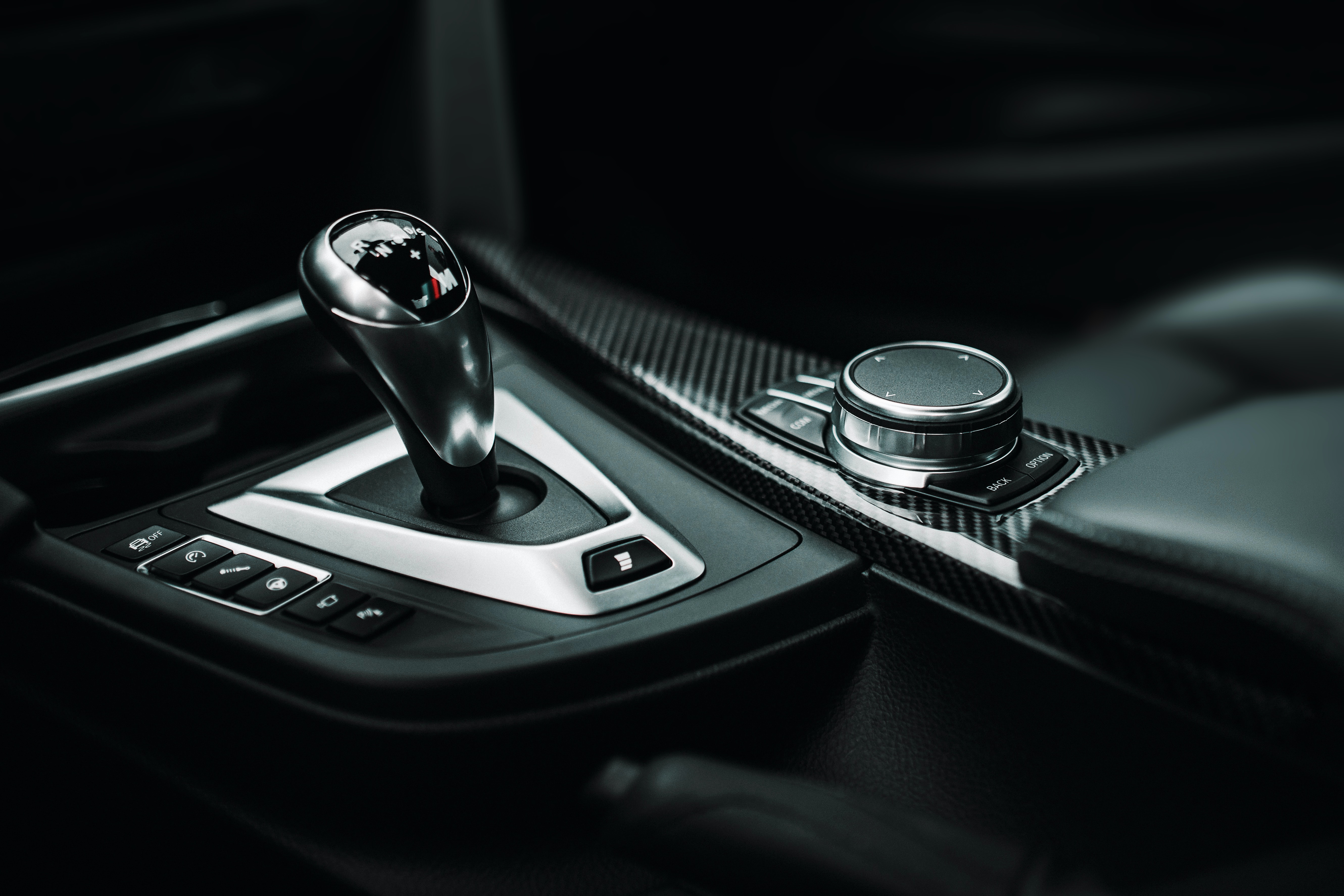
2. Automotive Parts
High-performance and luxury vehicles extensively utilize carbon fiber for:
- Chassis and frames: Enhancing structural rigidity while reducing overall weight.
