+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Let the world benefit from composite materials!
Aerospace composites
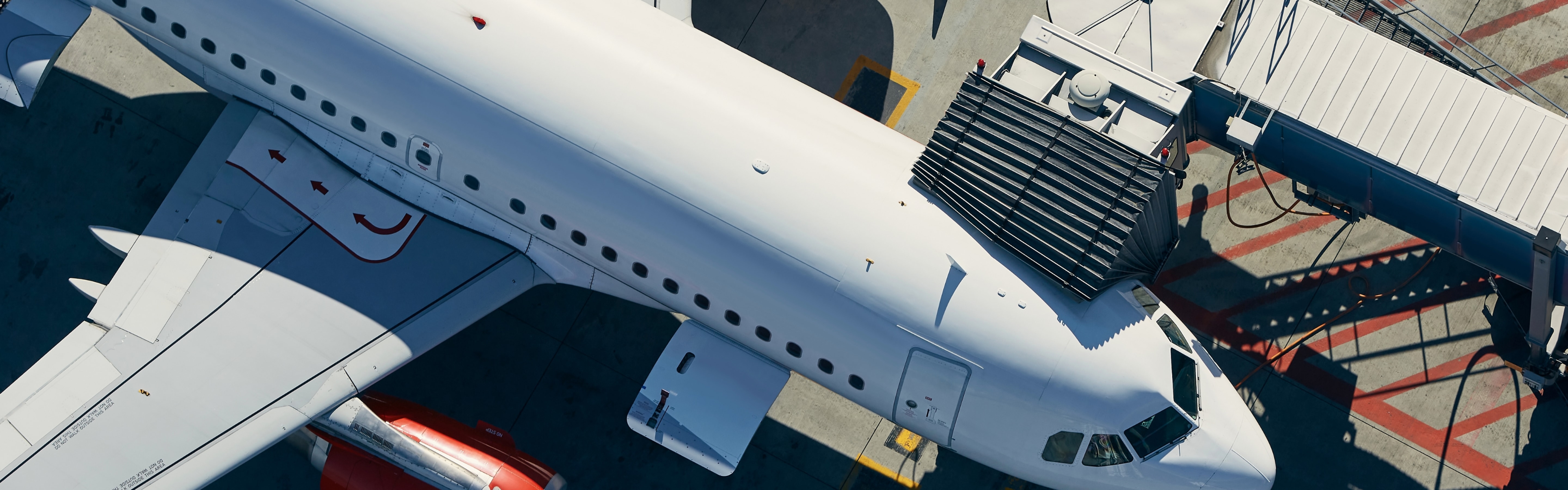

Aerospace composites
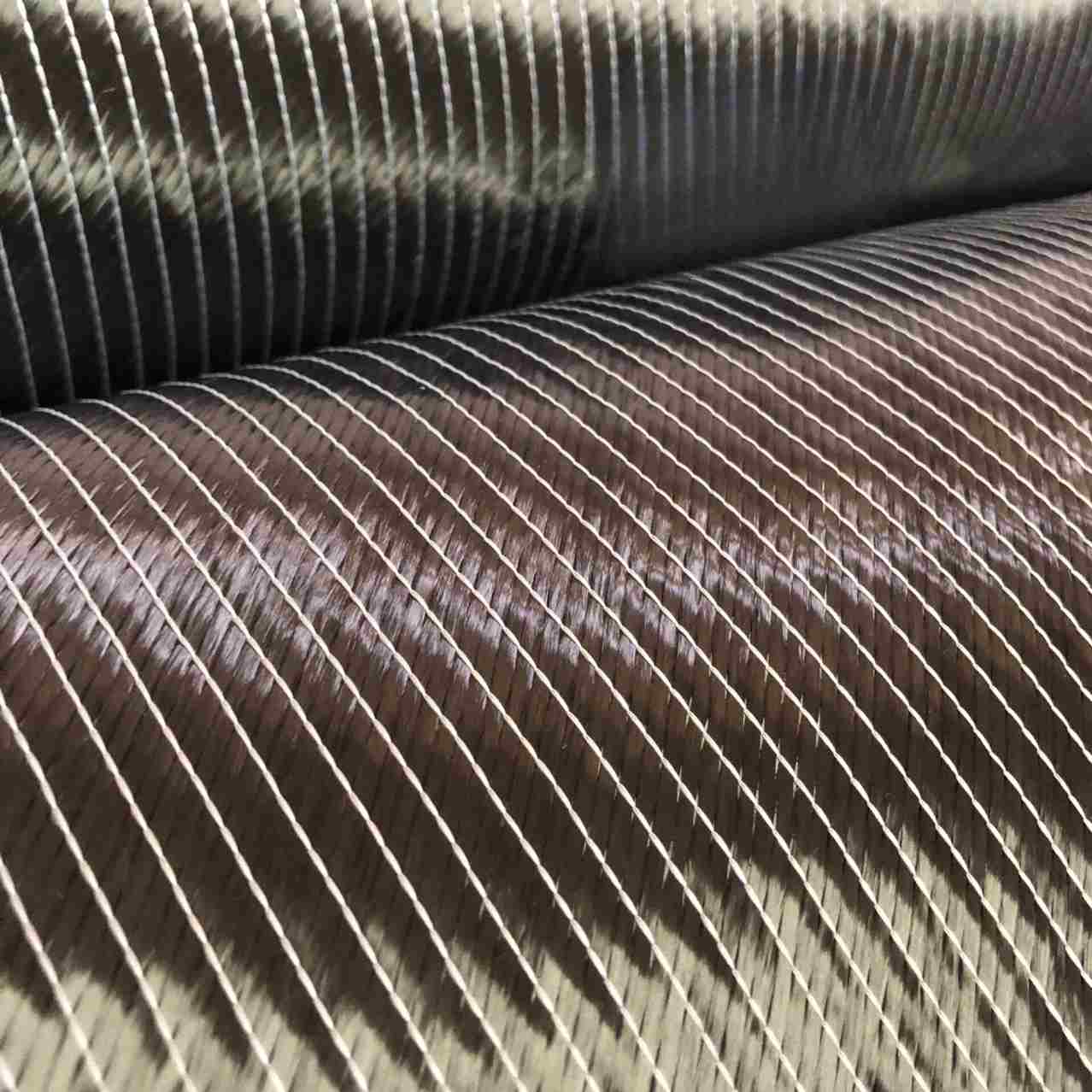
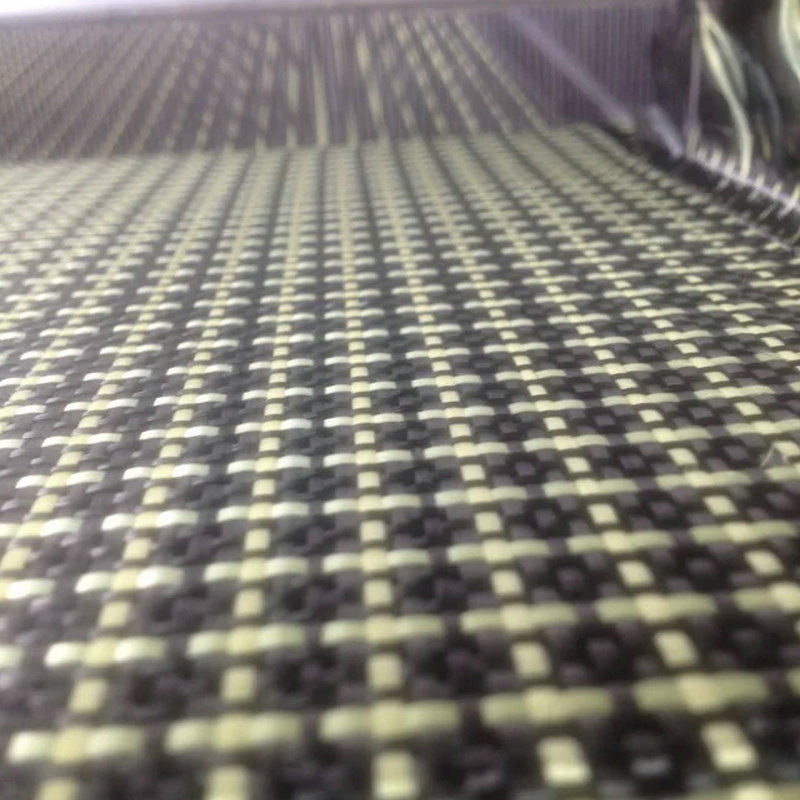