- Body panels: Including hoods, doors, and roofs for better speed and fuel economy.
- Interior trims: Sleek, lightweight finishes for a premium aesthetic.
- Wheels and spoilers: Increased durability and improved handling.
3. Sports Equipment
Carbon fiber is a game-changer in the sports industry, offering unmatched performance and durability. Popular items include:
- Bicycles: Lightweight carbon fiber frames and wheels for competitive cycling.
- Tennis rackets: Enhanced stiffness and power delivery.
- Golf clubs: Strong yet lightweight shafts for better swing control.
- Fishing rods: Durable, flexible rods for precision casting.
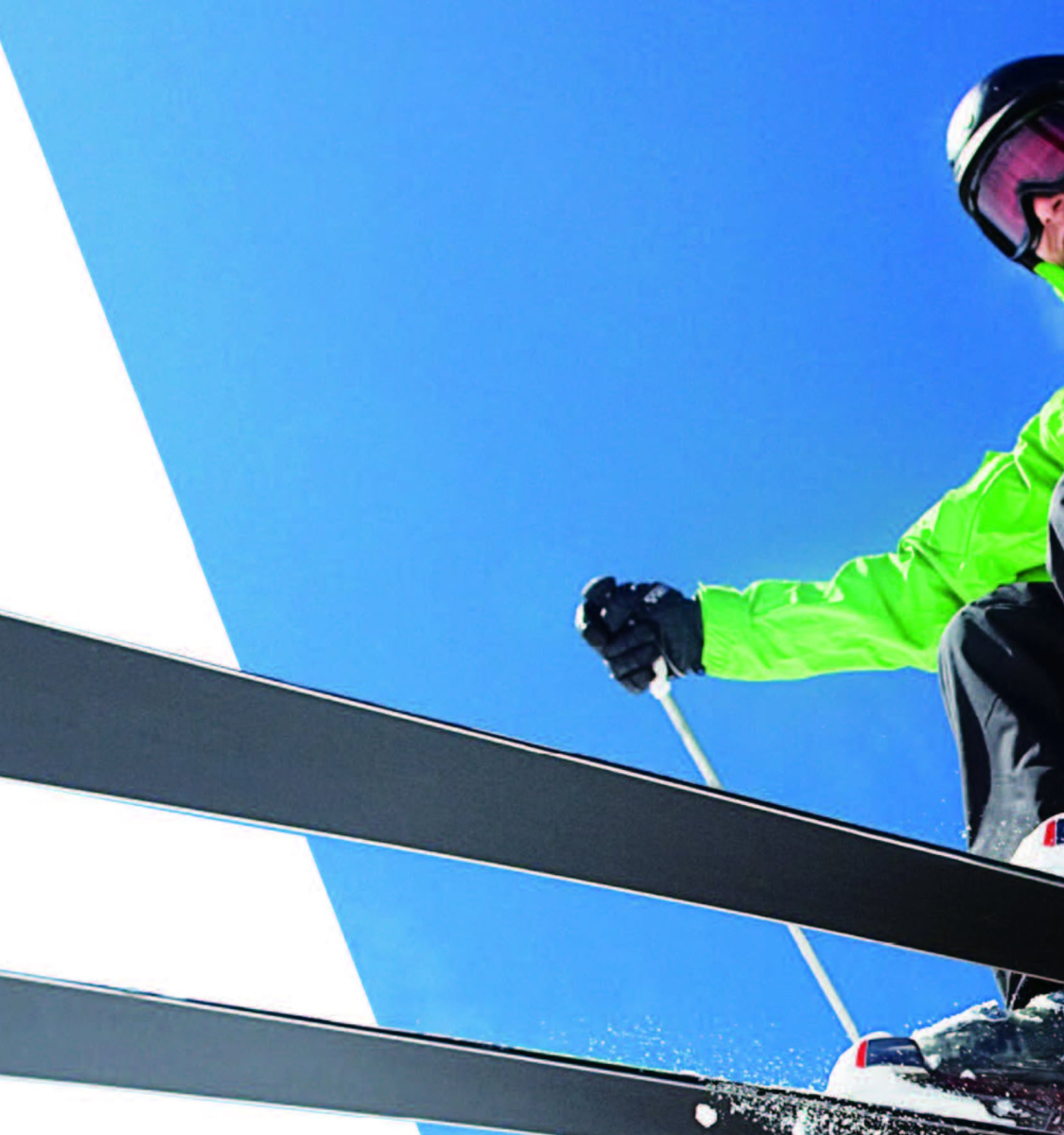
- Skis and snowboards: Improved maneuverability and strength.