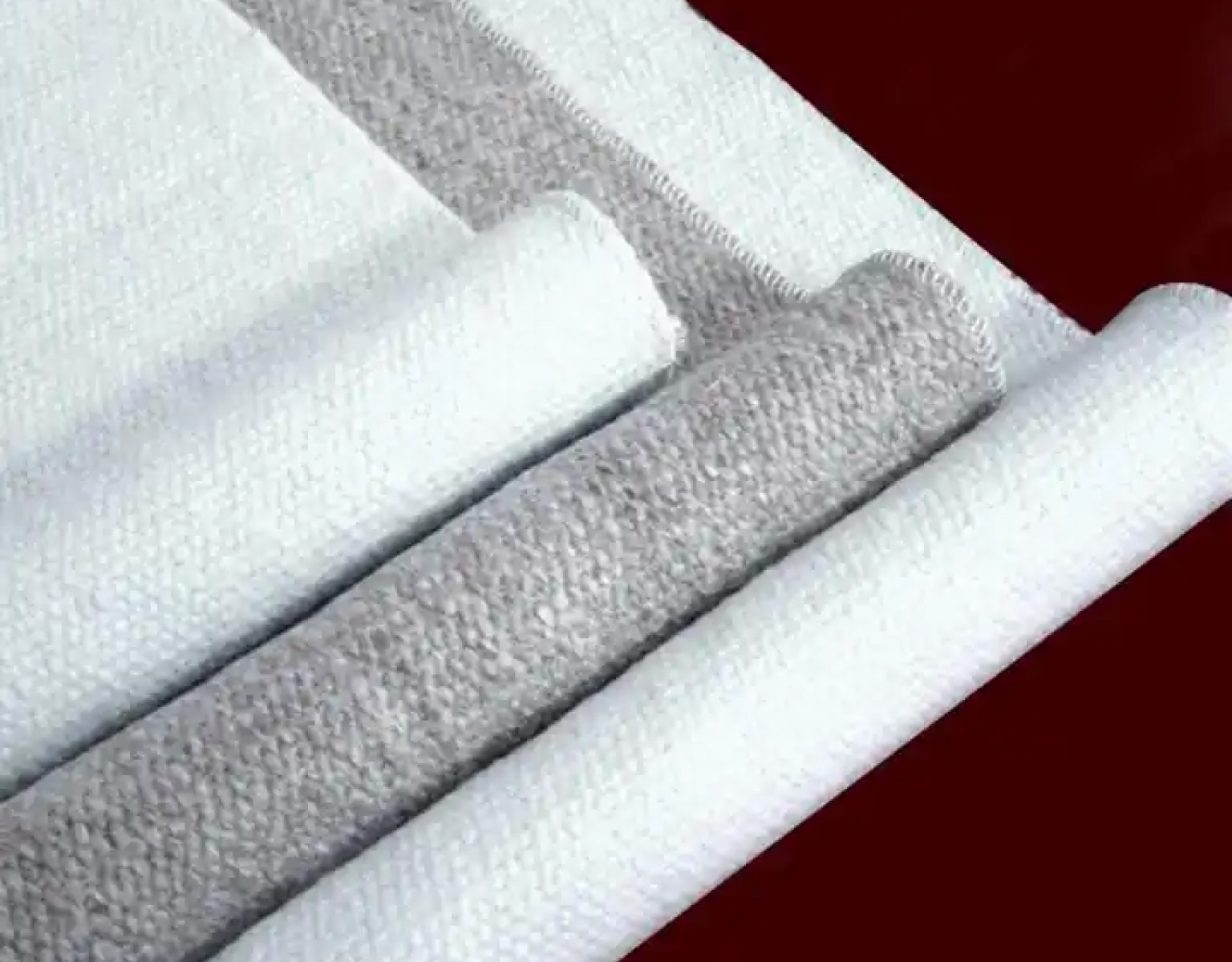
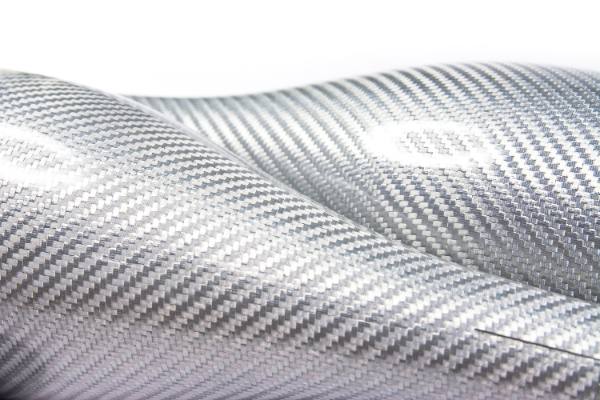
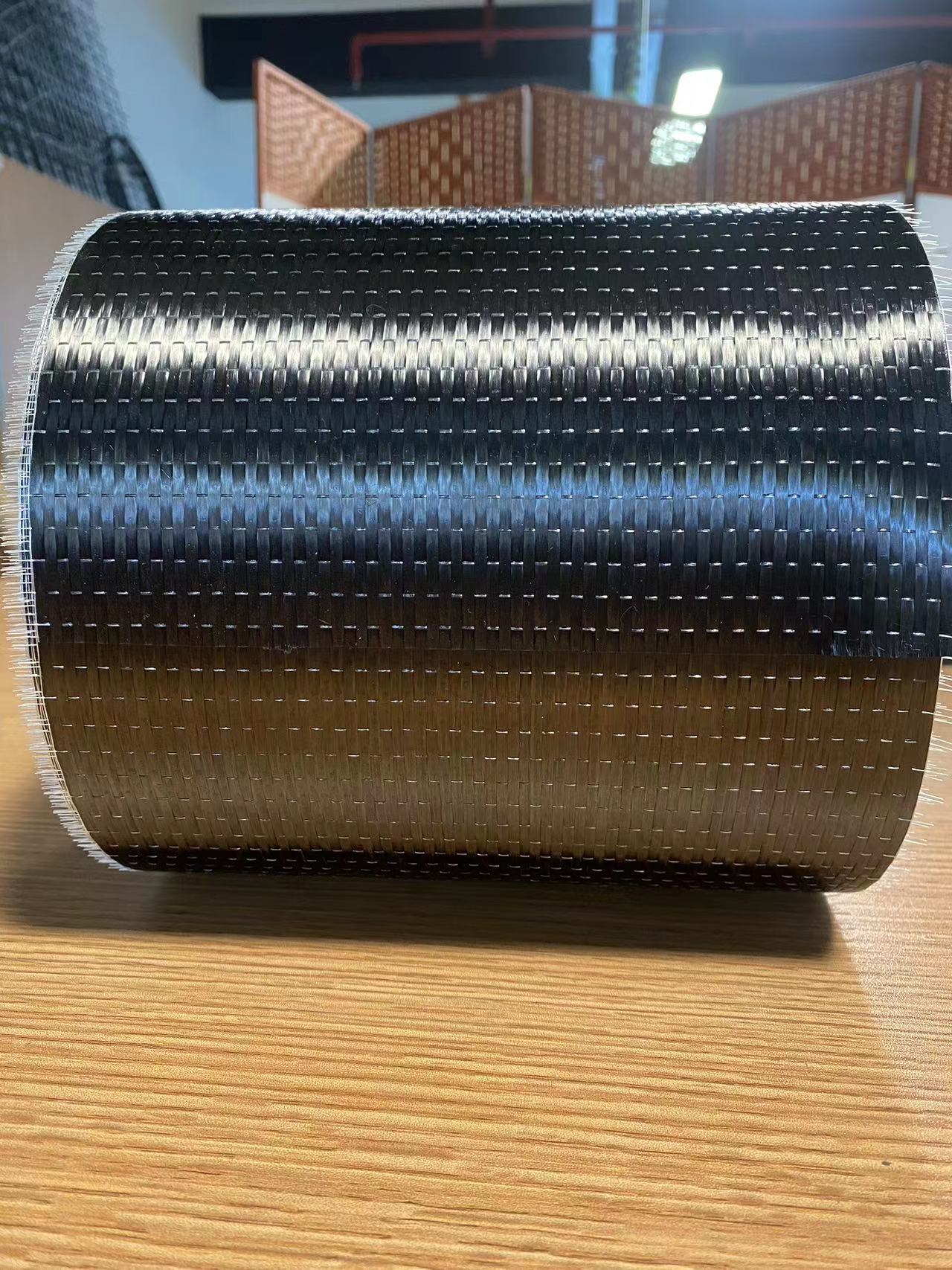
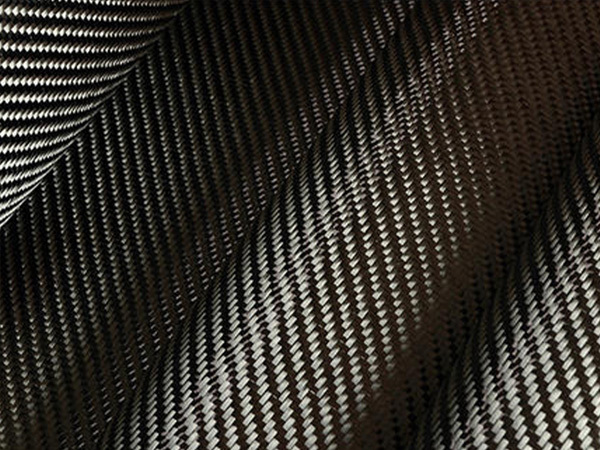
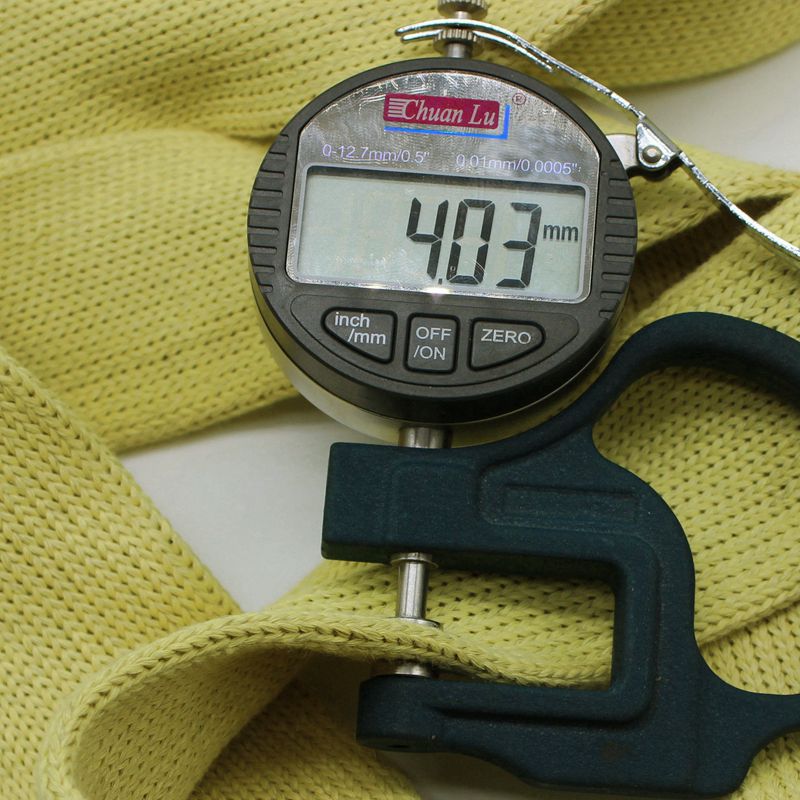
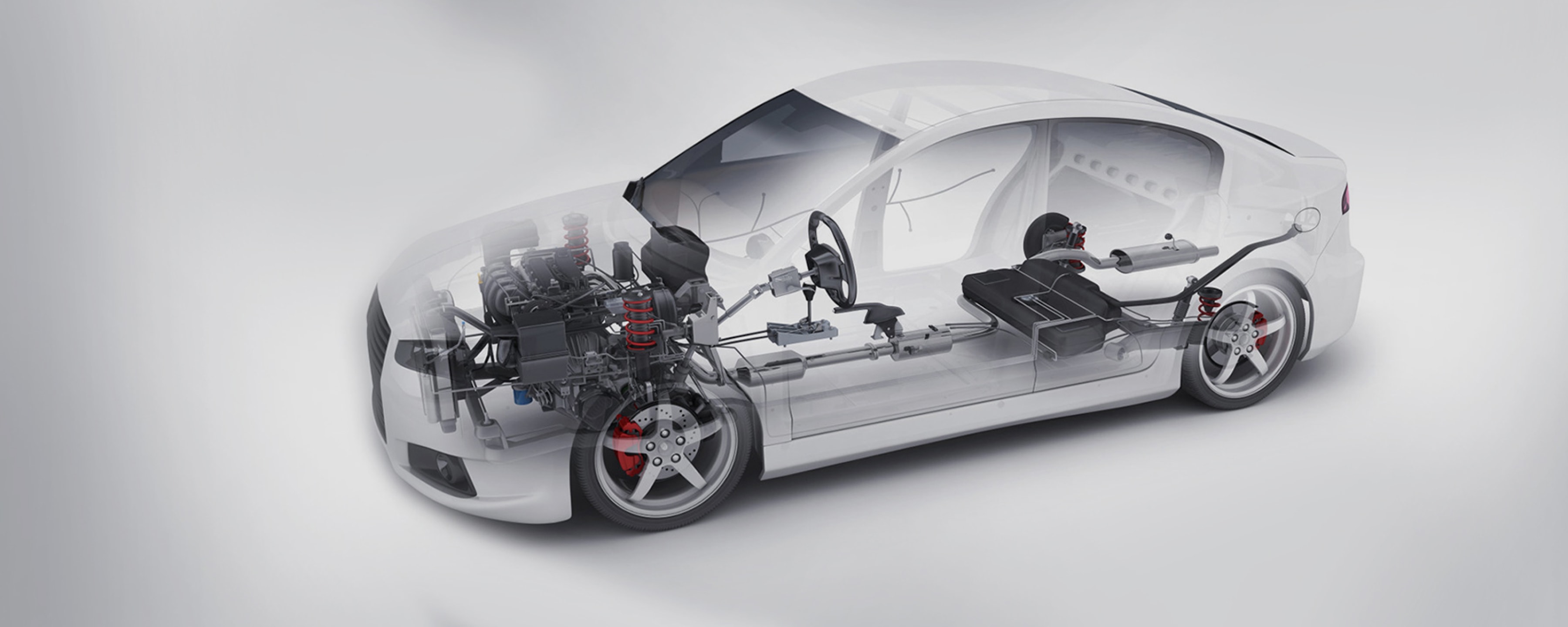
Carbon fiber aerospace materials are essential in aircraft composite materials, offering high strength, lightweight properties, and durability. They improve fuel efficiency and structural performance, making them ideal for modern aerospace applications.
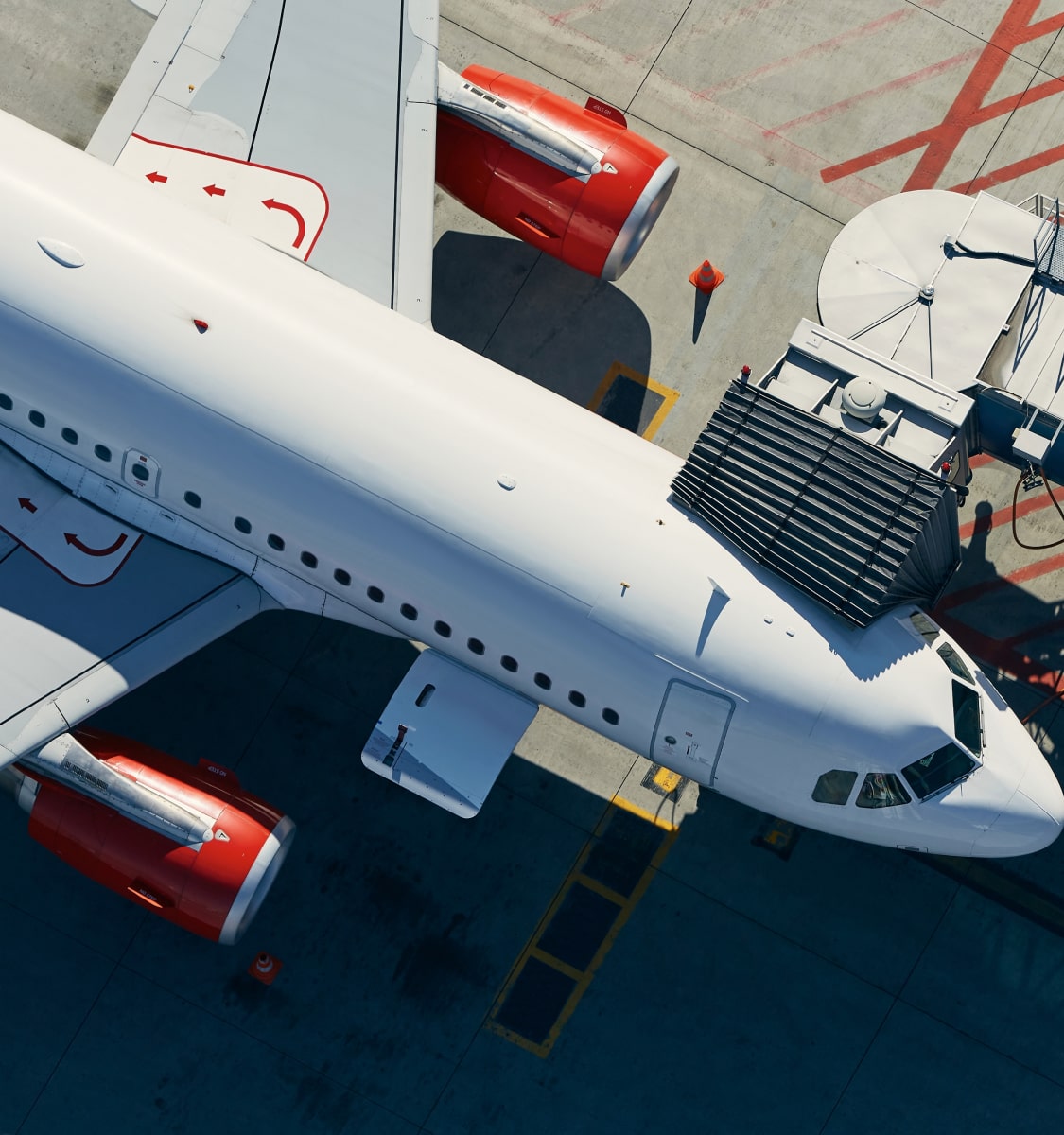

Aerospace composites
Carbon fiber aerospace materials are essential in aircraft composite materials, offering high strength, lightweight properties, and durability. They improve fuel efficiency and structural performance, making them ideal for modern aerospace applications.
Aerospace
Aerospace
The application and research of composite materials in the field of aerospace have revolutionized the pace of development within this domain. Despite having a history of just over 20 years, they exhibit tremendous advantages over traditional metallic materials.
The application and research of composite materials in the field of aerospace have revolutionized the pace of development within this domain. Despite having a history of just over 20 years, they exhibit tremendous advantages over traditional metallic materials.