4. Renewable Energy Solutions
In the renewable energy sector, carbon fiber plays a key role in:
- Wind turbine blades: Long, lightweight blades for increased efficiency.
- Hydrogen storage tanks: High-strength, lightweight tanks for storing compressed gas.
5. Medical Devices
Carbon fiber is favored in the medical field for its biocompatibility and strength. Common applications include:
- Prosthetics: Lightweight yet robust artificial limbs for better mobility.
- Orthopedic supports: Durable and lightweight braces and splints.
- Imaging tables: X-ray and MRI-compatible tables due to carbon fiber’s radiolucency.
6. Consumer Electronics
Carbon fiber's sleek appearance and durability make it ideal for consumer gadgets such as:
- Smartphone cases: Lightweight and highly protective.
- Laptop shells: Durable, thin, and lightweight materials.
- Drone frames: Strong yet light frames for improved flight dynamics.
7. Marine Products
Marine environments demand materials that resist corrosion and endure harsh conditions. Carbon fiber is used in:
- Yacht hulls: Lightweight and durable for speed and efficiency.
- Boat masts and rigging: Superior strength and resistance to wear.
8. Industrial Applications
Carbon fiber products are integral to many industrial processes, including:
- Pressure vessels: High-strength containers for industrial gases.
- Robot arms: Lightweight structures for improved precision and speed.
- 3D printing filaments: Carbon fiber-reinforced materials for additive manufacturing.
9. Fashion and Lifestyle Products
Carbon fiber's modern, sleek appearance has made its way into fashion and everyday items, such as:
- Watches: Durable and lightweight cases and bands.
- Wallets and cardholders: Slim, robust, and stylish designs.
- Eyewear: Lightweight and strong frames for glasses and sunglasses.
10. Construction and Infrastructure
In construction, carbon fiber products enhance durability and reduce maintenance costs:
- Reinforcement materials: Carbon fiber-reinforced concrete for bridges and buildings.
- Cables: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant cables for suspension bridges.
Advantages of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composite
- Exceptional Strength: CFRC can bear heavy loads without deforming.
- Reduced Weight: Ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial.
- Longevity: Resistant to environmental degradation.
- Customizability: Tailorable properties to meet specific application needs.
Challenges and Limitations
- High Cost: The production of carbon fibers and composites is expensive, limiting its use in cost-sensitive industries.
- Brittleness: While strong, CFRC can be brittle and susceptible to impact damage.
- Recycling Difficulty: Thermoset CFRCs are challenging to recycle due to their irreversible curing process.
Conclusion: The versatility of carbon fiber makes it a cornerstone material for modern engineering, design, and lifestyle products. Its lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant properties continue to drive innovation, making carbon fiber products indispensable across industries.
Future of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composite
Advancements in technology are driving down costs and improving the sustainability of CFRCs. Innovations in recycling methods, alternative precursors (e.g., bio-based materials), and 3D printing are expected to expand its applications further. The growing demand for lightweight, durable, and eco-friendly materials positions CFRC as a cornerstone of future engineering solutions.
Conclusion
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composite is a revolutionary material that combines lightweight construction, exceptional strength, and versatility. Its widespread use in aerospace, automotive, sports, and other industries highlights its transformative potential. As technology evolves, CFRC is set to become even more integral to advancing sustainable and high-performance solutions across multiple domains.
Popular Composite Materials
Popular Composite Materials
Composites Knowledge Hub
Composites Knowledge Hub