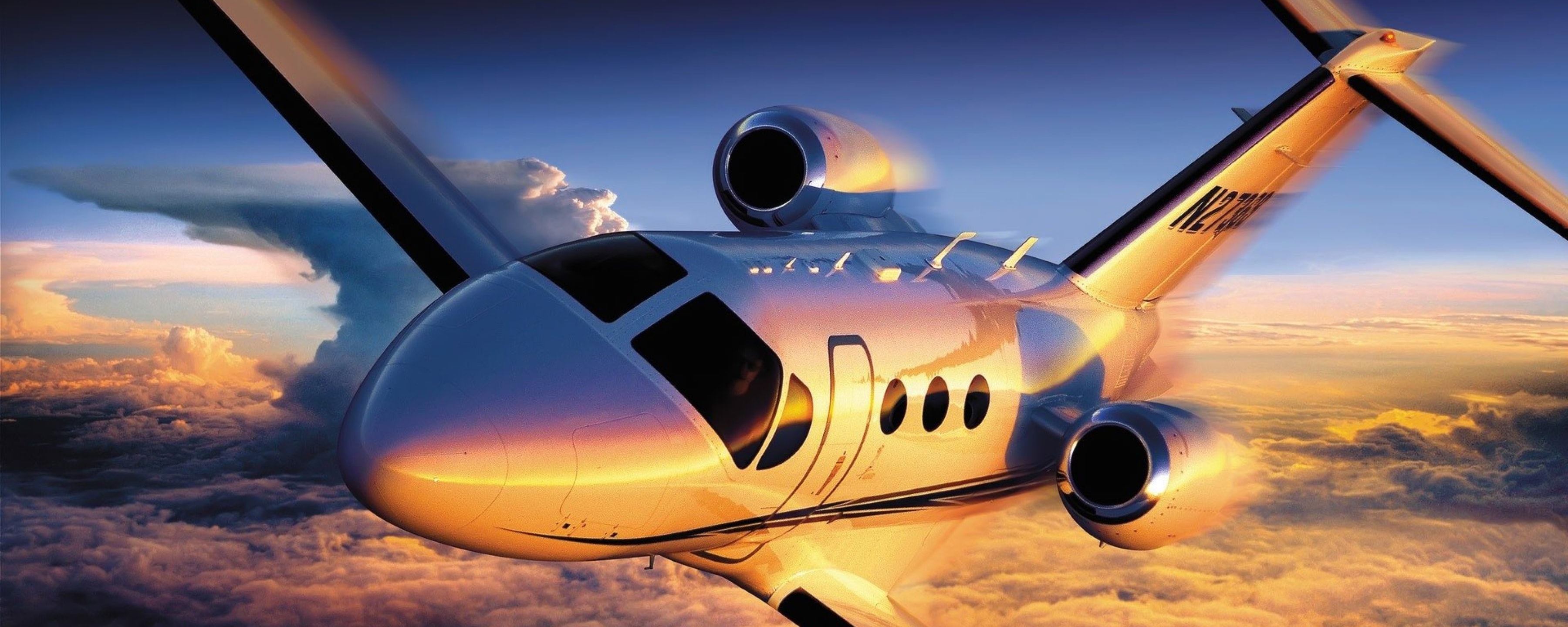


In the realm of civil aviation, globally renowned civil aircraft manufacturers such as Boeing and Airbus have made significant strides in the utilization of composite materials. In Boeing's production of the B777 passenger aircraft, composites account for 9% of the total aircraft structure weight, while in the B787 aircraft, carbon fiber-reinforced composites and glass fiber-reinforced materials constitute 50% of the total aircraft structure weight, leading to substantial fuel savings. Furthermore, Airbus's A350XWB aircraft incorporates carbon fiber-reinforced composites in components like fuselage panels, frames, window frames, and cabin doors, significantly extending the aircraft's maintenance interval from 6 to 12 years, thereby greatly reducing maintenance costs for customers.
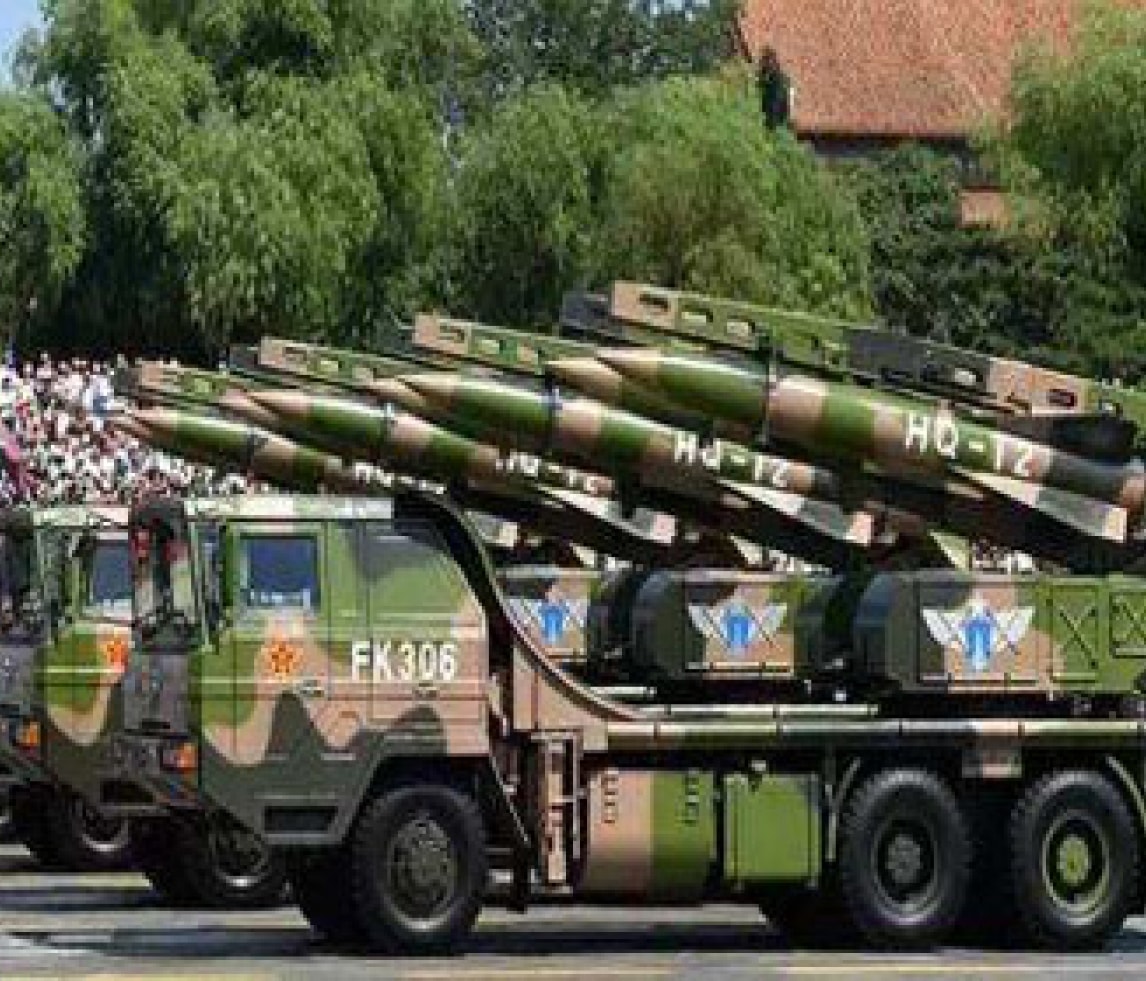
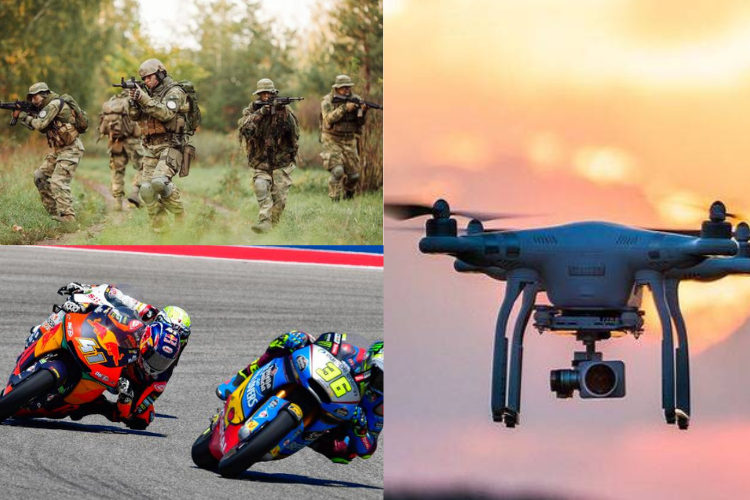
In the military aviation sector, since the mid-1970s, composite materials have gradually been employed in components such as vertical stabilizers and horizontal tail surfaces of military aircraft such as the F-15, F-16, MiG-29, Mirage 2000, F/A-18, among others. Subsequently, composite materials have been utilized in critical load-bearing components of military aircraft such as wings and fuselages in aircraft like AV-8B, B-2, F/A-22, F/A-18E/F, F-35, Rafale, JAS-39, Typhoon, S-37, reducing aircraft weight and significantly enhancing operational capabilities.
In the domain of unmanned aerial vehicles, the unique advantages of drones in modern warfare have fueled a rapid increase in demand. The wings, tail sections, engine nacelles, and rear fuselage of the advanced RQ-4 Global Hawk reconnaissance drone from the United States are all constructed from composite materials. Additionally, China's DJI MavicPro drone extensively incorporates composite materials in its airframe.
In the realm of civil aviation, globally renowned civil aircraft manufacturers such as Boeing and Airbus have made significant strides in the utilization of composite materials. In Boeing's production of the B777 passenger aircraft, composites account for 9% of the total aircraft structure weight, while in the B787 aircraft, carbon fiber-reinforced composites and glass fiber-reinforced materials constitute 50% of the total aircraft structure weight, leading to substantial fuel savings. Furthermore, Airbus's A350XWB aircraft incorporates carbon fiber-reinforced composites in components like fuselage panels, frames, window frames, and cabin doors, significantly extending the aircraft's maintenance interval from 6 to 12 years, thereby greatly reducing maintenance costs for customers.
In the military aviation sector, since the mid-1970s, composite materials have gradually been employed in components such as vertical stabilizers and horizontal tail surfaces of military aircraft such as the F-15, F-16, MiG-29, Mirage 2000, F/A-18, among others. Subsequently, composite materials have been utilized in critical load-bearing components of military aircraft such as wings and fuselages in aircraft like AV-8B, B-2, F/A-22, F/A-18E/F, F-35, Rafale, JAS-39, Typhoon, S-37, reducing aircraft weight and significantly enhancing operational capabilities.
In the domain of unmanned aerial vehicles, the unique advantages of drones in modern warfare have fueled a rapid increase in demand. The wings, tail sections, engine nacelles, and rear fuselage of the advanced RQ-4 Global Hawk reconnaissance drone from the United States are all constructed from composite materials. Additionally, China's DJI MavicPro drone extensively incorporates composite materials in its airframe.
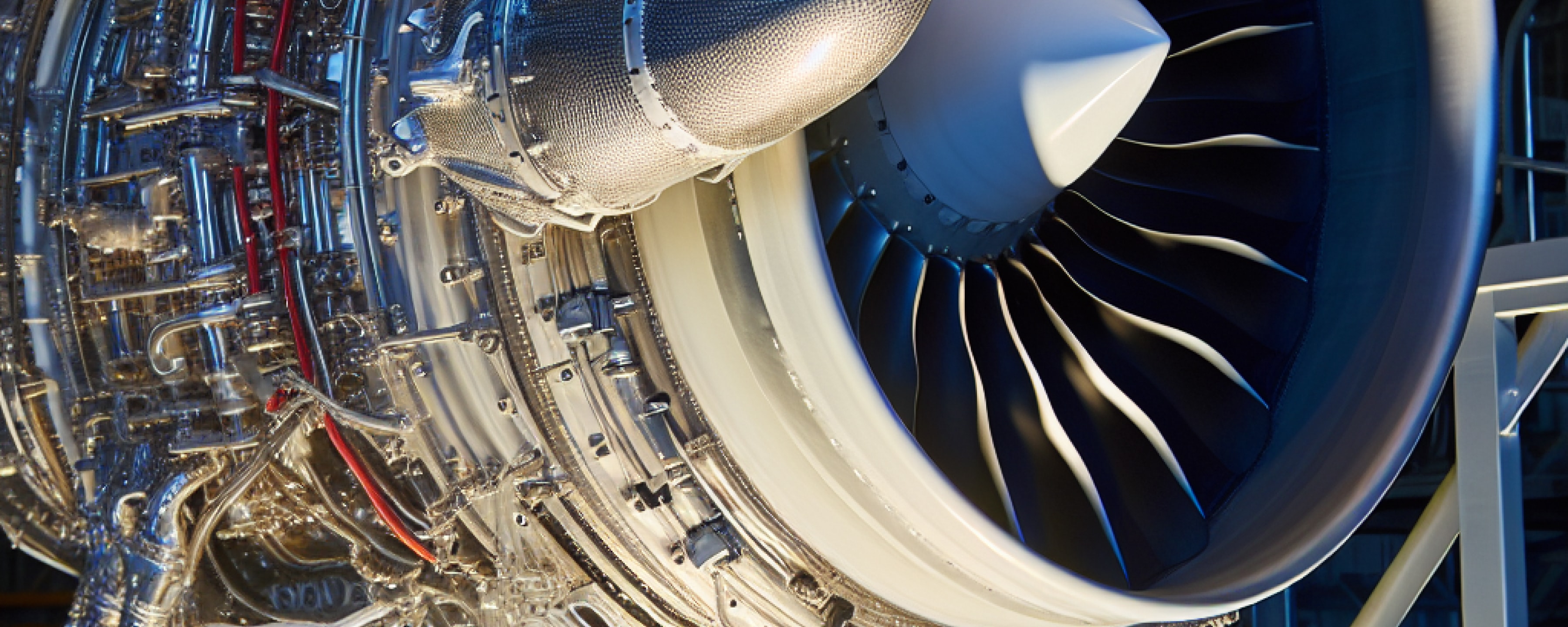


Helicopters, unlike traditional fixed-wing aircraft, operate at slower speeds, lower altitudes, and are exposed to harsh conditions like humidity, aridity, and sandstorms, demanding greater weather resistance and corrosion resistance from their structures. Moreover, the rotor blades of helicopters require materials with high fatigue resistance. Hence, due to their excellent fatigue resistance, vibration damping properties, and corrosion resistance, composite materials are well-suited for structural designs in helicopters.
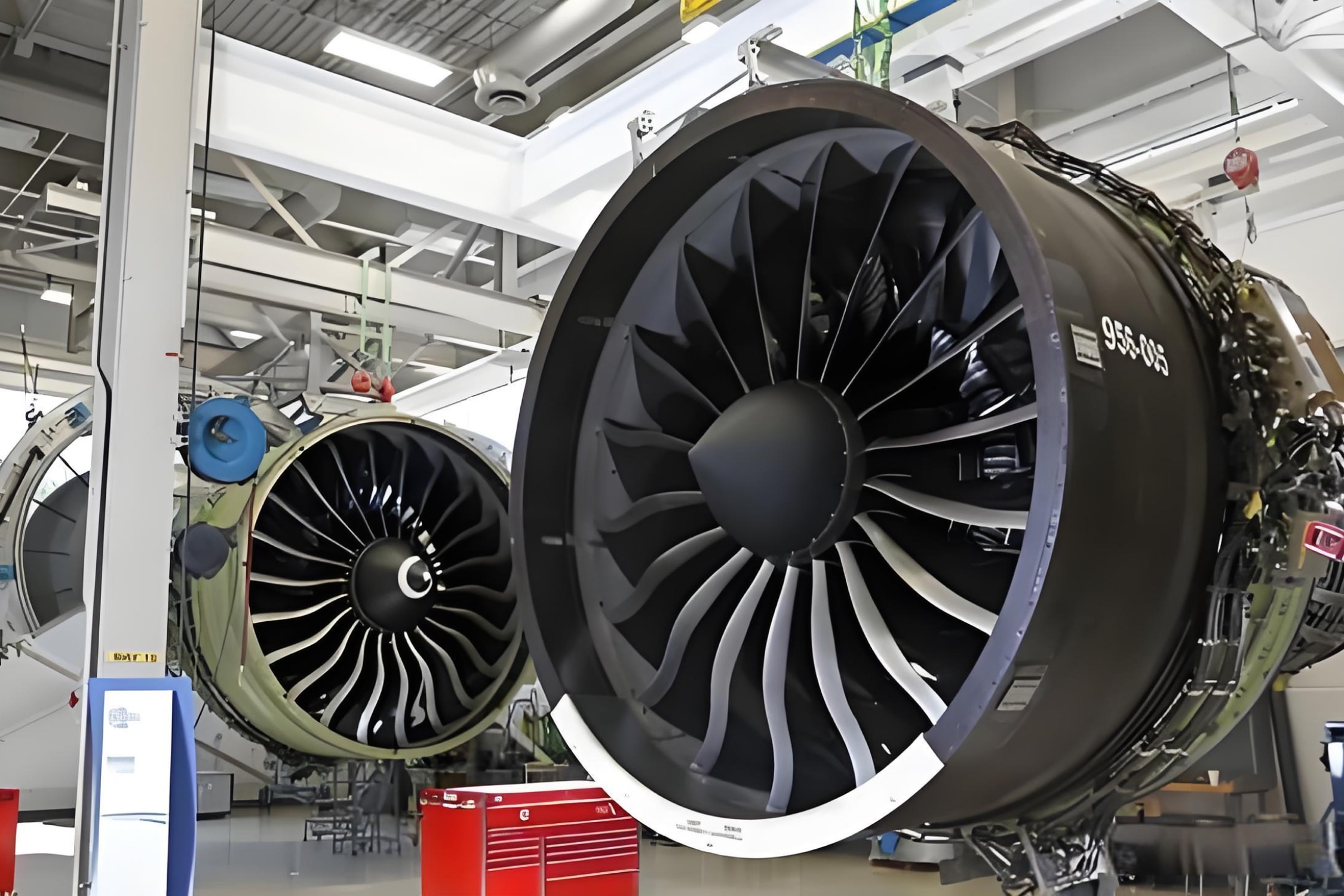
Within the realm of aerospace engines, known for their technical complexity and lengthy development cycles, they are hailed as the crown jewel of the industry. Goals pursued in the design of civil aviation engines include high thrust-to-weight ratios, low fuel consumption, reduced noise, and minimal emissions. To achieve these objectives, composite materials have found widespread application in civil aviation engines.
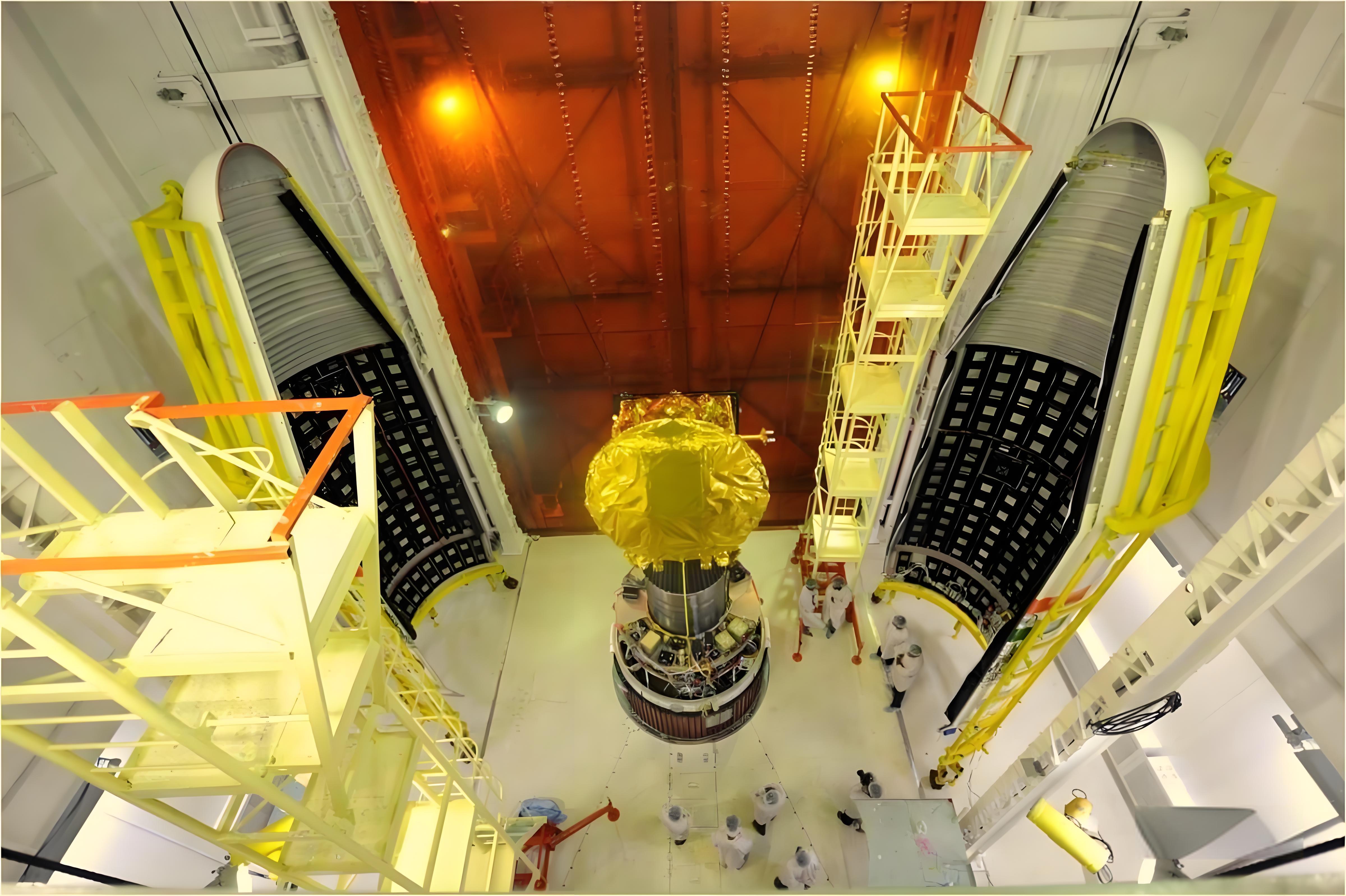
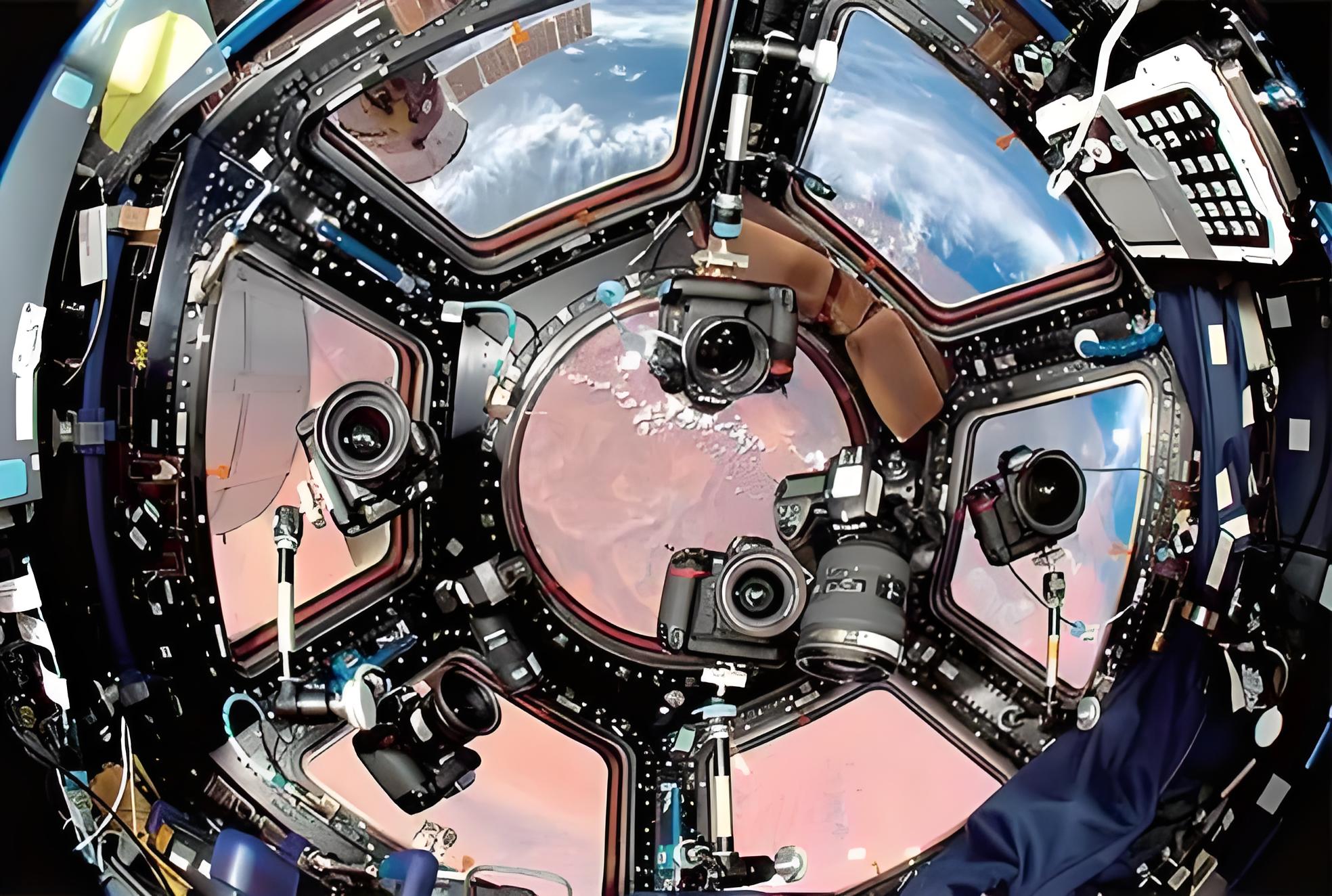
In the field of space launch vehicles, composite materials have also found extensive use. By utilizing composite materials, rockets can reduce their structural weight while ensuring strength and rigidity, thereby enhancing payload capabilities. Examples include Japan's M-5 rocket, France's Ariane 2 rocket, the European Vega satellite launch vehicle, and the US Atlas V rocket, all leveraging composite materials.
In the satellite domain, high-modulus carbon fiber-reinforced composites are widely employed in the construction of satellite structures, solar panel arrays, and antennas, further underscoring the immense potential and value of composite materials in the aerospace industry.
Helicopters, unlike traditional fixed-wing aircraft, operate at slower speeds, lower altitudes, and are exposed to harsh conditions like humidity, aridity, and sandstorms, demanding greater weather resistance and corrosion resistance from their structures. Moreover, the rotor blades of helicopters require materials with high fatigue resistance. Hence, due to their excellent fatigue resistance, vibration damping properties, and corrosion resistance, composite materials are well-suited for structural designs in helicopters.
Within the realm of aerospace engines, known for their technical complexity and lengthy development cycles, they are hailed as the crown jewel of the industry. Goals pursued in the design of civil aviation engines include high thrust-to-weight ratios, low fuel consumption, reduced noise, and minimal emissions. To achieve these objectives, composite materials have found widespread application in civil aviation engines.
In the field of space launch vehicles, composite materials have also found extensive use. By utilizing composite materials, rockets can reduce their structural weight while ensuring strength and rigidity, thereby enhancing payload capabilities. Examples include Japan's M-5 rocket, France's Ariane 2 rocket, the European Vega satellite launch vehicle, and the US Atlas V rocket, all leveraging composite materials.
In the satellite domain, high-modulus carbon fiber-reinforced composites are widely employed in the construction of satellite structures, solar panel arrays, and antennas, further underscoring the immense potential and value of composite materials in the aerospace industry.

Get In Touch With Us!
To know more about our composite products and solutions, contact our experts! Here is how you can reach us.

Get In Touch With Us!
To know more about our composite products and solutions, contact our experts! Here is how you can reach us.
Popular Composite Materials
Popular Composite Materials
Related Composite Materials Industries
Related Composite Materials Industries
Composites Knowledge Hub
Composites Knowledge Hub